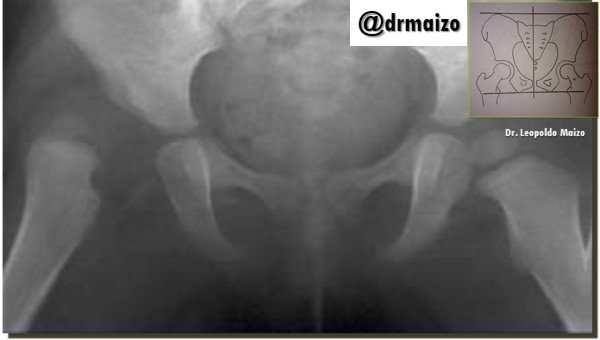
Hip dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is the abnormal development of the hip joint, which causes subluxation or dislocation; it can be unilateral or bilateral.
Hip dysplasia is due to the laxity of the ligaments surrounding the joint or to the intrauterine position. Asymmetrical skin folds of the thigh and groin are common, but this is also seen in infants without hip dysplasia. If dysplasia is not diagnosed or treated, over time the affected lower limb becomes shorter, and the hip painful. Hip abduction is usually limited by spasm of the adductors.
Screening is performed by physical examination in all infants. Since the sensitivity of the physical examination is limited, an imaging study should generally be performed on high-risk infants (and those with alterations detected during the physical examination).

Detection Maneuvers
Two systematic detection manoeuvres are commonly used. The Ortolani maneuver detects the femoral head slipping back into the acetabulum, and the Barlow maneuver detects the femoral head slipping out of the acetabulum. Each hip is examined separately. Both maneuvers begin with the infant in supine decubitus, and the hips and knees in 90° flexion (the feet will be outside the stretcher). To perform the Ortolani maneuver, the investigated thigh is abducted (i.e., the knee is separated from the midline to a frog's leg position) and gently pushed forward. A palpable, sometimes audible snap of the femoral head that moves over the posterior edge of the acetabulum and repositions itself in the cavity indicates instability. Then, in Barlow's maneuver, the hip is placed back in the initial position and then a slight adduction is made (i.e., the knee is brought across the body) and the thigh is pushed in the posterior direction. A click indicates that the head of the femur is coming out of the acetabulum. Also, a difference in the height of the knees when the child is in supine decubitus with hips flexed, knees flexed and feet on the stretcher (sign of Galeazzi).

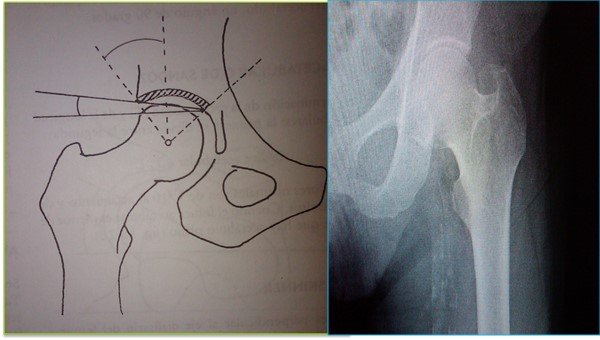
Studies and Treatment
Ultrasound of the hips at 6 weeks of age is recommended for high-risk infants, including those born in the breech position, those born with other deformities (e.g., congenital torticollis, congenital malformation of the feet), and girls with a positive family history of hip dysplasia.
Early treatment is crucial. Any delay steadily reduces the possibility of correction without surgery. Usually, the hip can be reduced immediately after birth, and with growth, the acetabulum can form an almost normal joint. The treatment consists of devices, most often the Pavlik sling, which keep the affected hips in abduction and external rotation. Frejka's pillow and other splints may be helpful. Padded diapers and double or triple diapers are not effective, and should not be used to correct hip dysplasia.
Dr. Leopoldo Maizo - Orthopedic Surgeon


Firma diseñada por @themonkeyzuelans, contáctalos vía Discord "themonkeyzuelans#9087"
Great projects from the Steemit community:
- My Fundition campaign: https://fundition.io/#!/@drmaizo/6f88ggj8h

.png)
Upvoted!
It is very helpful to know about this.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you @jmehta :D
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @drmaizo! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit