What is glycogen storage?
Glycogen storage is caused by genetic disorders in the production and analysis of glycogen.
Glycogen, a polymer, is composed of many molecules of mono-sugar-glucose, and is similar
In its chemical structure is the lava tree. When blood glucose rises, after eating, glycogen is generated
In the liver, in the muscles of the body and the heart muscle. During fasting or physical exertion
Glycogen breaks down into glucose and is essential for energy production and metabolism.
There are 12 types of glycogen storage disease known today, including:
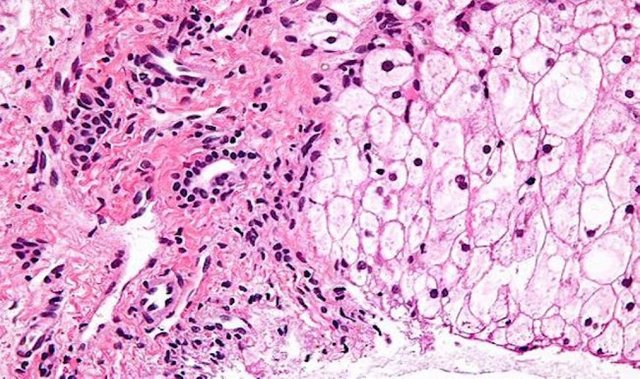
Glycogenesis I (GSD-I): a deficiency of enzyme activity that activates the last phase of glycogen analysis
And lead to low blood sugar during fasting for a few hours. Symptoms include: liver hypertrophy, facial features similar
Dummy features, short stature and delayed sexual growth, diarrhea and symptoms of nasal bleeding. Adults have benign tumors
In the liver and decreased renal function. Occasionally, some patients have recurrent bacterial infections
And inflammatory bowel disease, due to the decrease
Number and function of white blood cells. Apparently the strict maintenance of blood sugar
Which will improve patient growth and reduce the proportion of complications.
Glycogen II (GSD-II): What causes this type of disease is enzymatic deficiency in the process
The analysis of glycogen, which occurs inside internal cell organs called lysosome,
In most cases, the disease appears in infants in the form of: severe muscular dystrophy, heart failure and hypertrophy
The liver causes the death of the patient up to two years. It has been recently concluded that giving the enzyme is incomplete
The intravenous patient has contributed to improved patient status
Who have been supervised and followed for a limited period of time.
Glycogenesis III: The failure to analyze the glycogen molecule. Similar symptoms of the disease
Children have symptoms of glycogen I (GSD-I), but symptoms of this type improve
In most patients when they reach the first decade. A section of patients has 9 delayed complications
Such as liver cirrhosis and advanced muscle weakness. It is like treating these
Treatment of type I cases in children.
(GSD-IV)
It is caused by a defect in the formation of the glycogen molecule. The disease appears as a hepatic disease
Leading to the death of the patient at the age of 4-5 years, but there are other forms of the disease
The transplantation of the liver to some patients has been successful.
(GSD-V)
This type is caused by the lack of an enzyme that analyzes glycogen glucose within the muscle tissue
The disease is reflected in the inability to tolerate hard physical exertion. Sometimes we find
The patient's urine color became red due to damaged muscle cells.