GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a standard developed to describe protocols for second generation (2G) digital cellular networks. It was developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to replace the first generation (1G) analog cellular networks and to provide more efficient and secure mobile voice and data services. GSM technology has been the foundation for mobile communication advancements and has widespread adoption worldwide.
Key Features of GSM Technology
Digital Transmission: Unlike its analog predecessors, GSM uses digital signals to transmit voice and data, which improves sound quality and reduces noise and interference.
TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access): GSM uses TDMA to divide each frequency into time slots. Each user is allocated a specific time slot within each frequency channel, allowing multiple users to share the same channel efficiently.
SIM Cards: GSM introduced the concept of the Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card, a removable smart card that stores the user’s subscription information, such as phone number, network identity, and personal security keys. This allows users to switch phones easily by transferring the SIM card.
International Roaming: GSM standards enable seamless international roaming, allowing users to use their mobile phones in different countries without changing their phone number or SIM card.
Encryption: GSM uses encryption algorithms to secure voice and data communications, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept or eavesdrop on calls and messages.
SMS (Short Message Service): GSM supports SMS, allowing users to send and receive text messages.
Network Architecture
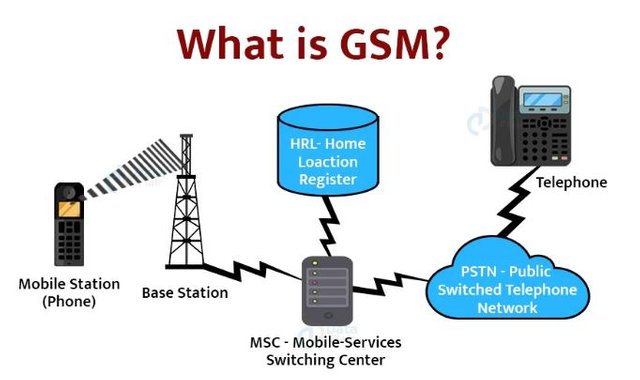
- Mobile Station (MS): The mobile device used by the subscriber, including the handset and SIM card.
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS): The equipment that communicates directly with the mobile station, responsible for transmitting and receiving radio signals.
- Base Station Controller (BSC): Manages multiple BTSs and handles radio resource management, call setup, and handovers.
- Mobile Switching Center (MSC): The central component of the network that performs call routing, mobility management, and interconnection with other networks.
- Home Location Register (HLR): A database that contains subscriber information and location data.
- Visitor Location Register (VLR): A temporary database that stores information about subscribers currently within the MSC's area.
- Authentication Center (AUC): Stores authentication and encryption keys to verify the identity of subscribers and secure communication.
- Equipment Identity Register (EIR): A database that tracks mobile equipment to prevent the use of stolen or unauthorized devices.
Advantages of GSM
- Wide Coverage: GSM networks have extensive global coverage, making it a preferred choice for international communication.
- Interoperability: Standardized technology allows for interoperability between different GSM networks and devices.
- Improved Security: GSM’s use of encryption provides better security compared to earlier analog systems.
- Efficient Use of Spectrum: TDMA and frequency reuse techniques allow for efficient use of the available spectrum.
- Support for Additional Services: Beyond voice, GSM supports various data services such as SMS, MMS, and internet access.
Disadvantages of GSM
- Limited Data Rates: GSM's 2G technology offers lower data transmission rates compared to newer technologies like 3G, 4G, and 5G.
- Latency: Higher latency compared to newer network technologies, which can affect the performance of real-time applications.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Despite encryption, there are known vulnerabilities in GSM encryption algorithms that can be exploited.
Evolution of GSM
GSM has evolved over time to incorporate newer technologies and capabilities:
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service): Introduced to provide higher data rates and enable internet access, often referred to as 2.5G.
- EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution): Further enhanced data transmission speeds, often referred to as 2.75G.
- UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System): Led to the development of 3G networks, offering significantly higher data rates and supporting a wider range of services.
- LTE (Long-Term Evolution): Represents the move to 4G, providing even higher data speeds, lower latency, and improved network efficiency.
GSM technology has played a foundational role in the development of mobile communications and continues to influence modern wireless communication standards.
Congratulations, your post has been upvoted by @upex with a 0.21% upvote. We invite you to continue producing quality content and join our Discord community here. Visit https://botsteem.com to utilize usefull and productive automations #bottosteem #upex
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit