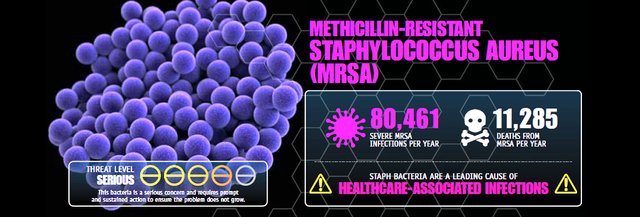
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is the multi-resistant variant of Staphylococcus aureus, known in ancient times as golden staphylococcus. The first strain of MRSA was detected in 1961, a few months after the introduction of methicillin. This microorganism is resistant to all beta-lactams (including cephalosporins and carbapenems) and usually to aminoglycosides, erythromycin, clindamycin, tetracyclines, sulfonamides, quinolones, and rifampin, while they are often sensitive to few antibiotics, as glycopeptides. In its evolution, MRSA continues to develop the mechanisms of resistance, as well as in 2002, the first strain of MRSA with resistance to vancomycin was detected in the United States, the acquired resistance to obtain a vain gene, identical to that of Enterococcus resistant to vancomycin.
As described above, bacteria such as S. aureus develop resistance mechanisms easily and in a short time, this rate of resistance is much higher than the creation or discovery of new antibiotics, which makes human look at the need to develop therapeutic alternatives derived from innovative sources. It is in this scenario that a man's war against bacteria like MRSA is developed, which has as a weapon its high rate of replication (like most bacteria) and therefore the possibility of making suitable mutations for its survival. Homo sapiens, on the other hand, does not have the capacity to self-replicate, its strength lies in the advancement of knowledge through research, which has allowed it to develop diverse strategies, some of which are mentioned below.
One of the most used today for research into therapeutic alternative substrates is plants. Both its crude preparations (extracts and essential oils) and the molecules derived from them have been studied, most of them in vitro, but some have already passed the phase of controlled clinical trials, this is the case of the metabolites obtained from the leaves of Melaleuca alternifolia, better known as tea tree, which is currently used as a 10% cream to combat dermal colonization by MRSA. Although the crude derivatives of plants and their molecules are widely studied by several research groups around the world, there are also other groups dedicated to studying other alternatives to combat bacteria resistant to multiple antibiotics. Mention may be made, among others, of oligopeptides such as omiganan (MBI-226), a cationic peptide composed of 12 amino acids that interact with the cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria causing changes in the polarity thereof with subsequent destruction of the bacteria. Other molecules that offer alternatives are originally produced by animals and chemically modified to be used as antibacterial agents, such as chitosan (polysaccharide derived from chitin by N-deacetylation) whose synergistic effect with beta-lactams (ampicillin, penicillin and oxacillin) has been studied against MRSA, obtaining results that demonstrate the synergy between the derivative Aminoetil-chitosan 50 and the three antibiotics mentioned previously, this synergistic combination dramatically decreases the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of such antibiotics. In the same line bacteriocins (bacterial toxins that fight other bacteria) have also been studied as another possible weapon against MRSA, an example of these is the bacteriocin chemically known as 2,2, 3-tribromobiphenyl-4,4 -dicarboxylic acid (from the bacterium Pseudoalteromonas phenolica O-BC30T), which inhibits clinical isolates of MRSA with MICs in a range between 1 and 4 μg / mL.
To win this war, man has reached levels as small as molecular and even atomic, in these areas nucleotide studies have been done, more precisely with an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide of interleukin 10, which has the ability to play a protective role against MRSA in situ, acting as a mediator in the formation of abscesses; the application of said molecule limits the infection and makes it impossible for the bacteria to migrate to the blood and therefore the production of sepsis. At the atomic level, we have worked with nanoparticles, one of these studies describes the use of polyacrylate nanoparticles linked to penicillin, this covalent binding means that beta-lactamases do not exert their effect against penicillin.

As we see the Homo sapiens is not defeated, because through of science human is taking charge of fighting on different sides, which would not have been discovered if the bacteria had not evolved to such a level of resistance. This suggests that the evolution of science is linked to the evolution of microorganisms and the desire of man to win a war that develops as fast as the microorganisms.
Sources
- Barber M. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1961;14(4):385–93
- Centers for Disease Control. Staphylococcus aureus resistant to vancomycin, United States. 2002
- Dae-Sung L, Young-Mog K, Myung-Suk L, Chang-Bum A, Won-Kyo J, Jae-Young J. Synergistic effects between aminoethyl-chitosans and b-lactams against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Bioorganic & Me-dicinal Chemistry Letters 2010;20:975-8
- Turos E, Reddy GSK, Greenhalgh K, Ramaraju P, Abeyla-th SC, Jang S, et al. Penicillin-bound polyacrylate nano-particles: Restoring the activity of b-lactam antibiotics against MRSA Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2007;17:3468-72.View publication statsView publication stats
Congratulations @royer94! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board of Honor
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDownvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @royer94! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board of Honor
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDownvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @royer94! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board of Honor
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDownvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
All I can say, is in my experience I've had two friends kill that shit with Colloidal Silver, topical and internal, where nothing else worked, maybe that falls under the "nano particle" treatment?
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hi @kimmysomelove42 ... the answer to your question is yes. Colloidal silver is an atomic level treatment and this had been useful in treatments in vitro and in vivo. Welcome to my board and any suggest will be keep in mind.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit