The ancient Mayan civilization, which thrived in the rainforests of Central America from about 2000 BC to the 16th century AD, was one of the most advanced and complex cultures of its time. The Maya were renowned for their impressive architecture, intricate writing system, advanced mathematics, and accurate astronomical observations.
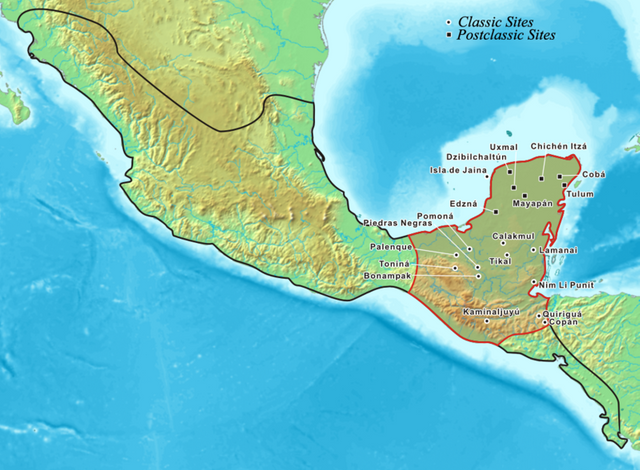
The Mayan civilization reached its height during the Classic period from 250 to 900 AD, when the Maya built massive cities such as Tikal, Palenque, and Chichen Itza. These cities were home to impressive temples, pyramids, and palaces, as well as bustling marketplaces and thriving communities of artisans, farmers, and nobles.
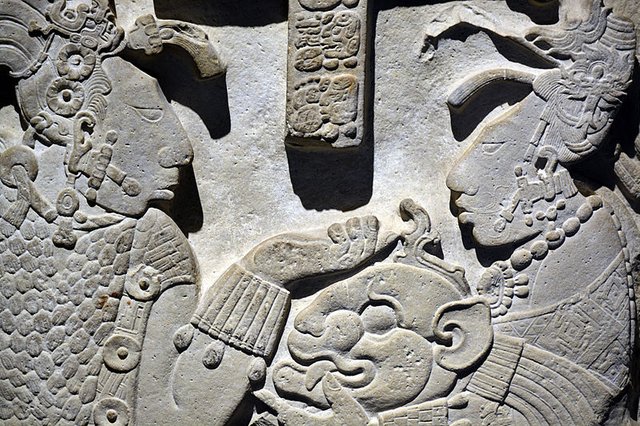
One of the most fascinating aspects of Mayan culture is their intricate writing system, which consisted of a combination of hieroglyphs and symbols. This writing system was used to record the history, religion, and daily life of the Maya, and has provided scholars with valuable insights into their beliefs and practices.

Despite their impressive achievements, the Mayan civilization began to decline in the 9th century AD, for reasons that are still debated by historians and archaeologists. Some theories suggest that overpopulation, resource depletion, or internal conflict may have contributed to their downfall, while others point to external factors such as invasion or disease.

Today, the Maya continue to be a source of fascination and inspiration for people around the world, with their achievements in art, science, and architecture leaving a lasting legacy that still influences modern culture.