For a long time, we have tried to understand Polkadot's meaning and status in the blockchain world. From various written materials to market information, we have concluded that Polkadot is currently the best one of the cross-chain solutions. But we always believe that cross-chain is just a solution, not a goal. So what exactly is Polkadot's ultimate goal to achieve? With such a question, the Prophet Lab began research and tried to find a complete logical chain to clearly locate the meaning of Polkadot.

Usually when we are studying a project, we will first understand the ideas of its founder. In the process, we learned that Dr. Gavin Wood, the founder of Polkadot, founded the Web3.0 Foundation before the creation of Polkadot, so we I thought that maybe we could find clues in Web3.0 to study Polkadot in depth. In April 2014, Gavin published his vision for the real Web3.0 in the Ethereum community. He hopes to reshape the Internet from the bottom of the software based on the P2P protocol, and create a network service with decentralization and privacy protection as the main feature .
By sorting out and collecting existing materials, we can summarize the development path of Web3.0 as follows:
Experience layer: decentralized identity, user interface
Application layer: DAPP
Architecture layer: decentralized storage, decentralized communication and computing
Basic layer: zero trust/low trust interaction protocol (blockchain)
After seeing this path, we immediately had a clear definition of Polkadot's meaning and goals. We should have understood Polkadot from a larger level, the next stage of the Internet, rather than the simple blockchain world. At the level, the defined Polkadot implements the very important decentralized data computing and communication functions in the Web3.0 architecture layer. This function and distributed storage together build the underlying architecture of the entire Web3.0. It will be the entire Web3.0 world. To understand Polkadot from this perspective, we can clearly understand Polkadot's technical implementation path, economic model, and ecological development, and perhaps make some reasonable predictions. Next, we will organize and introduce the industry and the Polkadot project itself.
The relationship between the Web3.0 Foundation and Parity and Polkadot
The relationship between the Web3.0 Foundation, Parity Technology, and Polkadot
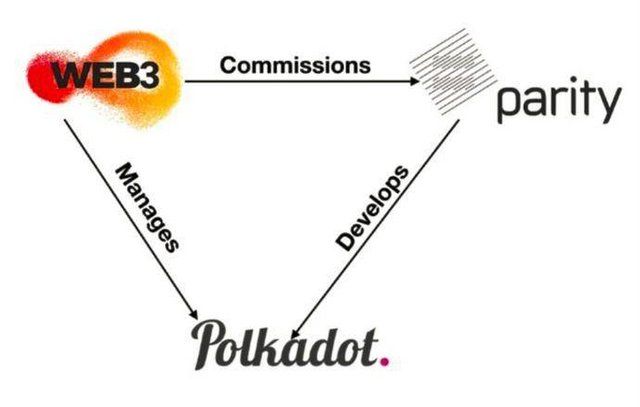
The Web3.0 Foundation has been funding research and development teams, and the technology stack of these teams constitutes the foundation of the decentralized network. The Web3.0 Foundation was founded in Zug, Switzerland by Dr. Gavin Wood, co-founder and CTO of Ethereum.
Web3.0 Foundation Vision
- Users should own their own data, not the company;
- Global digital transactions are safe;
- The online exchange of information and value is decentralized;
Web3.0 Foundation Key Project
- Polkadot: the underlying protocol project of the Web3.0 Foundation;
- Kusama: the previous version of Polkadot;
- XCMP: A subset of Polkadot, a decentralized messaging protocol that emphasizes privacy and security;
Summary
The Web3.0 Foundation implements the decentralized communication and computing functions of the architecture layer in Web3.0 through the management and development of Polkadot. It can be considered that once the Polkadot project is successful, the progress of Web3.0 will no longer be possible without Polkadot.
Parity Technology
Parity Technology is a software development company with the most cutting-edge technology of Web3.0. The company was founded by Dr. Gavin Wood, co-founder and chief technology officer of Ethereum, and Dr. Jutta Steiner, the former head of the security of the Ethereum fund, and created the Parity Ethereum client that has contributed greatly to the success of Ethereum.
Parity's mission is to give open source software developers a space to jointly build revolutionary new technologies and achieve the common vision of a decentralized 3.0 network. The Substrate framework it created can help build blockchains and decentralized innovative applications. Polkadot is written using the Substrate framework, and the parachain on Polkadot also needs to be written using Substrate.
Regarding the Substrate framework, perhaps a one-sentence summary is "the best blockchain building tool". The core idea is to make the development of the blockchain's state transition function as flexible and easy as possible. Substrate built-in all the core components required to build a blockchain are: database, networking, transaction queues, and consensus. (Quoted from "Polka one-key distribution chain, how to use substrate to build a blockchain")
Polkadot basic situation and valuation
basic situation
Polkadot's white paper defines Polkadot in this way. Through a heterogeneous multi-chain architecture, two very important parts of the consensus architecture (that is, consistency canonicality and validity) are essentially separated to support many heights. The differentiated consensus system interoperates in a trustless and fully decentralized federation, allowing trust-free mutual access to various blockchains.
We can also understand from a passage from the founder of Polkadot, Dr. Gavin Wood: Polkadot's design logic is not directly associated with interoperability. We are waiting for the launch of Ethereum's sharding technology. But sharding has not been implemented, and it has not been launched now. Therefore, I want to build a more extensible "Ethereum" by myself. In the design process, the concept of sharding is pushed to a more extreme level, so I don't want to shard at all, just design an independent chain. With this design, different chains can transmit information to each other, and the final result is to achieve communication through a shared consensus level.
At present, the main highlights of Polkadot include Substrate software development documents, nPos consensus mechanism, financial support from the Web3.0 foundation, and the automatic upgrade of chain governance features.
Polkadot interpretation
From the perspective of Polkadot's current functions, the most direct definition is cross-chain, but its implementation is very different from other solutions;
Using the relay chain to achieve cross-chain, although it increases the burden of the relay chain to a certain extent, it can ensure security. As long as there are enough verification nodes on the relay chain, then theoretically the mutual relationship between the parachains Communication can enjoy the accumulation of security brought by the increase of verification nodes, instead of designing a separate security mechanism for the communication between each chain;
Risk-free scalability, the parachain approach can theoretically be extended without risk. At present, the blockchain is still a relatively closed circle, but once traditional Internet companies enter the blockchain, especially some Internet giants with their own ecology, they Most of them will be accessed in the form of alliance chains, so Polkadot's scalability will become a core highlight that attracts them to access.
Polkadot has also officially funded a lot of cross-chain bridge projects to help parachains communicate directly. This is very practical for parachains that often need to communicate, and is somewhat similar to the state channel in the Layer 2 solution.
The combination of Parachain and Parallel threads is very friendly to the project party. You can participate in slot auctions, unconditional project parties can also use parallel threads to access, a bit similar to WeChat applets, which do not need to be online from time to time. Just do some interaction when you need it.
The function of the EVM virtual machine is also relatively friendly to developers, allowing many Ethereum developers to migrate to Polkadot very easily.
Technical progress
Substrate2.0
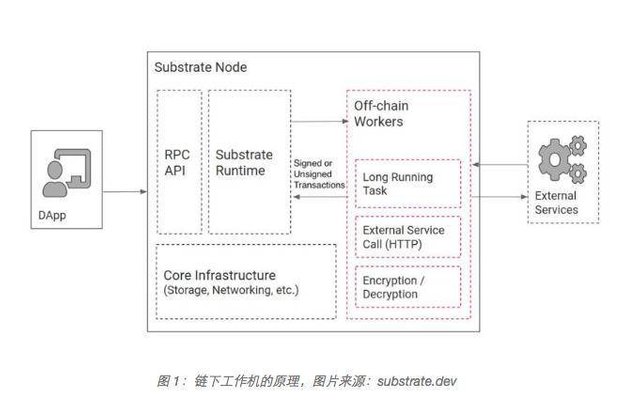
Substrate can be understood as a universal template that integrates various functions. Developers can call different modules (pallets) to accelerate development. Gavin used to write a chain in 15 minutes as soon as possible. The non-fork runtime upgrade is also one of the advantages of substrate. When the system needs to be upgraded, as long as the runtime upgrade is passed, the nodes in the network will automatically synchronize and comply with the new rules, without the need for hard forks.
In September 2020, Substrate launched version 2.0, adding more than 70 pallets and off-chain working machine functions. The newly added pallet provides support for smart contracts, voting on the chain, virtual machine migration, and treasury. The off-chain working machine is similar to the oracle, but it allows long-term or uncertain tasks to run.
Kusama Testnet (Token: KSM)
The kusama testnet was launched in August 2019, and staking and on-chain governance functions were launched in October of the same year.