Dear readers, this publication describes an insect that has expanded in different countries, because it is a pest that has a preference for the grass family, this arthropod is recognized by the FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) as a pest that threatens food security, as it can destroy corn plantations quickly if it is not controlled in time and can also negatively influence pasture crops.
| Budworm bioecology |
|---|
Spodoptera frugiperda is an insect native to tropical and subtropical areas and is known as the corn earworm or pasture sweeper, according to Angulo (2000), it is a larva of the nocturnal butterfly Spodoptera frugiperda, belonging to the genus Spodoptera, species frugiperda, order Lepidoptera and family Noctuidae. They have a chewing mouthparts causing a chopping effect on the leaves of plants, besides it is a polyphagous insect that causes numerous losses in various crops when the rainy season begins, decreasing slightly its attack when the rains are prolonged and intense.

| Biological cycle |
|---|
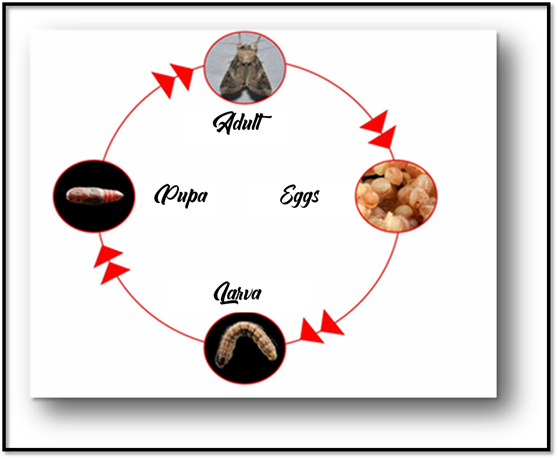
The phases of the biological cycle include the following:
*Egg stage: the eggs are deposited by the adult insect on the upper and underside of the leaves closest to the ground, according to the Farmer Service Foundation (2005), which indicates that the eggs hatch after approximately 3 to 5 days.
*Larval stage: when the eggs hatch, the larvae hatch green and as the days go by they turn black, they have three stripes or elongated yellow lines on the back with black dots and on the head they have stripes in the shape of an inverted Y. According to Chango (2012), these larvae go through six or seven instars or stages and during their development there are variations in size and morphology. This larval stage can last from 14 to 22 days approximately.
*Pupal stage: it is a transition stage where the insect ceases to be a larva and prepares to become an adult, the insect forms a kind of hard shell where it will remain for a certain time without eating and moving until it leaves the pupa and becomes an adult.
*Adult stage: the adult is a moth with a color between gray and brown, with an approximate size of 3 cm, these have nocturnal habits and remain among the leaves of grasses, weeds or any shaded place within the paddock. The adult female tends to lay eggs on the leaves and remains alive, according to some researchers, for approximately 10 to 21 days.
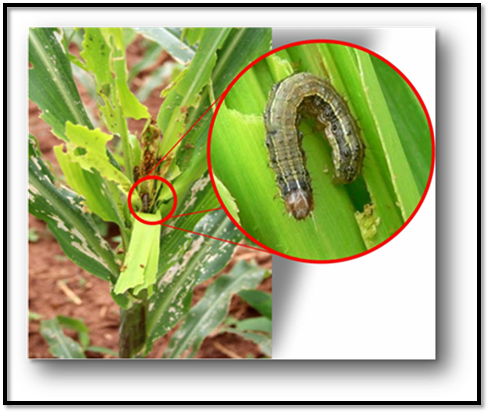
| Damage caused by Spodoptera frugiperda in pastures. |
|---|
When the eggs hatch, the larvae appear and in their first instars cause scratches on the tender parts of the leaves, presenting small translucent areas, because they only leave the lower cuticle of the leaves almost intact. Similarly, as the larvae develop, they begin to cause more damage to the leaves, as it is observed as a kind of cut or perforations in the leaf lamina, sometimes leaving only the midrib of the leaf if not controlled in time.
| Bibliographic references |
|---|
Chango, L. (2012). Control of the corn budworm. Unpublished graduate work. Technical University of Ambato, Ecuador.
Capinera, L. (2001). Handbook of plant pests. San Diego: Academic Press.


Image property of the @HeartSTEM community
From agrotecnia we reiterate our thanks to the HeartSTEM community for valuing our agricultural content, this commits us to continue sharing quality information. In the following publication we will describe some methods of control of spodoptera frugiperda.

