Just before I begin to answer the questions, I will like to give my own explanation of what hash means.
Hashes cannot be underrated in the world of blockchain technology, they are highly important and are greatly used. The complex and huge volume of information contained in a block can be transformed into a single hash and it is with the help of hash that the track of transactions is kept safe on the blockchain. Properties of hash functions include collision resistance, preimage resistance, and also second preimage resistance.
Now that we have an idea of what hash is, we can move swiftly into answering the questions for the week.

Resistance to Collision.

With Resistance to collision, it is computationally impossible to find two colliding inputs. A hash is collision resistant if nobody can find a collision (when two distinct inputs cannot produce the same output)

Resistance to Preimage.

Resistance to preimage is one of the basic components of a hash that is difficult to reverse, it is computationally impossible to locate the imputed data of the submitted element. One other great characteristic of hashes are that it is impossible to be reversed, it is impossible to find the imputed data that produced that hash, and this term clearly defines Resistance to Preimage.
The preimage function of hash makes it difficult for attackers to get in. Another name given to the pre-image resistance function is the ONE WAY function meaning that it is impossible for a reversal process to occur with this hash function.

Use Tron scan and ether scan to verify the hash of the last block and the hash of that transaction. The screenshot is required for checking.

Viewing on Etherscan
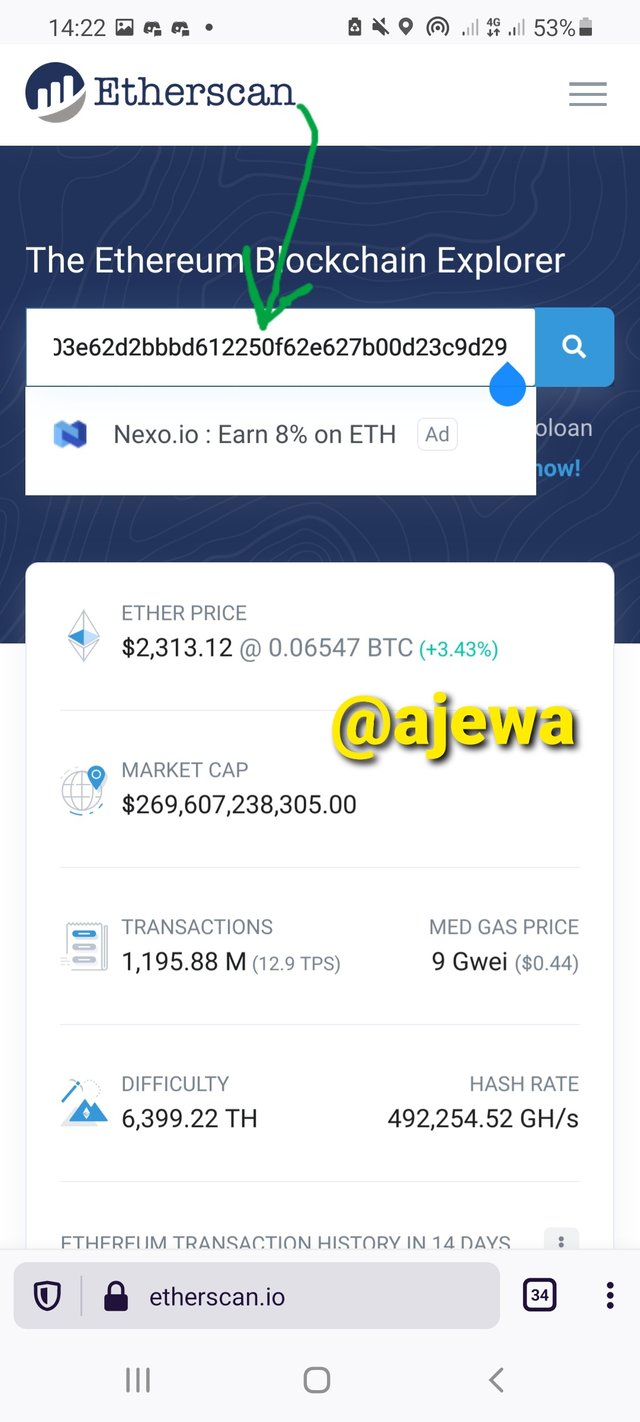
To check the block on etherscan, click on https://etherscan.io, click on blockchain and then click on View Blocks.
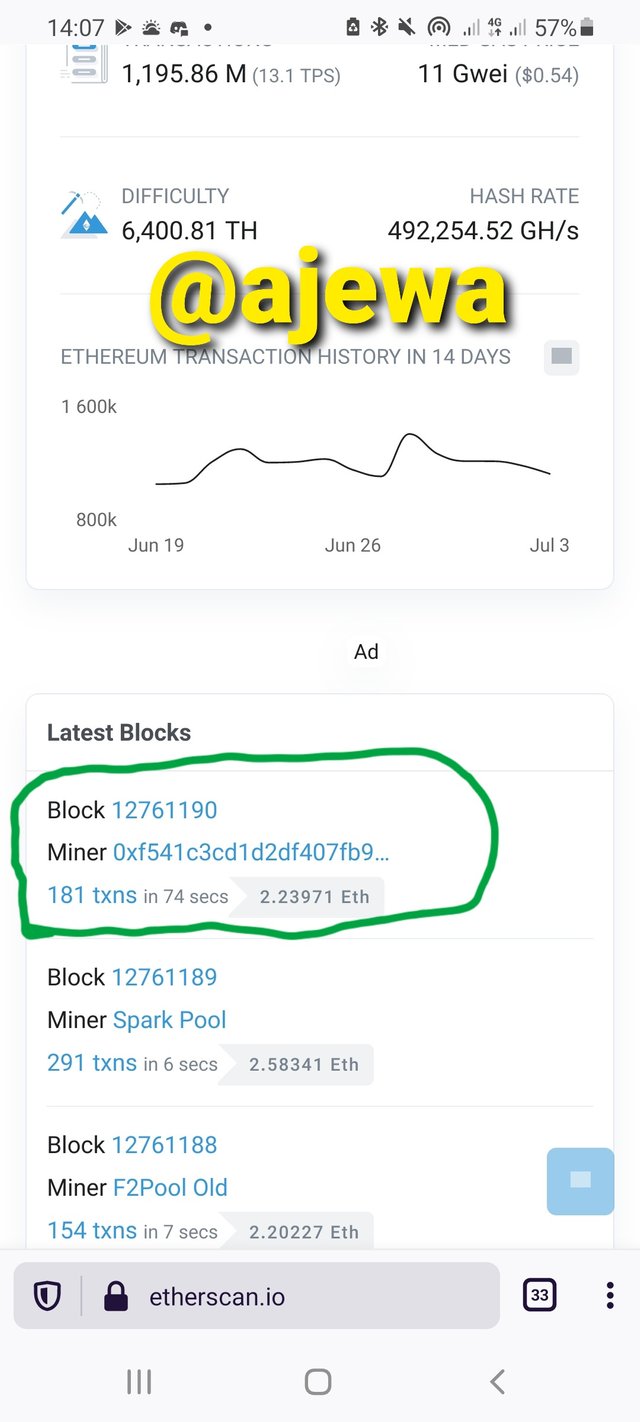
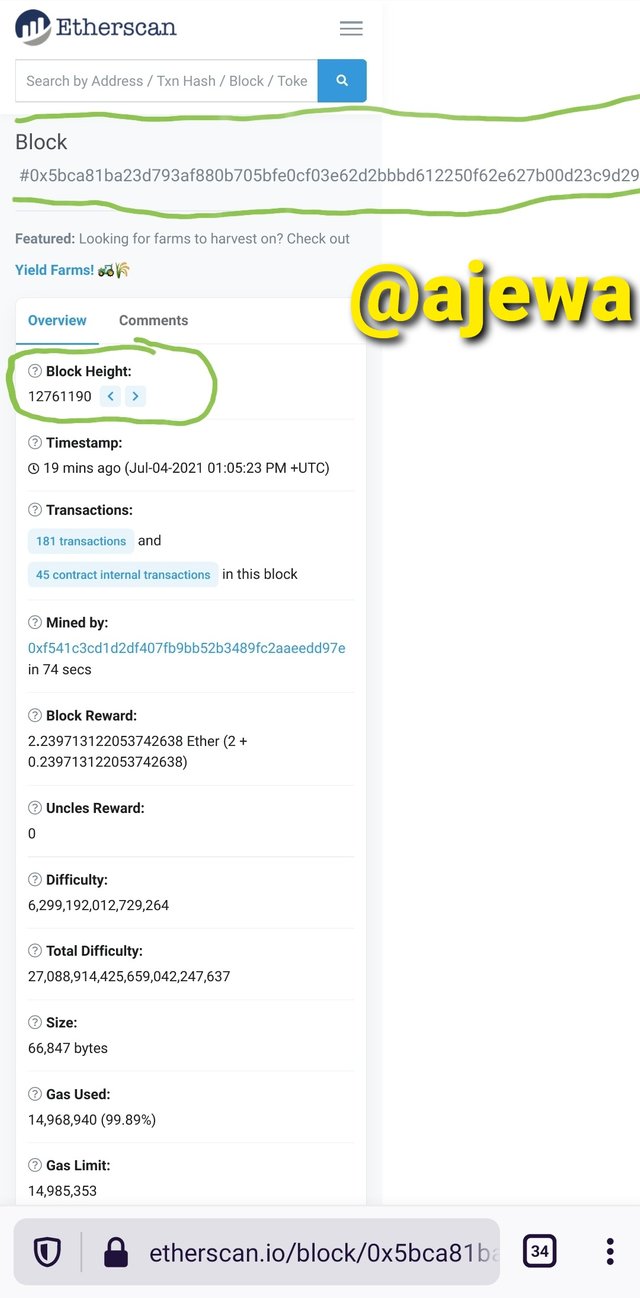
The list of Blocks is displayed on the Blocks page. Click on the latest block, for me, it is 12761190
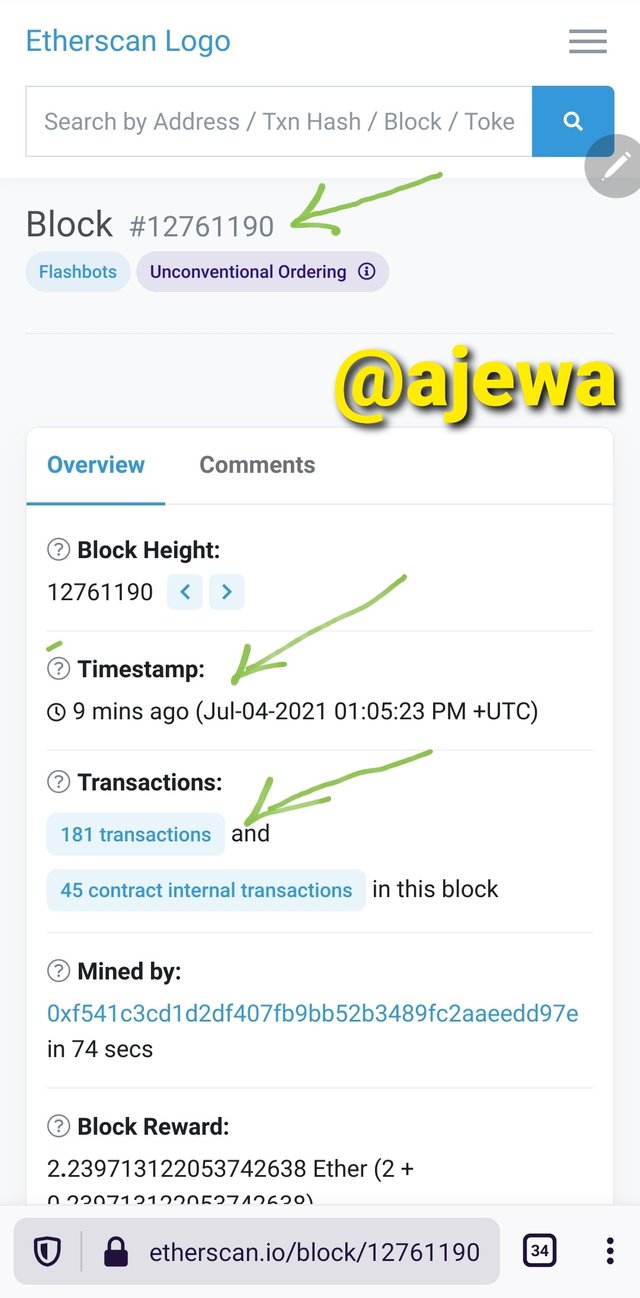
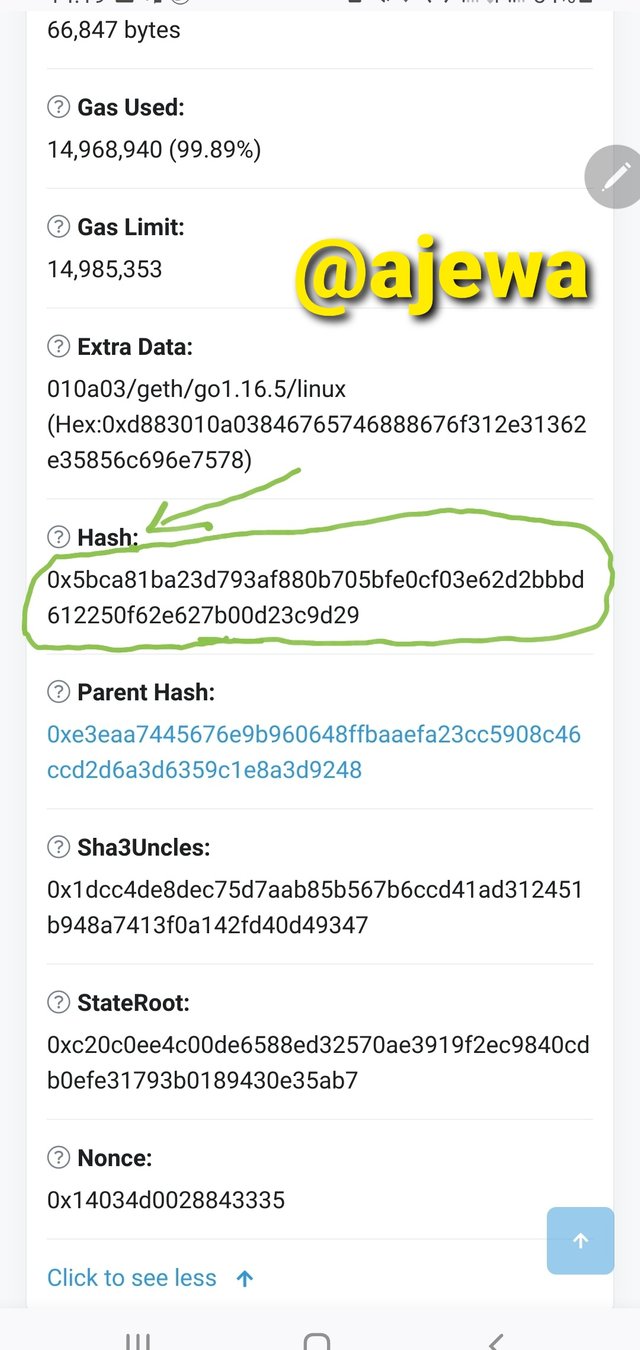
The Block Hash is viewed on the Block details.
A total of 181 transactions is embeded in the Block
Viewing the Latest Block on TronScan
Viewing the block on Tronscan, I visited the site https://tronscan.org, clicked on Blockchain, then click on Blocks.
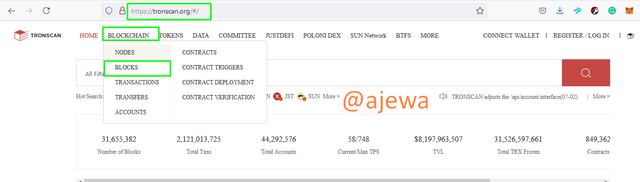
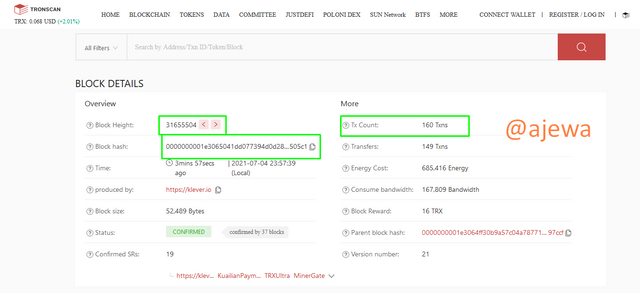
After clicking on Blocks, a list of Blocks are shown and I will be picking the latest block to get the hash of the block. The Block Height is 31655504
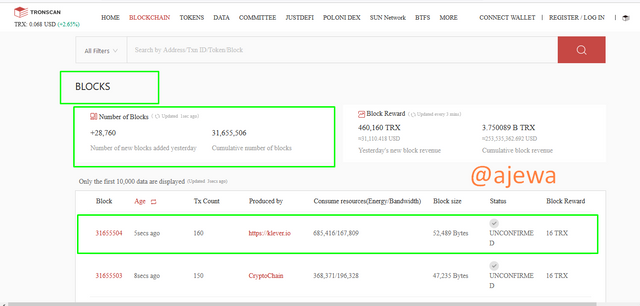
The Block Hash 0000000001e3065041dd077394d0d282a78824008f93d1025b1bf631fd6505c1 can be found in block data. To view the Hash, check the Block by clicking https://tronscan.org/#/block/31655504.

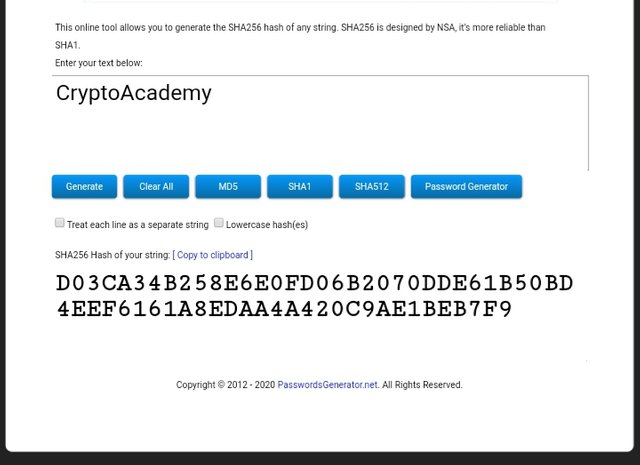
Generate the hash using SHA-256 from the word CryptoAcademy and from crypto academy. Screenshot required. Do you see any difference between the two words? Explain.

From the result of the screenshot I gave above, it is very clear that even if two similar words are imputed, the result of the hash produced will be completely different. CryptoAcademy and cryptoacademy are supposed to be similar words that should produce similar hash but in order to prove one of the basic functions of hash which is resistance to collision as described above, it is impossible to find two imputes that will give us the same output result as shown in the result.
As a result of that, the imputed word, CryptoAcademy gave us an output harsh of:
D03CA34B258E6E0FD06B2070DDE61B50BD4EEF6161A8EDAA4A420C9AE1BEB7F9
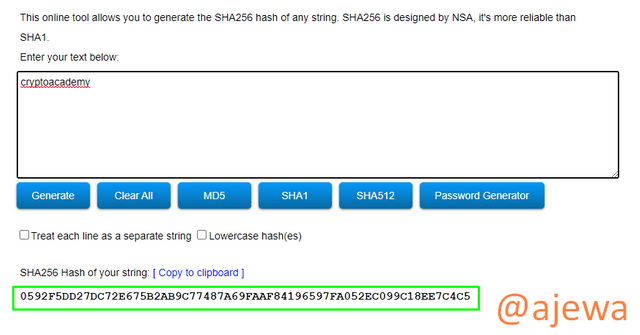
While the imputed word cryptoacademy gave us an output harsh of: 0592F5DD27DC72E675B2AB9C77487A69FAAF84196597FA052EC099C18EE7C4C5

In your own words explain the difference between hash and cryptography.

I have earlier explained the idea of hash but for the sake of this question, I will be giving some brief description of the word.
The concept of hash in cryptocurrency is used to produce the output of a fixed length irrespective of the length of imputed data. Hash is also known to produce different outputs irrespective of how similar the imputed words are.
The idea of cryptography in cryptocurrency term is to ensure that an information is encrypted well enough through the use of codes in order to ensure that the meaning of the codes can only be unveiled by those whom the message is intended for.
| Hashing | Cryptography |
|---|---|
| Hashing operates as a one way mechanism, which makes it impossible for the imputed data to be unveiled | Cryptography operates as a two way mechanism, the encrypted message can be unveiled and read by the intended receiver. |
| Irrespective of how long or short the imputed data is, hashing produces characters of a fixed length | The coded characters are not of the same length, they can be presented in different lengths. |
| In the concept of hashing, keys are not required | The purpose of encryption is done with keys. In asymmetric encryption, public and private keys are required while symmetric encryption only requires public keys. |
Conclusion.
This topic was indeed eye opening to the world of hashing and encryption, a big thank you to the amazing steemit team for this initiative and a big thank you to professor @pelon53 for this week’s topic and other professors who are doing a good job as well.
