
At this point, I believe is safe to say that blockchain technology has become commonplace. Aside from the popularity it has gained, the attention and structure of the new blockcain projects that are being created is truly remarkable.
Most of the new blockchains are positioning themselves to be able to favourably compete with the existing superpowers like Bitcon and Ethereum. In this way they try to improve on the limitations and deficiencies in these earlier projects.
Avalanche blockcain is one of the interesting blockchains that have been launched in recent times. Prof. @pelon53 has exposed the details of Avalanche to us and its most prominent features. I will proceed to tackle the assignment questions below.

Explain in detail X-Chain, C-Chain and P-chain.
Avalanche blockcain has been able to successfully build some of the vital components of blockchain operations into its ecosystem. There is awesome speed of transactions and building smart contracts.
Avalanche stands as the fastest smart contracts platform. It also boasts of very secure network with the multiple number of validating nodes and allows for greater participation of users in its administration.
The network is really particular about the its smart contracts features which has a lot of special packages for the development of decentralized applications especially those of finance.
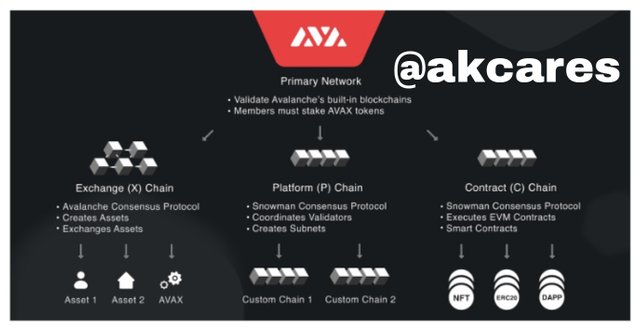
The speed in the Avalanche network is a function of the presence of three individual chains coming together to form the Avalanche main chain. With this, Avalanche is able to allocated specific operations to the separate chains and also adjust each blockchain to be adequate in supporting specific functions. These separate blockchains are the X-Cain, P-Chain and C-Chain.
X-Chain
The X here fully stands for Exchange. Thus, this is the section of the network that allows for the creation and exchange of digital smart assets. In this section, the major function is to facilitate the swapping or trading of assets. Here, one asset can be swapped for another. This exchange is made possible by the use of X-Chain API.
With this application programing interface, users can develop assets and also trade the assets they own already such as the native assets of the network like AVAX and other assets like the ERC-20 assets which are highly compatible and interoperable in the Avalanche network.
The X-Chain is an instance of the Avalanche Virtual Mechine (AVM). It uses rules such as: "can’t be traded until tomorrow" or "can only be sent to US citizens.", to govern the behavior of the assets and regulate the exchange. The AVAX token is used to settle gas charges in on this blockchain.
P-Chain
This is simply the Platform Chain. It is called such because is it where validating nodes are being coordinated, subnets are monitored and new subnets are are developed. It is like the administration unit of the Avalanche network.
The application programming interface in this blockchains makes it possible for individuals to develop subnets, add validators, and attach blockchains to the network. This blockchain makes use of the Snowman Consensus protocol to facilitate it functions.
C-Chain
The letter C here stands for Contract. The Contract Chain is just as the name suggests. It is the blockchain for establishment of smart contracts which are carried out through the use of its unique application programming interface.
Decentralized apps of various kinds can created here as well as non-fungible tokens. This compares to the Ethereum Virtual Mechine and the smart contracts created here are interoperable and compatible with the Ethereum blockchain.

Explore the Avax Network platform . Screenshots required.
Speaking of a blockchain ecosystem that is stocked with features, we have Avalanche. There are so many reasons to believe that this project very credible. Landing on the official page, one will quickly notice the abundance of features present.
On the homepage, there are list of different sections on the top bar. On the page, there is a short video animation demonstrating the process of creating or building which is very prominent in this ecosystem.
Infact, this is listed as one of the two buttons found immediately on the page with the other one being a button to interact with the platform.

Swiping down the page, you will see a section containing the major things that can be done on the platform most of these have links which redirect to the specific pages.
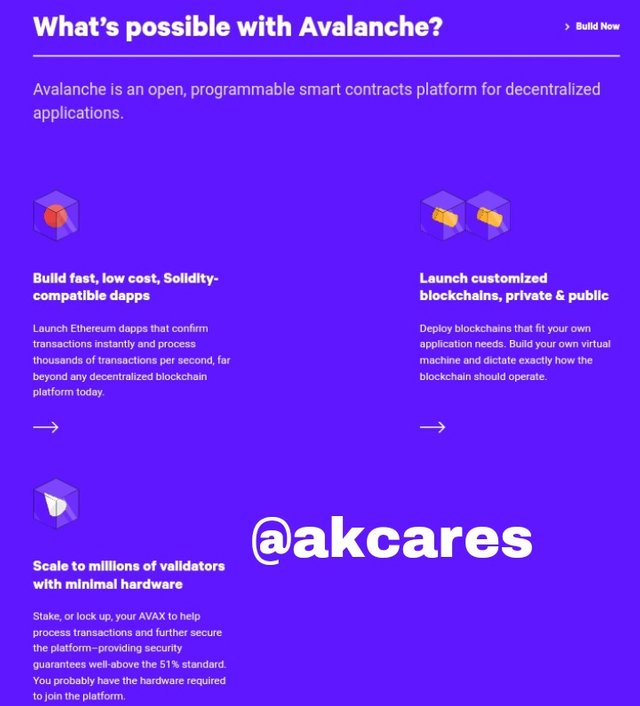
What a user can do on the Avalanche Platform.
This include things like launching a decentralized application, creating and attaching a blockchain and becoming a validator of transactions.
There is a display of news items and articles concerning Avalanche.

A short display of icons of applications and other softwares present in the Avalanche ecosystem is shown.

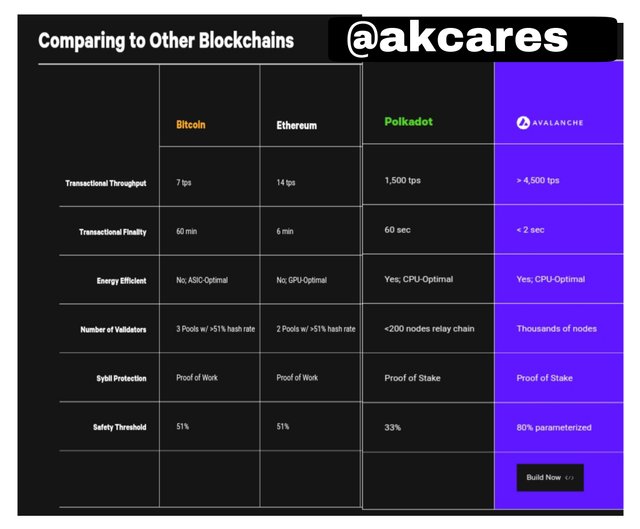
There is a table comparing the features of Avalanche with other blockchains.
Still on the page there is a highlight of the services offered on the platform like the decentralized finance, creation of assets, and minting of NFTs.

You can as well get a link to create a wallet, use the explorer, view proposed projects and upgrade, analyse the token and join the social media groups of this platform through this first page.

On the whole, the cover page simply contains a rundown of all the different components present on the platform
At the foot of the page, there is a rundown of all their different components of the menu listed on the top bar.

From these list, I selected some features to analyse.
Build
In the Avalanche ecosystem, there is promotion and encouragement of users to build. If one should click on the build button, a section opens where a user can create or build a range of products.

Here one can launch an Ethereum DApp, mint a token, create documentation for a project, integrate an exchange or add a validation node.
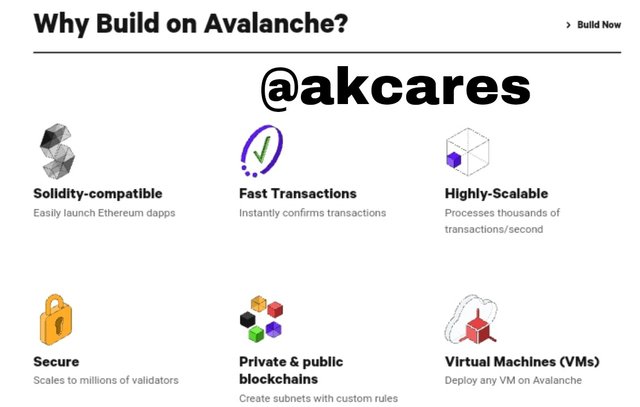
Advantages of building in Avalanche
Decentralized Finance
This specialized applications used to offer and facilitate financial services to users are available also on this platform. A user can make use of one like Pangolin or can build one using BZN protocol app which helps in setting up deFis.
NFTS

There is a provision which allows users to mint non-fungible tokens in the platform. Already, there are some gaming dApp created which supports this like the TOPPS. POLYIENT GAMES can be used to launch other gaming dApps.
Avalanche Downloads

These contain developer scripts, protocols, codes and algorithm that can be used to carry out the creation or building of anything on the platform.
Some of the specific areas I explored were under the list of menu as follows:
- DEVELOPERS
This is concerned with all aspects of creation, building or developing applications it tools on the platform. It gives different options for building and express some strong points of building in Avalanche. The architecture as well as options to build are also given here.

Architecture for building.
Dev Doc
This is the section that gives a kind of summary and report about some aspects, concepts and processes used in the platform.
Validators
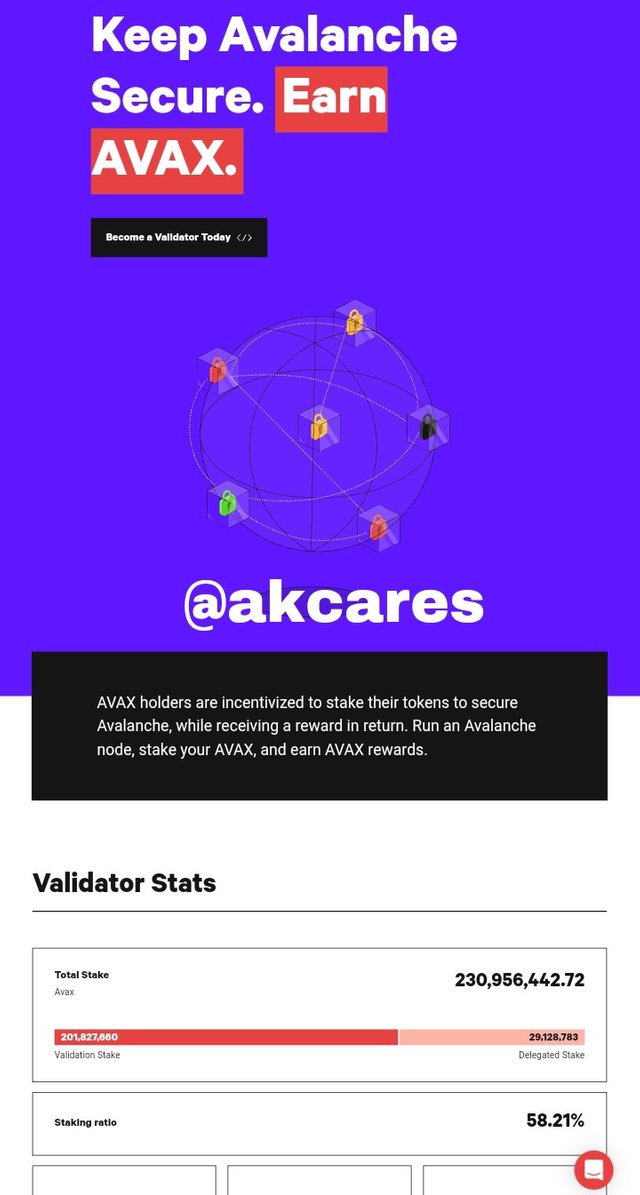
With this interface, a user can lock up or stake his assets to be used for governance of the ecosystem for which he receives rewards and dividends as can also take active part in validating transactions by having a node. The staking ratio of the platform is also shown here.
White Paper
This space contains a record of all the algorithm and codes used to build all the various aspects of the network. There are white papers for the platform, the consensus protocols, the token and the stablecoins.

Clicking on any if these will bring out a report of all the procedures and processes used to develop these sections.
- INDIVIDUALS

This is a space for a user to get access to services and features of the platform like getting a wallet, exploring transactions using the explorer, checking token statistics and others. There is also a list of exchanges and wallets which support the AVAX token and have listed it.
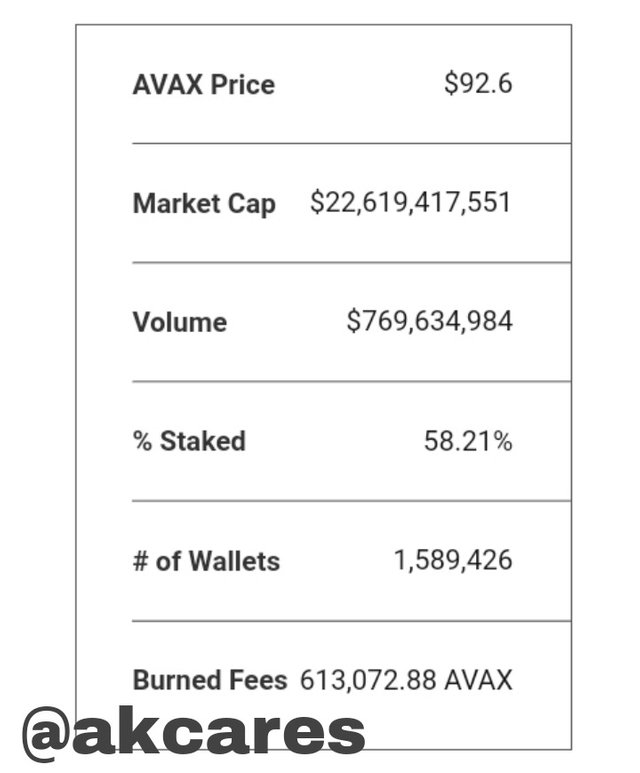
Brief token statistics.
Road Map
This is a section where there is an outline of the activities outlined for the platform. There are both past and future projects listed here and grouped according to specific time interval which is quarterly basis.

A user can select to view the details about the Avalanche platform, the major milestones and ecosystem projects for a certain quarter. Once a heading is selected, the details appear in a drop-down format.
Ecosystem
This is the section that showcases everything connected and linked with the Avalanche platform.

Here, dApps created, exchanges launched, games developed, wallets linked, explorers and a host of all other products that has connection to the network.
Avalanche Bridge

In this ecosystem area, I found and interesting feature which the bridge. It is a tool created which helps to create a pathway and a linkage between the Avalanche network and other distinct blockchains. In the bridge, there is a list of various wallets with which one can connect to other blockchain networks.
Wallet
In this section a user can create a fresh wallet or access an existing wallet on the platform. The wallet operated here is a non-custodial type.
Explorer
This is a tool one can use to access all the details and information about the transactions and activities in the platform. The platform has a separate explorer for the Exchange and the Platform sub chains and a different one for the Contract chain.
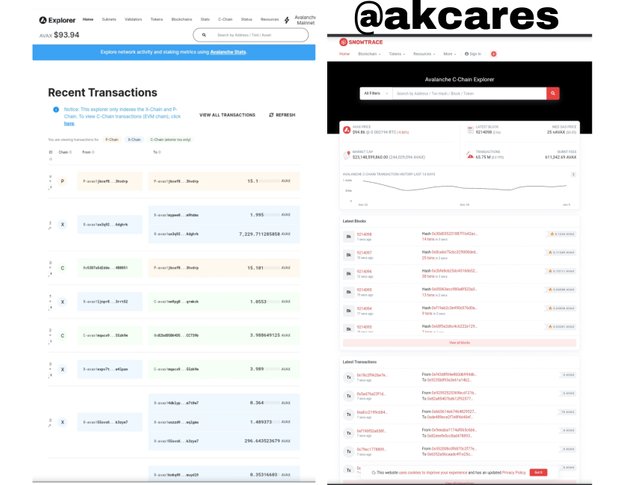
On the X and P chains explorer, one can find a list of lastest transactions and their hashes. The specific chain where the transaction took place is also stated.
To check the details, one will have to click on the specific transaction hash. This explorer shows only transactions hashes as there are no creation of blocks on this chain.
For the C-Chain explorer, there is a list of lastest block hashes and ID for one to select from since blocks are created here. A user can also find information about the price of AVAX, market capitalization, number of transactions and other information.
- AVALANCHE-X
This is a space for facilitating the development of dApps. Here is used to request for permission to launch an application.

There are free grants that can be exploited by users. This can be used to fund the development and launching of projects.
Also, users can submit their proposals for new projects here for approval. Here, a list of several kinds of grants are given and also instructions for submitting proposals.
- PRESS

In this section, happenings around Avalanche ecosystem are recorded. News, articles, publications concerning Avalanche are also displayed here.
- COMMUNITY

Here, is a list of all the interaction channels and media hosted by the platform. There is a list of social media icons or various types as well as chat channels.
- CONTACT
This interface provides users with means of reaching out to the administrators of the platform. There are spaces for name, contact email and others.
All screenshots in this question were taken from the AVAX official page

Show the last contract verified in the C-Chain network and show the Smart Contract that was generated at that address. Screenshots required.
To do this, I visited the explorer page. On landing on I found some menu on the top bar. I checked the blockchain menu and I was able to see a list of options. I found verified contracts on the bottom of the list and clicked on it.
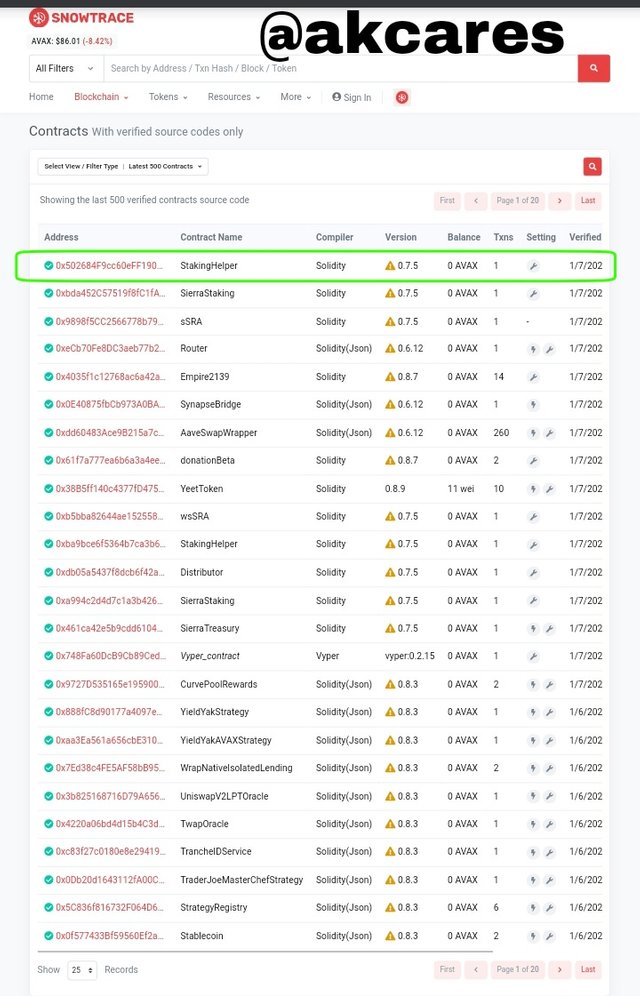
It opened up to a long list of many contracts that have been verified.
I picked the first option on the list since they were arranged from the latest down.
Details of the contract were displayed in the next page that opened. I was able to find things like the:
Name of the contract which was StakingHelper
The contract address was 0x502684F9cc60eFF190F9c2A32F7184e4B06808D3
The Compiler Version was v0.7.5+commit.eb77ed08
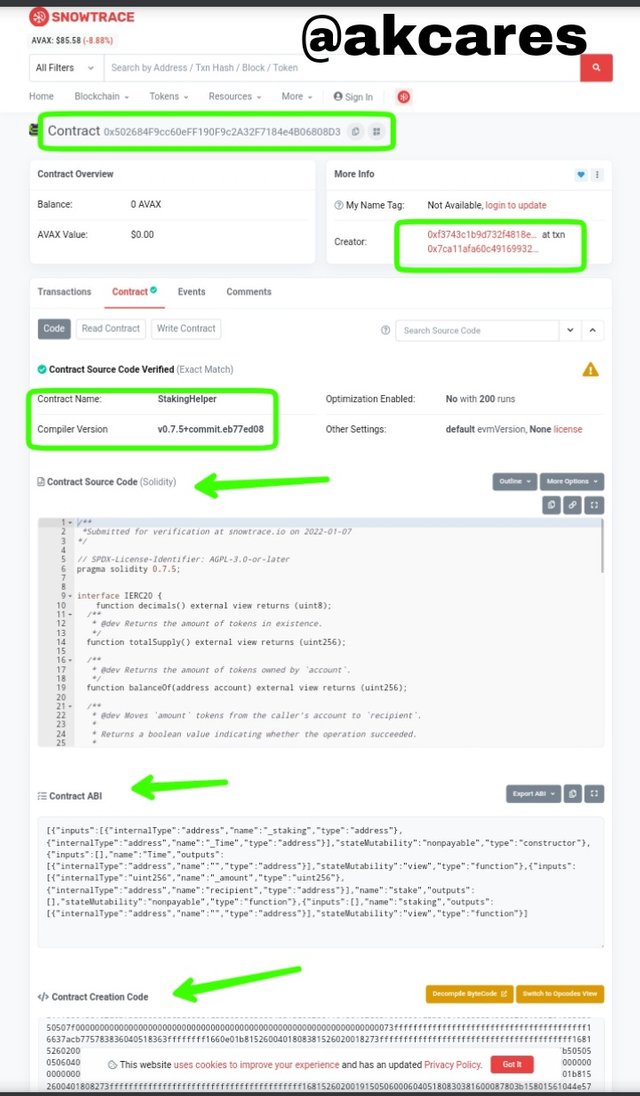
Other details of the contract like the source code, the ABI, creation code and others were detailed on the page.
All screenshots in this question were taken from the explorer page

Explore the last block generated in the C-Chain network. Screenshots required.
I still went back to the explorer page. From the same blockchain menu, I was able to find view blocks option.
I selected the option and a list of blocks were displayed in the next page.
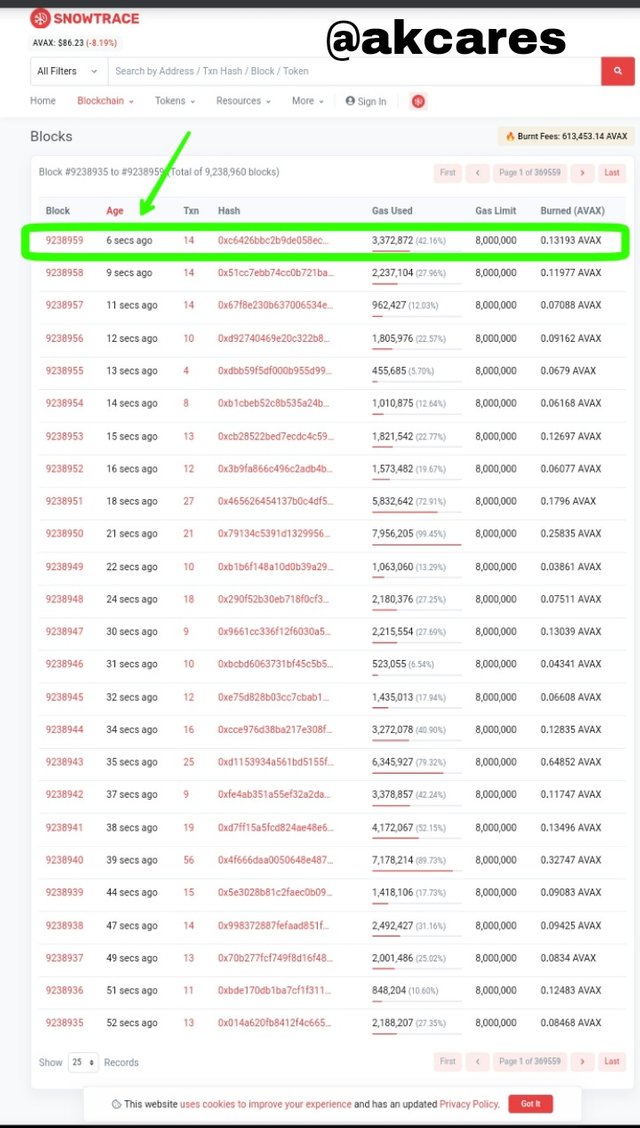
I picked the latest block which was the one on top being formed about 6 seconds ago and clicked on the block's hash.
This opened up with a display of several details. Some of them include:
The block height which was 9238959
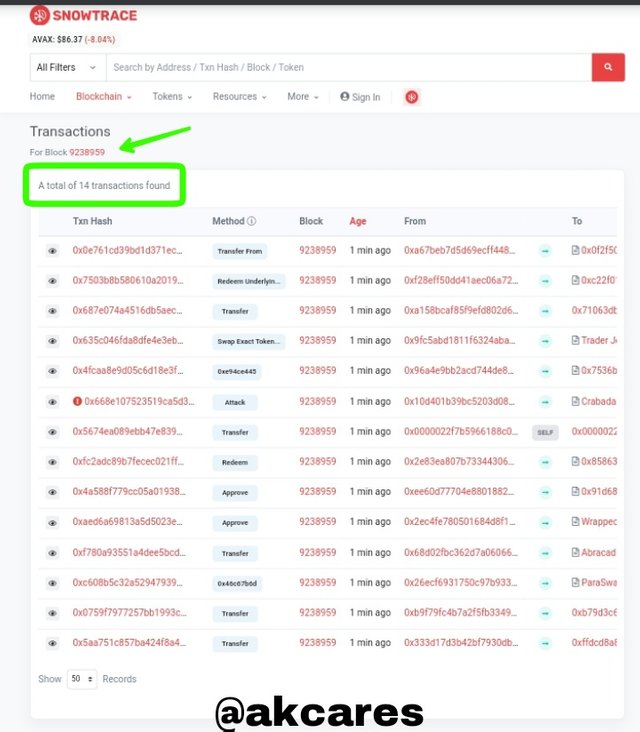
Timestamp was Jan-07-2022 04:27:20 AM +UTCThere were 14 transactions in this block.
The burned fees was 0.13193193006757572 AVAX
- The block hash was 0xc6426bbc2b9de058ec69016b1208510e54bae33e84949785be85676087019270
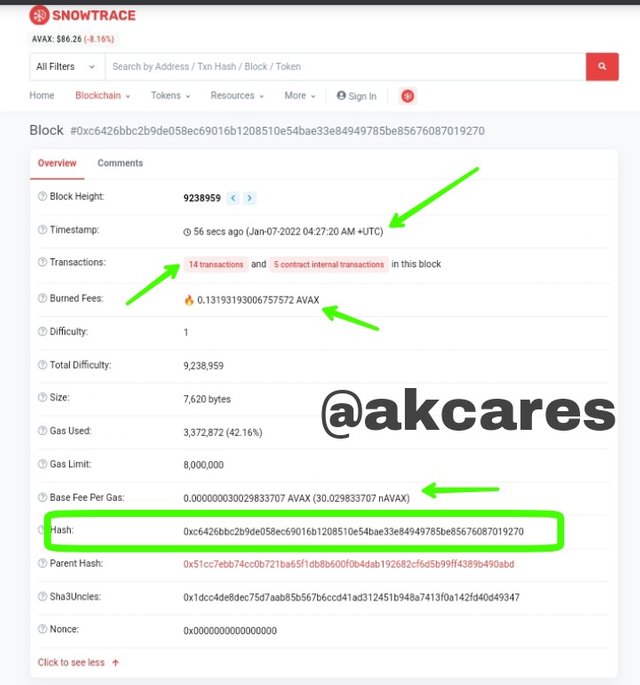
Other details were given along with these.
All screenshots in this question were taken from the explorer page

Explain in detail the Avalanche consensus protocol and the Snowman consensus protocol.
An amazing feature of the Avalanche network is the presence of multiple blockchains. These blockchains are operated by two separate protocols. Let me drop some details about these below.
AVALANCHE CONSENSUS PROTOCOL
This consensus protocol comes with a very unique system of functioning. On a general note, the protocol processes transactions in a parallel pattern. Here, the validating nodes make use of the Directed Acrylic Graph (DAG) mechanism which perfoms random ordering of transactions.
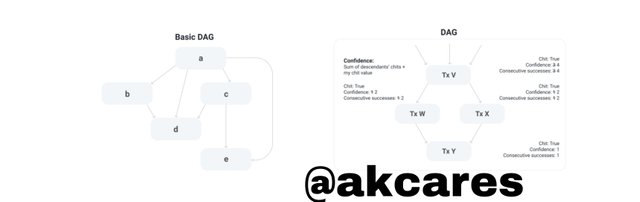
DAG is used to process transactions simultaneously such that as the transactions are being confirmed, verified and finalized concurrently.
A repeated sub-sampled voting technique is used to where validators conduct a sampling of a small group of other validators about the acceptance or rejection of a transaction.
This sampling is done repeatedly among clusters of validators. The results of the sampling is compared. If a greater number of validators accept or rejects a transaction, then the transaction will be accepted or rejected accordingly.
In this system a validator finds a transactions and goes ahead to verify it. He then shares his verdict with a other validators. If majority of the validator feel the transaction is authentic and validates it, then the transaction will be accepted. Otherwise, if the bulk of the group invalidates a transaction, then it will be rejected.
This protocol allows a validator to pick out other validators in a randomized fashion using a repeated random subsampling method. The validator then asks the other validators from the samples group what their preference is.
The processes for validating a transaction are broken down below.
i. Firstly, one validator is shown different initiated transactions to decide if is is accepted or rejected.
iI. If accepted, he will add the transaction to a list of valid transactions.
iii. Then a group of validators are picked randomly based on size of their stakes.
iv. They are queried about their preference for the transactions. A voting is done to reach a quorum for the transactions. Those accepted by majority of the group are passed while every other conflicting ones are rejected.
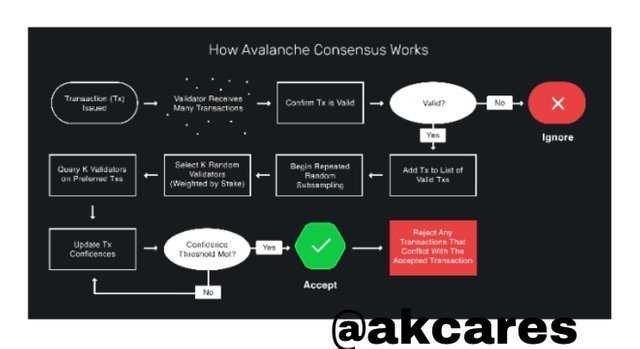
v. When the votes are not in agreement, the voting is repeated until an Alpha number of validators (larger majority) reach an agreement.
vi. In instances of conflicts, honest validators are picked to form a group and vote on the conflicting transactions and their feedback is used to judge valid transactions and discard faulty or repeated ones.
This is the protocol used by the exchange chain of the Avalanche network.

How Avalanche Consensus Protocol compares with other existing consensus protocols.
SNOWMAN CONSENSUS PROTOCOL
Snowman consensus protocol is employed mostly in smart contracts. Here, blocks are created from verifying linearly ordered transactions. This is an outgrowth from the Avalanche consensus protocol but here, transactions follow a linear sequence through the process of verification. It is used in the Platform and the Contract chains.
All screenshots not referenced in this assignment are taken from the AVAX official page

The things that attract human beings to a new product are mostly the improved package and promise of better functionalities. In blockchain spheres, the ability of a blockchain to address some inherent problems in the industry is a major selling point for any new blockchain.
For Avalanche blockchain, the presence of a well-structured consensus mechanism, excellent scalability and high interoperability are some of the improvements that have been built into the system as compared to some other blockchains that are lacking in these.
The division of the blockchain into subnets has gone a long way to improve its features. It is no surprise that this project has been widely accepted even though is has not spent much time in the public domain.
With the periodic upgrade and packaging, Avalanche project has come out to be very formidable and highly placed amongst others. Wonderful lesson by Prof. @pelon53.

Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit