
INTRODUCTION
The world is fast changing with a lot of new concepts being developed on a regular basis. Barriers are being broken and solutions are coming up faster than ever. We experienced the rise of blockchain technology and have witnessed its development and success for years. Even in 2020, the quiet world of blockchain saw light when a lot of people began to show interest in it. This interest extended to other promising concepts and the Hashgraph was one of them.
In this post, I’m going to explain the subject of the Hashgraph technology in response to professor @pelon53 ‘s homework.
Let’s get right into it...

Hashgraph
Hashgraph is relatively new in the tech world. The concept was initially developed in the mid 2010s by Leemon Baird and is already gained a lot of traction and for good reasons. Much like blockchain technology, Hashgraph is a Distributed Ledger Technology that relies on independent nodes to function. However, the Hashgraph technology is said to be a lot better than blockchain.
Hashgraph uses a Directed Acyclic Graph that replaces the regular blocks on blockchain. It relies on an asynchronous Byzantine Fault-Tolerant (aBFT) consensus algorithm that uses concepts like “gossip about gossip” and virtual voting for validating transactions. This technology is said to be way faster than blockchain as it can handle thousands of transactions per second. With all the hype around it, Hashgraph is sef to replace blockchain technology.
But what really makes this Hashgraph better? Let’s discuss some properties below.

The gossip Protocol
Large decentralized networks face the challenge efficient information dissemination. They do not have a central resource for adequately spreading information to different nodes. Instead of looking at the process from a wide angle view, we try to understand how to reach a large audience by considering stepwise and small information dissemination among nodes. This is what the gossip protocol is all about.
Initially developed in the 1980s and used in the routing systems of the internet predecessors, the gossip protocol gives an idea of what it is simply by its name. It is a peer-to-peer communication protocol that has become really popular over the years.
Basically, a node receives information from another node and randomly selects other nodes to share it with periodically and at a particular frequency. The nodes continue to spread the information they receive it until it gets to every node in the network all for the goal of reaching consensus.
The gossip protocol was named after the simple human behavior of spreading rumors. Let’s say in a University class, Nonso starts a rumor by telling Florence that John, his roommate, sleeps with a Teddybear. Florence receives this information as a hot rumor and one thing about hot rumors is that they become the gist of the day or even week or longer. So Florence is having lunch with Lucy and tells her. Lucy goes to study with Mark and tells him too. As Nonso, Florence and Lucy have passed the information, they don’t stop and so they randomly choose who to tell the rumor at any opportunity. This way, even if Mark does not tell anyone, the rumor stays alive. That’s the gossip.
As the Ancient Greek author Aeschylus once said, “Rumors have wings”.
This is also the same with an epidermic. A viral epidermic in a biological habitat knows no limit. It spreads indiscriminately and quickly and from person to person. By this, the gossip protocol is also referred to as the Epidermic Protocol.
Advantages of the Gossip protocol
1. Scalability: This protocol is highly scalable as it can be used to disseminate information faster and with low costs.
2. Decentralized: All nodes are independent in this system. This feature of autonomy gives full control to every member involved. This gives rise to other advantages like fairness and equality.
3. Fault Tolerance: The failure of a node in the system does not affect the dissemination of information. Even if a node fails to pass on a message, other nodes will keep passing it on until consensus’s reaches.
Disadvantages of the Gossip protocol
The main problem of the Gossip protocol is in the case of an affected piece of information. A malicious node can modify information to be wrong or affected and then spread it to other right nodes. These right nodes then uninterruptible spread this affected information.
Gossip protocol in Hashgraph
Now, Hashgraph uses this gossip protocol in its consensus algorithm to form itself. Gossip about gossip, as it is termed in the Hashgraph whitepaper, is a history of how events are related to one another through their parent hashes. Normally, two nodes take part in a gossip sync where they synchronize information. The gossip sync ends with each node creating an event. The event would normally contain four things:
- A Timestamp
- Two hashes of former events (self- parent and other-parent hash)
- The Transactions
- A cryptographic signature
The self-parent hash of a node is the last event it completed before the sync while the other-parent hash is the last event the other node completed before the sync.
Now, the history of related events are found in their parent hashes. The history takes the form of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) that is a Hashgraph. This Hashgraph keeps growing and recording the history of node communications storing itself in each node.

Tolerance to Byzantine Faults in Hashgraph
One of the features of Distributed Ledgers is the ability to resist faults. A Byzantine Fault is a type of fault that is caused by a failed component or node in a decentralized system. By this, Byzantine fault tolerance is a feature of a system to reach consensus even in the presence of malicious nodes.
Hashgraph uses an asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT). Consensus will be reached on the ground that:
- Only 1/3 of the voting power in the consensus are attacked.
- a message from an honest node will eventually get through no matter how long it takes.
If an attacker controls about 1/3 of the nodes in a system, the consensus can still be reached if at least one message gets passed from an honest node. The attacker can try to delay messages or delete them but eventually one would get through. This would be the case as long as the nodes are at the 1/3 limit. Any number exceeding this then consensus would not be reached.
Example, if 60 nodes are involved, the attacker would have to control just at or below 20 nodes to be harmless. Any number above 20 would be really bad.

Comparison between Hashgraph and Blockchain
To compare between two concepts, we have to consider any similarities. So for this task, I would talk about some similarities before I look at the differences.
Similarities
The two systems are distributed ledger technologies (DLTs).
The two systems are both decentralized peer-to-peer systems.
All transactions are transparent.
Differences
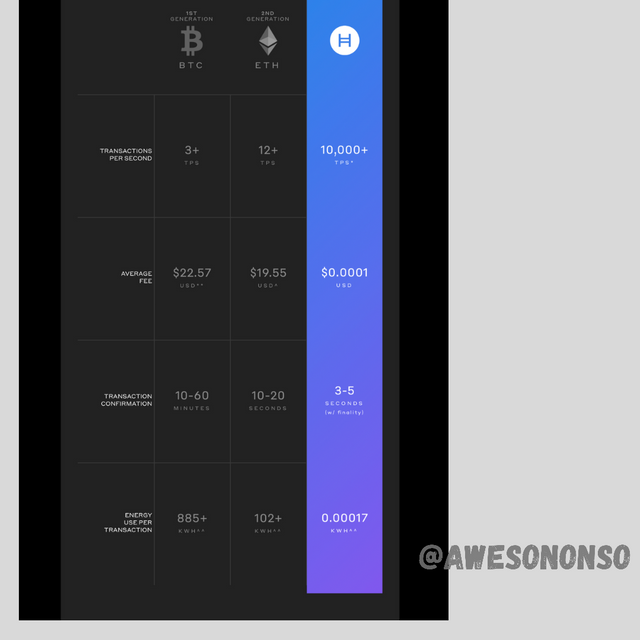
1. Speed: Blockchain speed really depends on the blockchain in question. However, when compared to Hashgraph, the Hashgraph technology beats the blockchain in speed. Hashgraph can go as high as 10,000 TPS.
2. Transaction costs: Again, costs depends on the blockchain in question. Still on a general note, blockchains cost way more than Hashgraph. Using the model crypto which is bitcoin and comparing it to Hashgraph, we can say for sure that the Hashgraph costs way less. Bitcoin blockchain costs about $22 per transaction while Hashgraph costs $0.0001 per transaction which is negligible. This makes the Hashgraph really convenient.
3. Adoption: Blockchains have been in existence long before the Hashgraph idea was born. Blockchain technology has been employed in a lot of areas to solve a lot of problems. It has been adopted by major organizations and companies.
Hashgraph, on the other hand, is fairly new. The Hedera Hashgraph is even still in the development stage. The Hashgraph has not solved much problems compared to blockchain. A lot of people don’t even know about Hashgraph technology. I even just heard about it in February.
4. Consensus Algorithm: A decentralized system has to have some sort of agreement system for validating transactions. Blockchain technology started with bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work consensus to the proof-of-stake and to the numerous consensus protocols available nowadays.
The experimental Hedera Hashgraph network works with the gossip about gossip protocol that enables virtual voting.
5. Data storage: This data storage point is the approach of the systems. Blockchain stores data in blocks and arranged these blocks in a sort of chain. Hashgraph however stores data on an directed acyclic graph that forms the Hashgraph.
6. Open source: Blockchain is open source and forks can be created from them. Developers can learn from them and make their own systems.
Hashgraph however is not open source and so forks cannot be made out of it.
Which I would choose for voting in my country
For this question, I’m certain a lot of people would choose Hashgraph mainly because of the topic. For me I would go for Blockchain for good reasons too.
First, I am from Nigeria which is a not so developed country. We’re still learning about blockchain over here and it’s not been going really well. Introducing a whole new technology into a highly ignorant community might not be the best move to make.
Second, I Trust blockchain. It is human nature to be skeptical about new ideas. Honestly, we haven’t really seen Hashgraph technology solving any real problems compared to Blockchain. Blockchains have been used to solve a lot of problems in the world for decades. Of course it can be used for voting.
Thirdly, I know that Hashgraph allows for virtual voting but people get the idea all wrong. Blockchain is about decentralization. It means you don’t have to be at a place to perform an action. That’s the whole point of decentralization and blockchains can achieve that.
Fourthly, let me talk about costs and speed. Blockchains have been evolving for years correcting errors of old versions. I mean, Blockchains like Trx, Ripple, Stellar and a vast majority have dealt with problems of cost. On the subject of speed, EOS has an average speed of 50,000 TPS. If that can be done then more can be done ok blockchain. Hashgraph is still experimental for now.
From the lecture, one thing that really caught my attention was when the professor said that Hashgraph’s “efficiency is mathematically proven but not in real life”. This statement calls for some scrutiny on the whole system.
I would choose blockchain because Hashgraph is still theoretical. Statement caught my attention. Use blockchain for voting because it has been in use. Human nature to be skeptical.

Hedera Hashgraph
Now I will explore Hedera Hashgraph to the best of my abilities.
First visit the website https://hedera.com/
On the homepage of the website, there is a greeting message, a search bar, an options tab and a floating globe

I clicked on on the Watch Video option because I was really curious. The video basically talks about the vision and plan of Hedera and the different partners involved. Some of the things emphasized on in the video were the fast, fair and secure nature of the Hashgraph run by a stable government.

Scrolling down a bit we discover the different partners of Hedera. Hedera has quite a lot of powerful partners.

Scrolling down more we see a comparison among bitcoin, ethereum and Hedera Hashgraph. I was blown away by the comparison. I mean, Hedera has a TPS rate of 10,000. That’s really impressive.
If we keep scrolling we would get to a section that explains the different Hashgraph services.

A little below is a video by Dr. Leemon Baird explaining the Hashgraph technology. The video was really informative. It really explained all that we learnt in this lecture with simple illustrations.

The options tab
Now let’s look at the options tab at the top right. Clicking on this tab we notice 6 tabs.

Network Tab: This tab includes smaller tabs to information on the Hedera services and helpful info on how the network works, explorers and the dashboard activity.

Devs Tab: This tab includes developer information for software enthusiasts and any other person interested in going deeper on the subject.

Use cases Tab: As the name goes, this tab highlights the various Hedera Hashgraph use cases.

Hbar Tab: This tab focuses on the Hbar which is Hedera’s native currency.

Governance: This tab when clicked on leads to a different window that explains the Hedera Governance council.

Hbar
Hbar is the native currency of the Hedera Hashgraph. According to the website, this coin serves as “fuel” as it lowers the Hashgraph. It is used to pay transaction fees for activities on the Hashgraph.
The Hbar token is a special cryptocurrency as it is the first Hashgraph cryptocurrency. It is really and experimental cryptocurrency for now. Below are some stats of the Hbar Token as of the time of writing this post.
| Price | $0.221 |
| All Time High | $0.4495 |
| Rank | #51 |
| Market cap | $1,911,194,571.13 |
| Trading volume | $213,767,556.13 |
| Curculating supply | 8,577,696,667 HBAR |
| Total Supply | 50,000,000,000 HBAR |

Conclusion
Hashgraph is an interesting piece of technology that would go a long way with proper planning and management. The goals of the developers are good and clear and can be achieved.
This technology is clearly stated to be better than blockchain but it can only be so if it is adopted by people. In my opinion, I feel like Hashgraph still has a long way to go.

Special thanks to @pelon53

Gracias por participar en Steemit Crypto Academy:
Espero seguir leyendo tus publicaciones.
Calificación: 9.5
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit