Introduction
Hello wonderful people, how are you today? I hope you're having a fantastic week. I'm ecstatic to be a part of this unforgettable lecture. In this article, I'll share my experience with Crypto Trading With Avalanche Blockchain.


1- Explain in detail X-Chain, C-Chain and P-chain.

X-Chain :
The standard blockchain on Avalanche is X-Chain, which is short for Exchange Chain and employs the Avalanche consensus process. It is a chain where assets may be transferred and generated, as the name of the chain implies. Users and programmers may use X-chain to generate new resources, exchange assets, switch resources, and move funds across subnets. Exchange Chain is another name for it. The chain enables users to exchange and produce tokens relying upon that Avalanche blockchain's guidelines and norms.
The X-chain is Avalanche's standard or core blockchain. The Avalanche blockchain is made up of three different blockchains. The Avalanche Consensus Protocol is the foundation for this chain. AVAX tokens are used to pay transaction fees. The X-Chain is where digital smart assets are handled, so clients may develop and exchange digital assets there.
C-Chain :
Developers may use the chain to create decentralized applications on the network. As a result, DApp programmers may use this chain to design their smart contracts. Snowman is a protocol that is utilized by the Contract Chain (C-Chain). Because the C-chain is compatible with the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine), Ethereum-based Dapps could well be operated on Avalanche. As a result, DeFi, which is based on Ethereum, may now deploy a variant of its goods on the Avalanche network.
P-Chain :
The Snowman consensus process is also used by the P-chain. The P-Chain, also known as The Platform Chain, is the third chain in the Avalanche ecosystem. It is in charge of organizing validators, generating new Avalanche subnets, and maintaining a list of current Avalanche subnets. The term Subnet refers to a set of validators who provide consensus on specialized networks. Avalanche Blockchain's durability and transaction verification speed are far superior to those of other blockchains at the time. Validators and active subnets are tracked by the P-Chain.

2. Explore the Avax Network platform. Screenshots required.

- To learn more about the Avax Network Platform, go to https://www.avax.network and you'll be taken to the homepage right away.
- When you get to the homepage, check to the top and see some of the Avax Network Platform's capabilities, such as Developers, Individuals, Avalanche-X, Press, Community, and Contact. Let's take a closer glance at each of them individually.
Developers Feature

- Developers can use Avalanche's developer function to create Ethereum Dapps. Here on Avalanche network, it enables developers to construct without boundaries, mint tokens, run a verifier, connects Exchanges, and use their own Developer guide.
Individual Feature
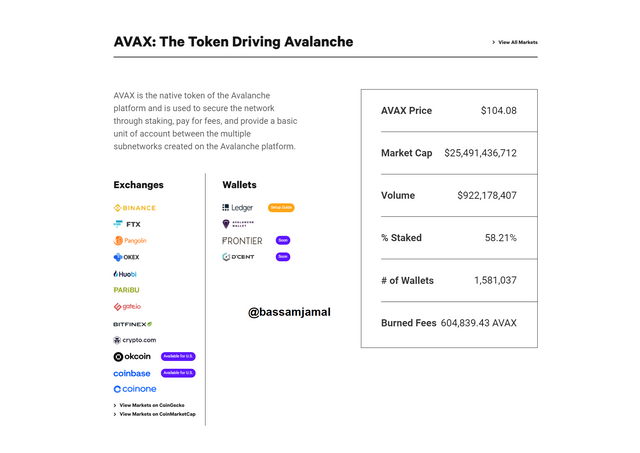
- The Avalanche roadmap, solution, wallet, Avalanche ecosystem, Avalanche Bridge, and Avalanche explorer are all contained in the developer section. The Avalanche Wallet is a non-custodial wallet that enables people to generate and retrieve their funds in an easy and safe manner. As you move down, you'll see a listing of platforms that handle Avalanche's native token, AVAX Token.
Avalanche-X
Users can apply for Avalanche-X grants and fund their speculative investments using the Avalanche-X functionality. When presenting a generic plan, there are 3 phases. These are the phases:
- Is for you to send in your request.
- If the platform requires your assistance, they will call you right away.
- Obtain approval and begin construction right away.
Press Feature

The news and activity on the Avalanche platform are included in the media. Consumers can stay up to know about the Avalanche network's current and future initiatives by visiting the press section.
Community

Designers from all around the planet can participate and connect with other Avalanche developers in the forum. Telegram, Facebook, Discord Chat, Linkedin, Meetup, Clubhouse, YouTube, and Reddit are all part of the Avalanche Network.
Contact
Whenever consumers or developers were using the Avalanche contact, they can communicate directly with the avalanche network anytime they have an issue. When contacting the platform, you must fill out the application form, which includes your name, email, and the sort of person you are, as well as your text, before clicking on I'm not a robot and then sending.

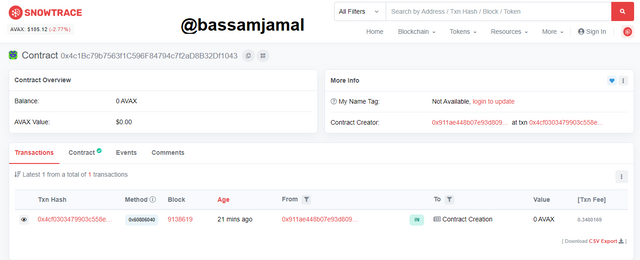
3. Show the last verified contract in the C-Chain network and show the Smart Contract that was generated at that address. Screenshots required.

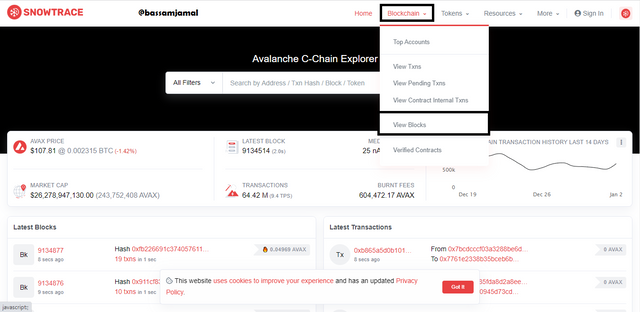
- To see the most recently verified contract in the C-Chain network, I visit https://snowtrace.io, touch on Blockchain at the top of the column, and afterward select on Verified contract, as seen in the image.
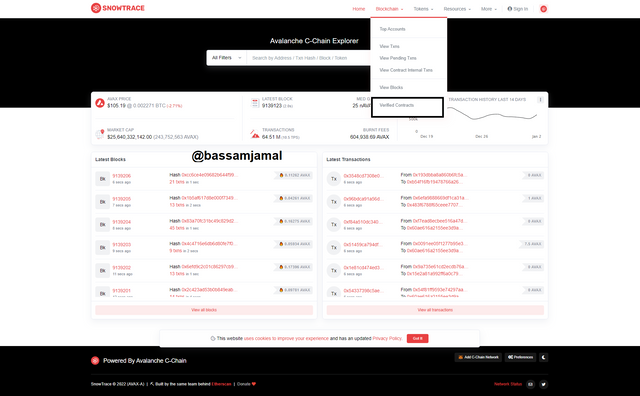
- When I click on Verified contract, a list of verified contracts displays instantly. The first contract on the listing is the most recent Verified contract in the C-Chain network, as illustrated in the image beneath.
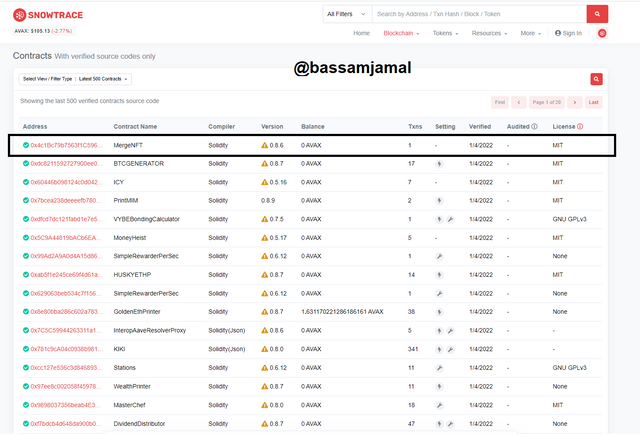
- MergerNFT is the name of the last contract 0x4c1Bc79b7563f1C596F84794c7f2aD8B32Df1043 at the moment of composing this assignment problem.

4. Explore the last block generated in the C-Chain network. Screenshots required.

For answering this question, First I visited to snowtrace.io
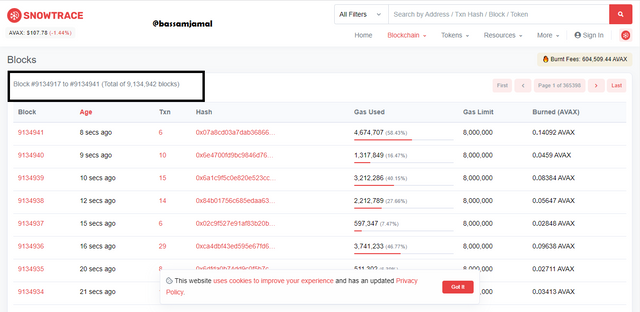
- Then I got an interface as shown below, Here i go to the Blockchain option and then choose View Blocks.
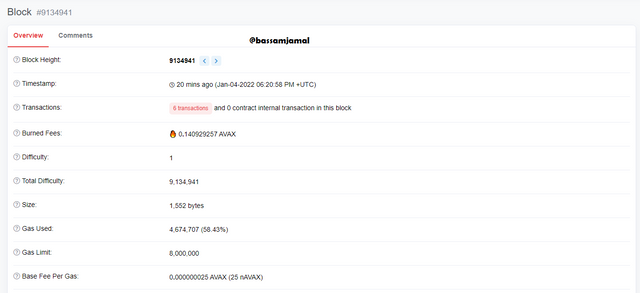
- A page containing a list of blocks is shown. A total of 9,134,942 blocks are visible.
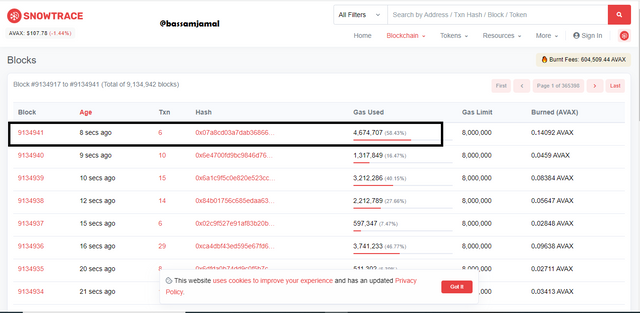
- The block at the top blocks 9134941, which was produced last. It has 6 transactions and 4,674,707 total gas use.
- At the time of writing, the block height (block number) is 9134941, with a timestamp of 20 minutes ago (Jan-04-2022 06:20:58 PM +UTC), 6 transactions, and 0 contract internal transactions. Block # 9134941 has a burned fee of 0.140929257 AVAX, A size of 1,552 bytes, a gas usage of 4,674,707 (58.43 percent), and an 8,000,000 gas limit.

5. Explain in detail the Avalanche consensus protocol and the Snowman consensus

Avalanche Consensus Protocol:
The Avalanche consensus protocol is a consensus technique developed by Avalanche that uses probability to minimize the possibility of a mistake. Because there is no leader to validate transactions, this is a truly decentralized system. Validators are used in Avalanche since it is a voting mechanism. These validators authenticate transactions using a hearing procedure. In this consensus mechanism, all transactions are confirmed and verified at the same time. This indicates that all sites are present in equal numbers and that the transaction is verified quickly.
A validator in the Avalanche consensus protocol can choose additional validators at random known as Repeated Random Subsampling. The X-chain, whereby AVAX tokens, as well as other crypto-assets, are marketed and further tokens are produced, uses this consensus system.
Distinct from other consensus mechanisms like proof of work, proof of stake, and others, Avalanche Consensus Mechanism does not necessitate a lead to obtain consensus, therefore all peers must check transactions using a directed acyclic graph. The lack of leadership promotes the blockchain's decentralization, although sustainability is unaffected. All transactions are handled and verified quickly, resulting in faster transaction speed.
Snowman Consensus Protocol:
The Snowman Consensus Protocol is based upon that Avalanche Consensus Protocol, but rather than operating with parallel nodes, it does not function with them. It's the Avalanche consensus protocol in its most comprehensive form. Because the transactions are arranged linearly rather than parallelly, this consensus mechanism differs from the Avalanche consensus protocol.
The Snowman consensus mechanism is in charge of generating blocks and is used to create linear chains that rank transactions in a linear way. When it comes to smart contracts, the Snowman consensus protocol is most commonly used. The Snowman protocol is used by the Platform Chain and Contract Chain because they are more suited for smart contracts than the Exchange chain.

Conclusion
Ava Labs invented or developed the Avalanche network. It employs three distinct blockchains: X-chain for token creation, P-chain for validation coordination, and C-chain for token formation suitable with Ethereum-based smart contracts.
Avalanche's principal goal is to give devs the flexibility to develop good projects or Dapps for the system independent of their financial situation because Avalanche allows them to apply for funding.