
Question 1
What is a Multi-sig wallet? How is it different from a Single key wallet? What are the different uses of a Multisig wallet?
Source
Multi-sign wallets are decentralized wallet that requires multiple (two or more) signatures to sign and broadcast a transaction within a network. The multi-sign feature on the wallets (multi-sign) is evident as each user has a private key connected to the wallet and access to the Master public keys (MPK) shared between the co-signers that enables them to sign and broadcast the transactions within the network.
This is very similar to a joint account in the banking sector where the account is controlled by multiple signatories and signatures of the signatories are required to perform a debit action on the account.
The multi-sig wallets are created by determining the number of cosigners denoted with n, allowed access to sign, and the number of signatures denoted with m, required to effect the transaction, this is set by the signers of the wallet.
The combination of m of n comes in ratios of 2 of 2, 2 of 3, 3 of 5, 5 of 7, etc. Where the number of agreeing signatures is higher than nonparticipating cosigners.
Difference between multi-sign and single key wallet
The Single key wallet is a decentralized wallet that the owner has sole access to the private keys, and can initiate, sign and broadcast a transaction within a network. Unlike the single key wallet, a multi-sign wallet requires Multiple signatures from cosigners of the wallets to sign using their private keys and MPK and broadcast the transaction within a network after the transaction has been initiated.
Uses of Multi-sign wallet
The multi-sign wallet has a very efficient use case when it is deployed in a business/organizational setting and can also improve security on individual-owned wallets. Some of the uses are:
Improved Security
The multi-sign wallet improves the security feature on wallets as multiple keys are required to effect a transaction. This cuts across individual-owned wallets and business/organizational models.
An individual can set up a multi-sign wallet on different devices (smartphone, PC, offline wallets) to serve as a two-factor authentication before accessing the wallet and initiating a transaction.
Similarly, businesses can assign the private keys to different individuals that have to sign before transactions can be broadcasted to the network. This improves security as access to multiple keys is required before effecting a transaction.
Joint Account
Similar to a bank joint account, a multi-sign wallet provides a similar feature that requires multiple signatories to approve (sign) a transaction before it can be processed.
This can be used in family accounts, corporation accounts, business accounts, school accounts, etc.
Escrow Services
Multi-sign wallets can be adopted in escrow services where a buyer and sellers are required to sign a transaction using private keys. But in an event of disagreement between the buyer and seller, an arbitrator can cosign a transaction in an attempt to resolve the dispute based on verifiable facts presented.

Question 2
Download, install & set up a 2-of-3 BTC Multisig wallet(Electrum)? What is the difference between Seed key and MPK? Would you share the seed key or MPK with your co-signer and Why?
Source
Downloading & installing Electrum wallet
To download and install Electrum multi-sign wallet, visit the website and download the version supported by your device.
I will be downloading the windows based version. Click on windows installer
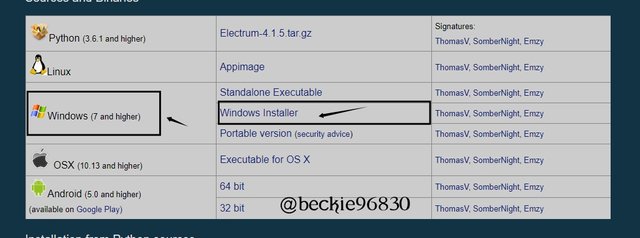
After the software download, open the downloaded file and install the software. Click on install.
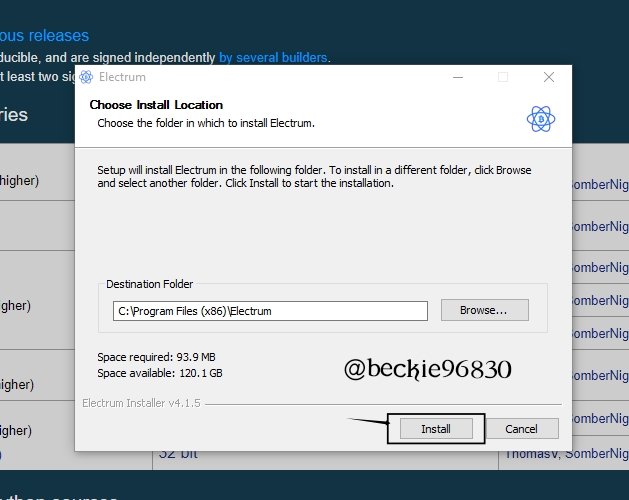
After the program installation, open the software.
Setting up a 2 of 3 BTC multisig wallet
To set up the 2 of 3 Electrum wallet follow the steps:
Open the installed program, and choose a wallet name, and click Next.
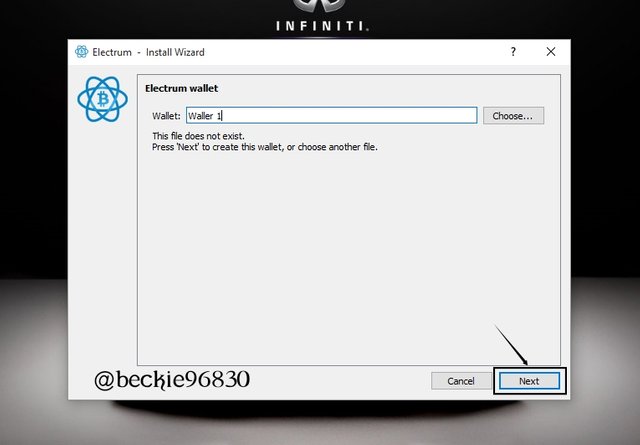
Next, choose the wallet type (Multi-signature wallet in this case) and click Next.
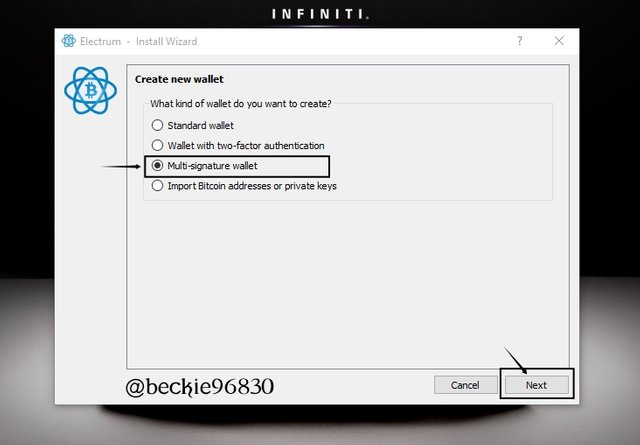
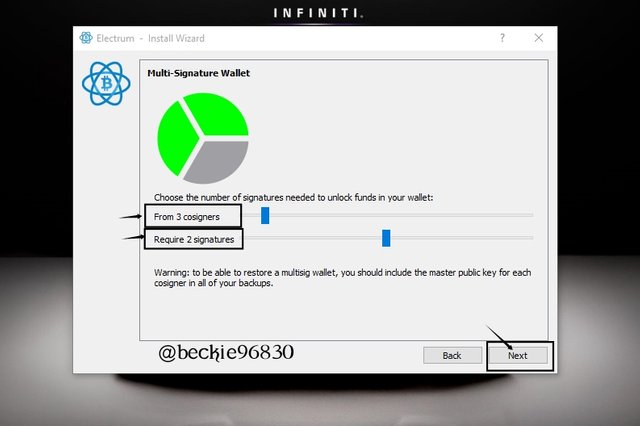
Next, select the number of cosigners and the number of required signatures for approval. Then click Next.
The requirement for this wallet will be 3 cosigner's and 2 signatures (2 of 3) will be required to approve, sign and broadcast the transaction.
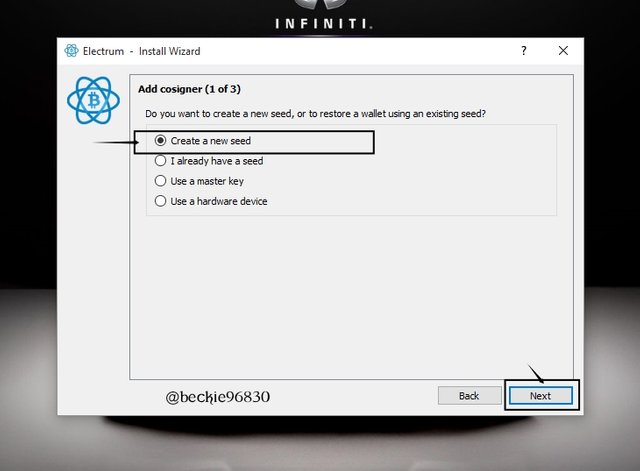
Next choose account verification type (private key), Select Create a new seed. Then click Next.
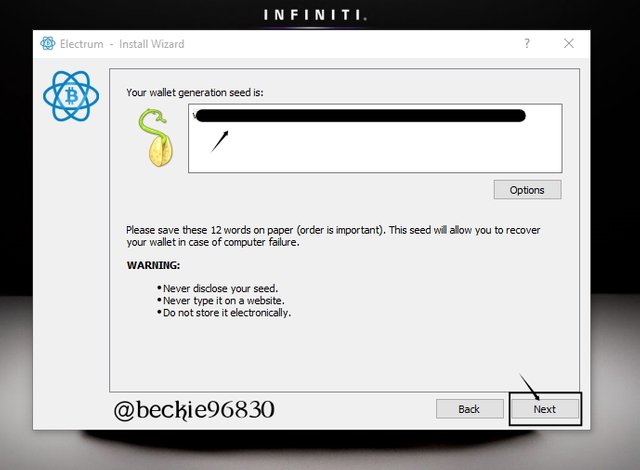
The seed key will be displayed. The seed is a unique combination of twelve (12) words phrases peculiar to each cosigner (each cosigner will get a unique seed key upon sign up).
Create a secured backup for the seed key, preferably offline copy.
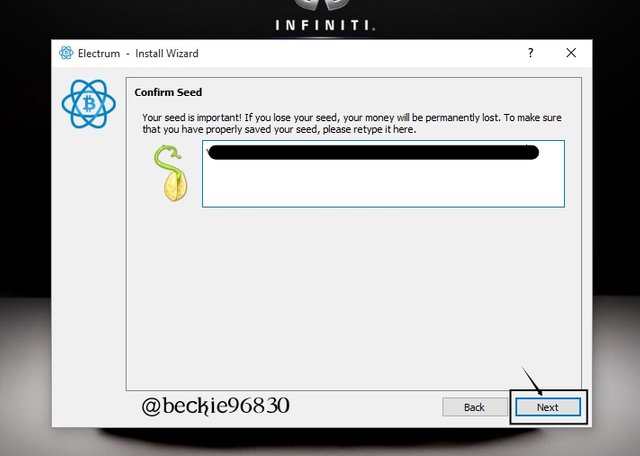
Next, confirm the seed key by re-entering the seed key, and click Next.
Next, the Master public Key is displayed. This is the key to be shared among the cosigners to enable authorized access to the wallet.
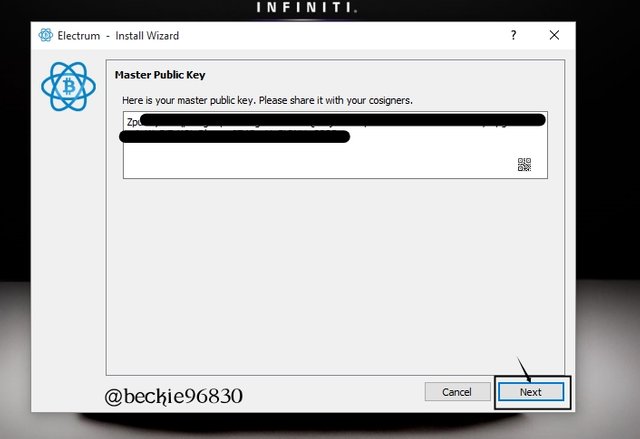
Next, is to reach out to other cosigners to create and send their Master public key (MPK). In this case, the other 2 co-signers must send their MPK to enable the wallet setup.
The cosigner will follow the same process to set up their access authority. The MPK of all three signatories should be kept secured by each of the cosigners, preferably offline.
It's important to note that only the Master Public Key should be shared and not the Seed Key
Next, input the MPK of the cosigner 2 of 3. Select Enter cosigner Key then, click Next
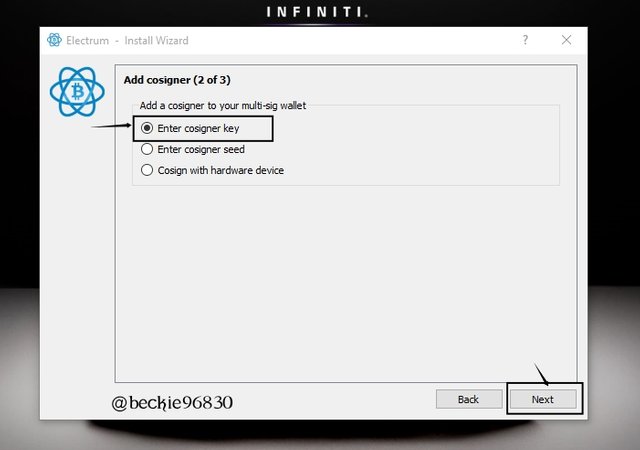
Next copy and paste the MPK of the second cosigner and click Next.
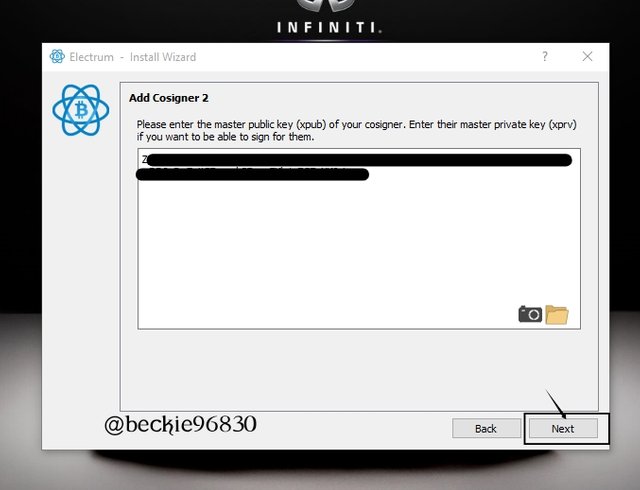
Next, input the MPK of the cosigner 3 of 3. Select Enter cosigner Key then, click Next
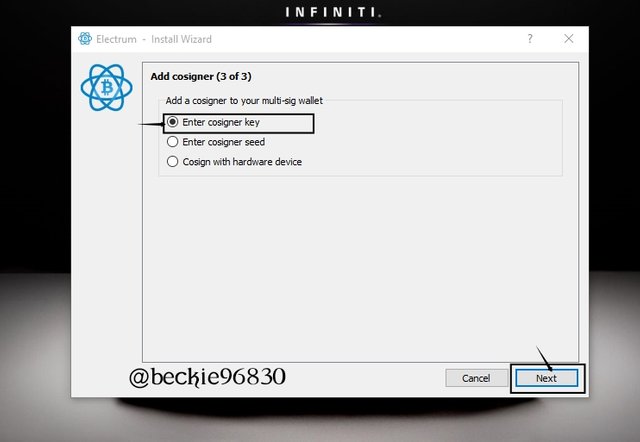
Next copy and paste the MPK of the second cosigner and click Next.
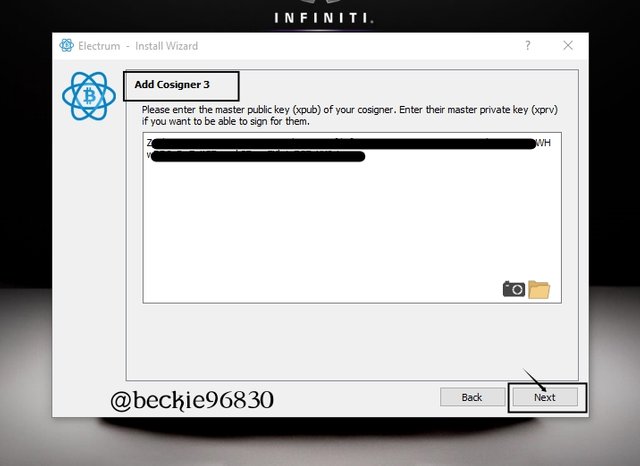
Next set the password to encrypt the stored keys. Re-enter the password to confirm the password is correct. Then, click Next.
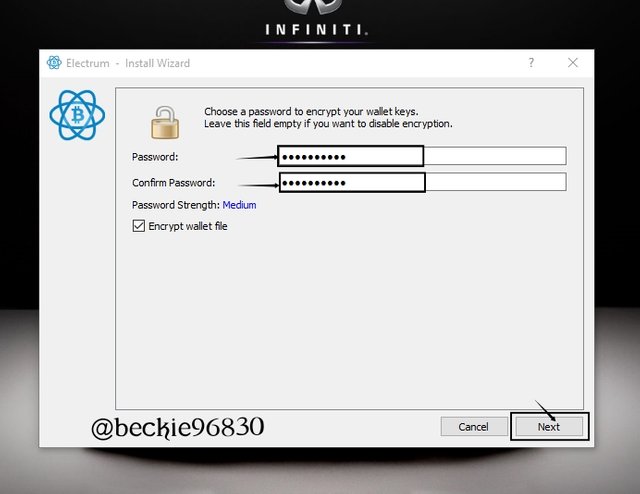
The Multi-sign wallet is set and ready for use.
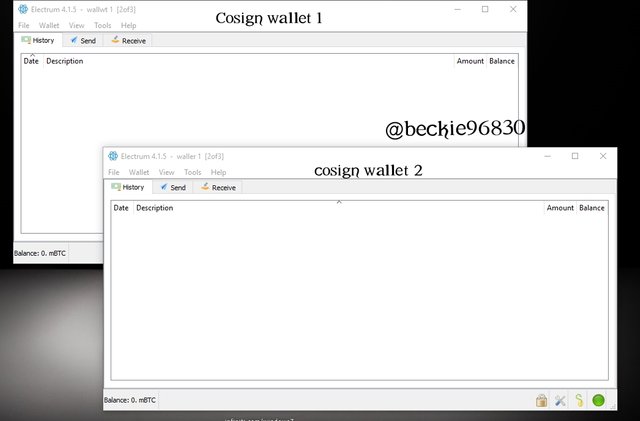
please note: The third cosign wallet was created on my mobile phone.
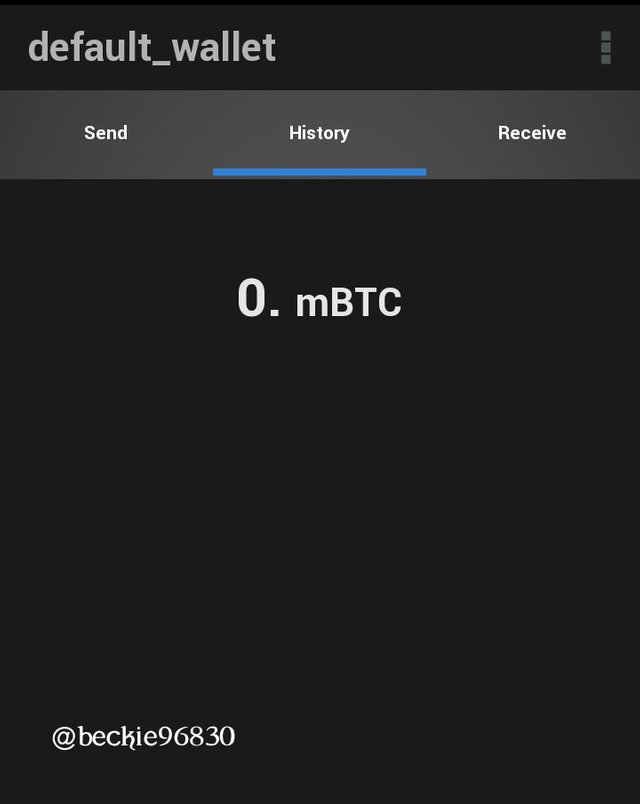
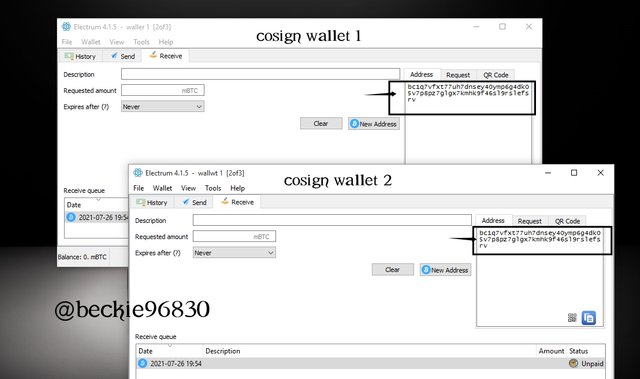
The Next step is to verify the New Address generated across the three cosign wallet is the same. To do this, click or the Receive tab, set the expire after duration to Never, and click New Address.
This will display the address of the wallet.
Note that the address of the multisig wallets should be the same regardless of the number of cosigner's.
Next is to verify the addresses are the same. The other cosigners should follow the same step and send their generated addresses to each of the signatories.
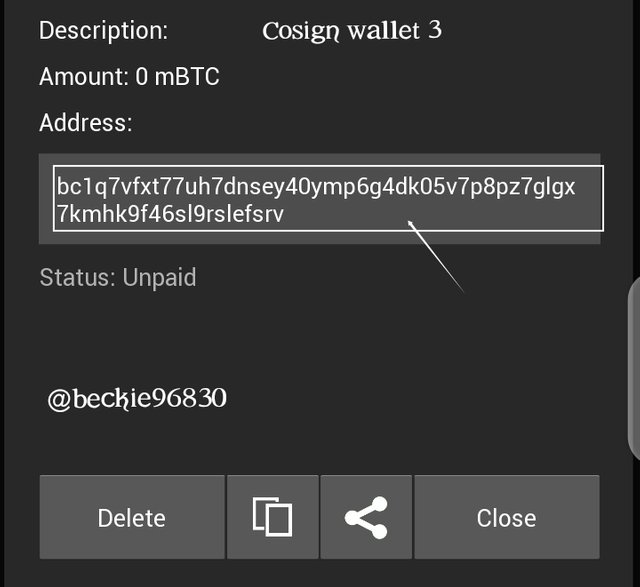
please note: The third cosign wallet was created on my mobile phone.
Now the multisig wallet has been created and verified to be connected.
Difference between Seed key and MPK
Seed Key
The Seed is a unique combination of 12-word phrases that serve as a private key (account security), which only the creator of the account should know and have access to. In the multisig wallet scenario, each cosign member has a seed key that is kept secret from other members of the multisig wallet.
This prevents false authorization and broadcast in event of a cosign seed key compromise. When the seed key of a cosign wallet is compromised, it poses a minor security threat depending on the number of required signatures.
For instance, a multisig wallet with 3 co-signers, that require 2 of 3 signatures. When one cosigner wallets seed key is compromised, the other 2 signatories can prevent the transaction from occurring.
Master Public Key (MPK)
The Master public key is a set of unique characters keys that usually starts with the letter Z. This public key is sent across to each signatory of the wallet to enable authorized access to the wallet.
Without each signatories creating and sharing their Master public keys, the wallet can not be fully set up. If a multisig wallet has 5 cosigners, each signatory of the wallet should have one (1) seed key (private key) and access to (4) Master public keys, including their MPK will complete the 5 MPK required to set up the account.
Would you share the seed key or MPK with your co-signer and Why?
Each signatory will be required to share their Master Public Key to other cosign members to enable the wallet to be fully set. Without sharing the MPK, the consigners can not set up the wallet or access the wallet.
If there are 3 cosign members attached to a wallet, each of the cosigners should have access to one (1) private key(seed key) and two (2) MPKs, including theirs, will make it 3 MPKs.
The seed key is meant to be kept private, and should only be known by the creator of a wallet(cosign member). In this case, each cosign member has a seed key only known by them.
Question 3
How many different "m of n combinations" Multisig wallets you can construct in Electrum? How do you Export your Seed & Private Key(Electrum) in a Multi-sig wallet?
Source
M of N combination in Electrum wallet
The Electrum wallet can allow up to 15 cosigners in a single wallet and can be set to require 15 signatures to sign and broadcast transactions within a network, i.e a 15 of 15 combinations. This implies that each of the cosign members will have access to one (1) private key and fourteen (14) Master public keys before the wallet can be set up.
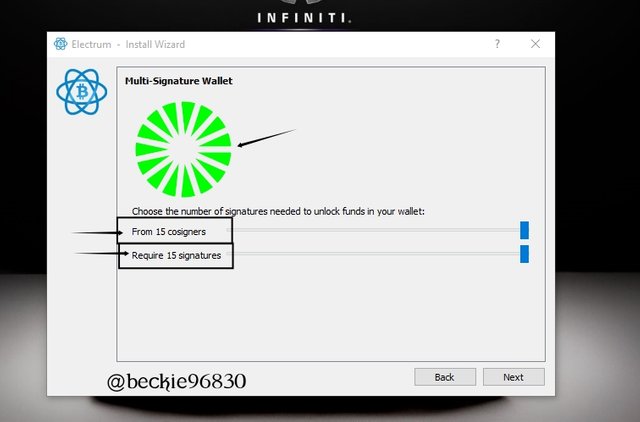
If the number of required signatures is set to the maximum (i.e 15), all cosigners must sign and broadcast the transaction before it can be processed, since they share the same address.
Exporting seed and Private Keys
Exporting Seed Key
To export the seed key, click on the Wallet tab and select Seed
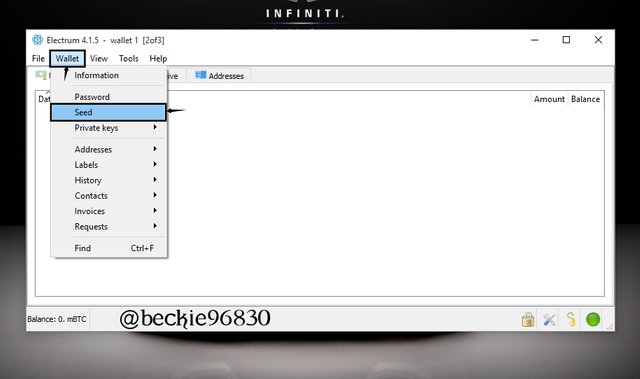
Next, enter the password to reveal the seed key. The export is achieved by duplicating the seed key.
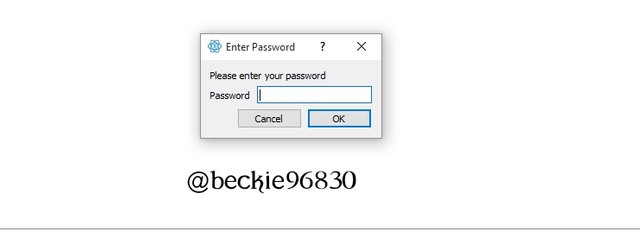
Next, the seed key will be displayed for a duplicate to be made.
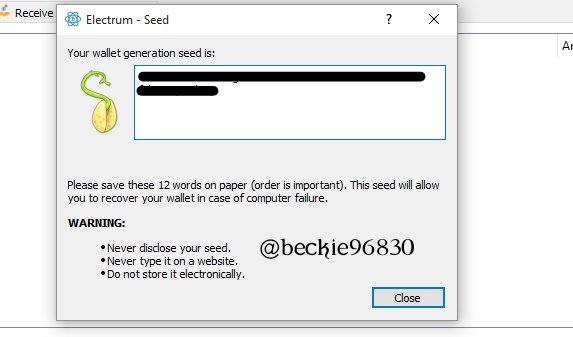
Exporting Private key
To export private key, click on the wallet tab and select Private Key then select Export
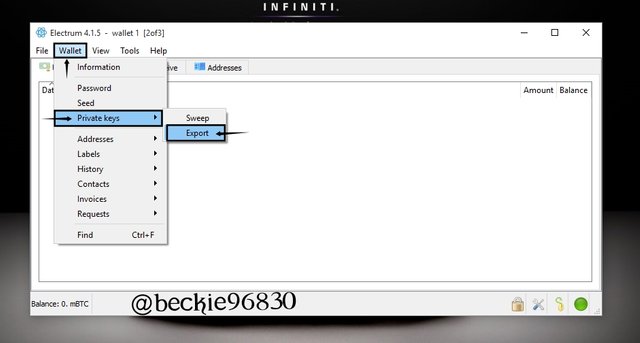
Next, enter the password to reveal the private key.

Next, the private key will be displayed after a warning that the private key is not to be shared.


Question 4
Perform a real transaction(Send BTC) to another Address using a 2 of 3 Multisig wallets? (You can perform a micro-transaction for this Task, also send a partial amount to demonstrate your experience with Change Address
Source
To perform a multisig transaction, close the wallet and open it again.
Click on File and select Open. Sign in using the password created.
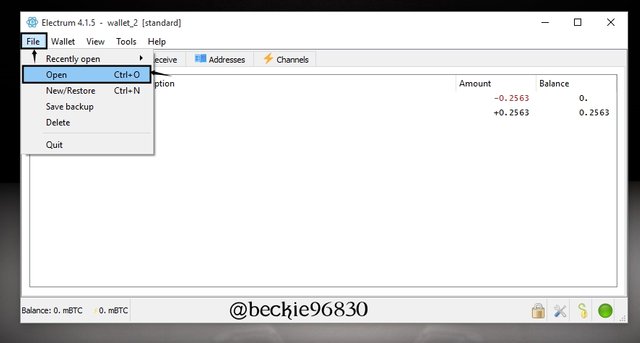
Next enter the password to access the wallet.
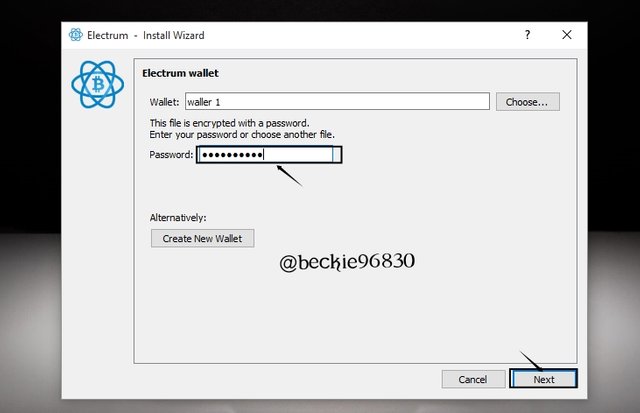
2 of 3 Multisig transaction
To perform the transaction, click on the Send tab, and fill in the required information.
Enter the receiver address (pay to), description of the transaction, and the amount in mBTC to be sent, then click pay. Only the receiving addresses should be sent and not the change addresses.
I have a balance of 0.24mBTC, I will be sending 0.12 mBTC to illustrate the change address effect.
Enter the pass word and Click send
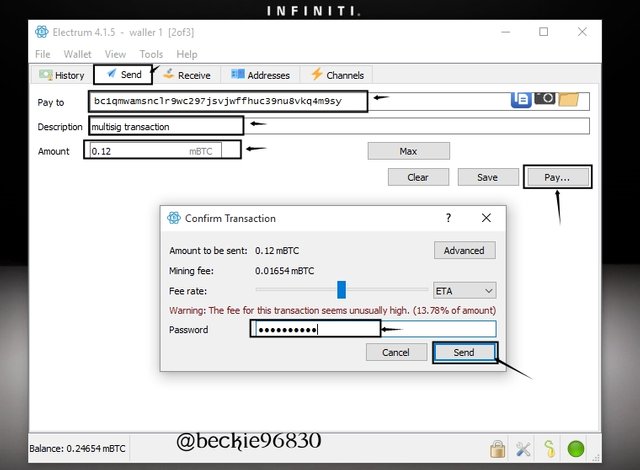
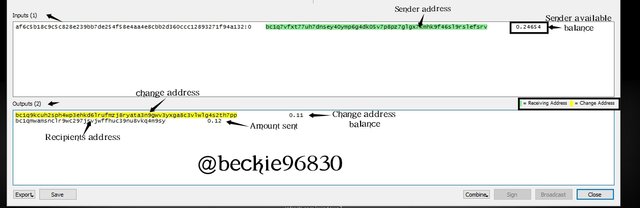
The wallet will display details of the transaction, showing the transaction ID, transaction input (sender address and available balance), transaction output (recipient address and change address). The change address indicates that the Unspent transaction output UTXO of 0.24654 mBTC on the wallet will be spent totally, as the available balance 0.11mBTC after the transaction is transferred to the change address.
The wallet automatically transfers the balance of a transaction to the change address.
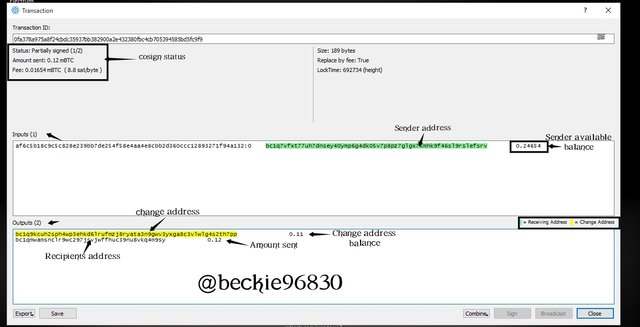
Since it is a 2 of 3 multi-sign wallets (indicated by the transaction status as partially signed) the initiator has signed, another cosigner is required to sign and broadcast the transaction. To do this in this instance, export the transaction file and save it.
Click on Export, then click Export to file and save it. QR codes can be used for this method as well.
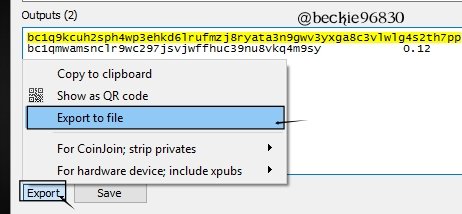
Next is to sign the transaction using another cosigner's wallet to complete the transaction.
Login to cosigner 2 wallet using the password created.
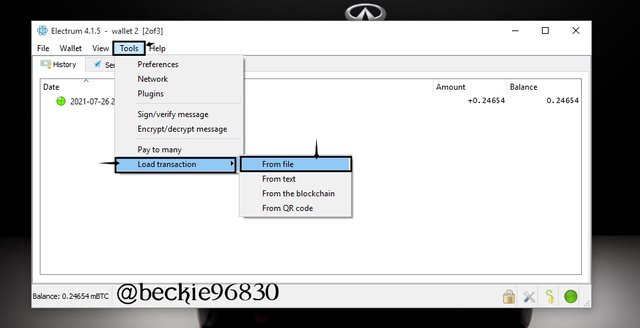
On the cosign wallet 2, Click on Tool and select Load transaction then select from file
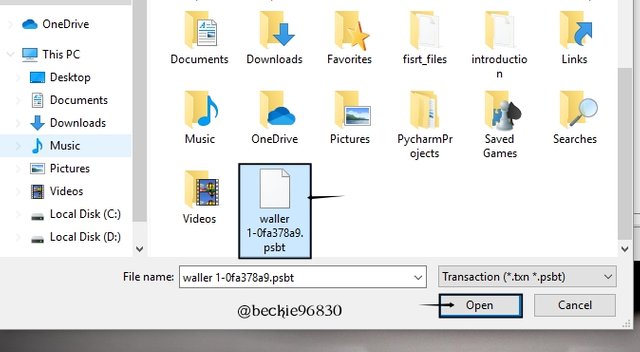
Next select the file and click Open
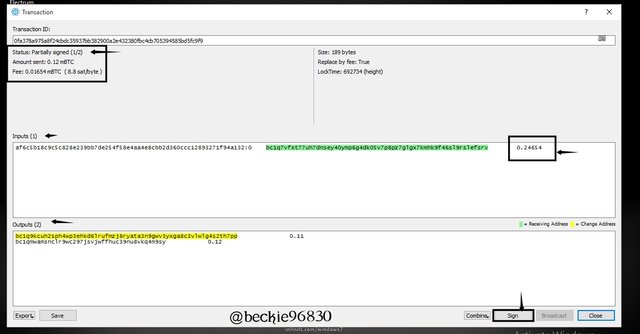
The opened file will display details of the transaction sent by the initiator, with the status of the transaction stating partially signed (1/2) this indicates that another cosigner's signature is required as the transaction can only be validated by 2 signatories (2 signatures).
Click on sign
Next, Enter wallet password and click Ok
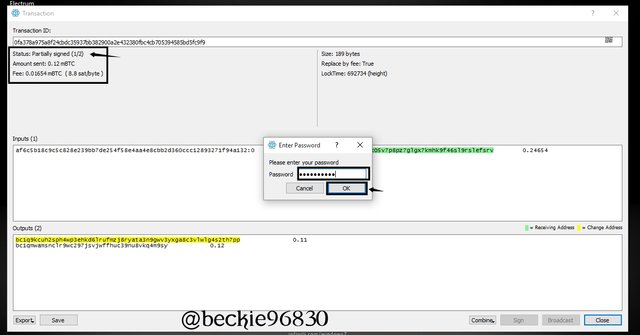
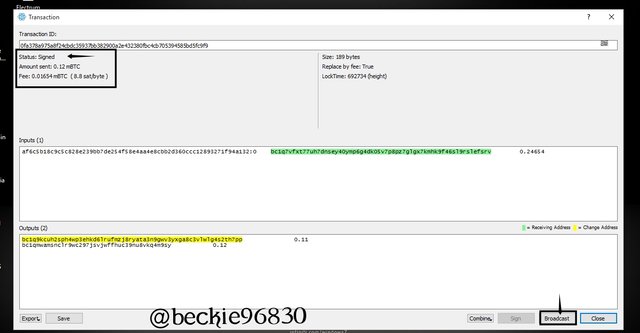
The status of the transaction will change from partially signed to signed this confirms that the transaction has received the 2 of 3 signatures required. Next is to Click on Broadcast
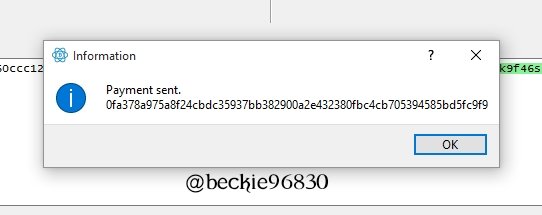
A prompt will appear indicating that the payment has been sent.
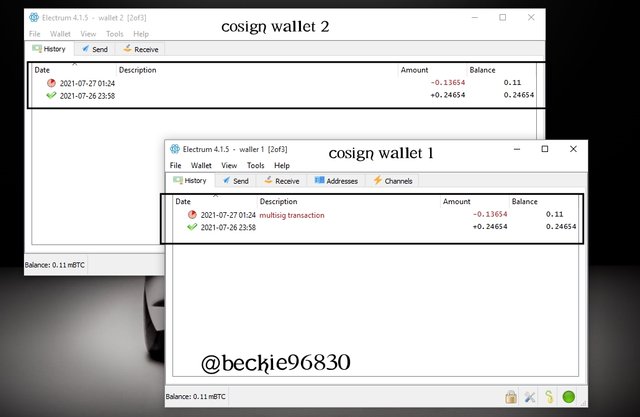
The details of the transaction are logged on the history tab of the cosign wallets 1 and consign wallet 2.
To verify the transaction using Blockchain explorer Link, copy and paste the transaction ID
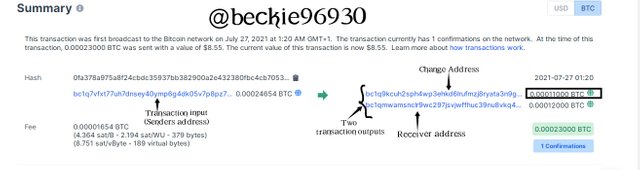
In the above image, the change address is included in the transaction output, because it contains the balance from the UTXO that was totally spent.

Question 5
What is the difference between Receiving Address & Change Address? Demonstrate your experience with a Change Address?
Source
Difference between Receiving Address and Change Address
Receiving addresses are unique wallet identifier addresses sent by a receiver to the initiator (sender) of a transaction that forms the transaction output (or part of transaction output like in the case of Electrum multisig wallets).
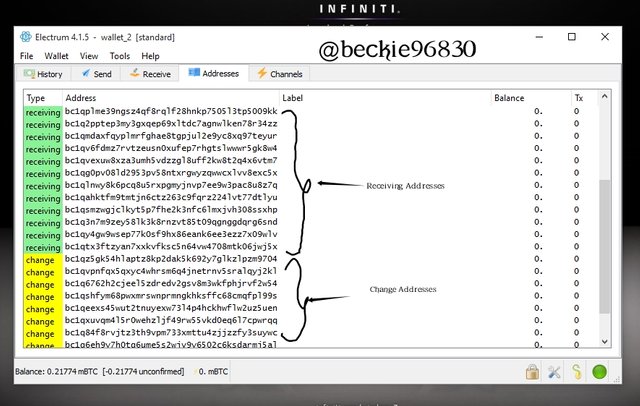
When a transaction is performed in an Electrum wallet, the unspent transaction output UTXO has to be totally spent, to this effect, the change address holds the balance of the unspent transaction output after the transaction has been done. This is usually done automatically and it forms the other part of the transaction output.
In the transaction carried out above, the UTXO was 0.24654 mBTC, and 0.12 mBTC was spent from the UTXO, this moved the reminder 0.11 mBTC to one of the Change addresses attached to the wallet.
The change address balance is added as an input when the next transaction is initiated.
conclusion
The multi-sign feature on decentralized wallets provides broad use cases for cryptocurrency in business and organizational structure and also improves the security of individual wallets.
The approval of transactions by the cosigner's of a multisig wallet indicates that a ratio of the signatories agreed on the details of the transactions, this is very similar to the joint accounts in the traditional banking system, where a consensus is reached between the signatories of the account before a transaction can be processed.
Thank you professor @sapwood for this insightful lesson.
Amazing presentation from you. Well explaied with simple words.
#affable #india
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit