Steemit is a platform that combines blockchain technology, social media, and cryptocurrency for the creation of user-generated content and community building. The social community helps to produce content and curate it, while it gets rewarded with two main cryptocurrencies: 50% in Steem Power and 50% in Steem Dollars.
Steemit is the platform where users publish content, and the Steem is the cryptocurrency and Blockchain protocol underlying it.
Contents [show]
Understanding the Steem ecosystem
Before we move forward, let me explain shortly how blockchain-based applications work (so called dapps or decentralized applications). Where in a web-based economy most of the value might be captured at application level.
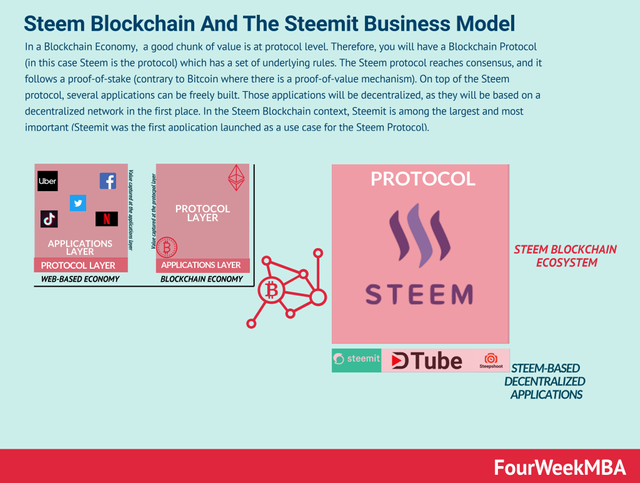
In a Blockchain Economy, as of now, a good chunk of value is at protocol level. Therefore, you will have a Blockchain Protocol (in this case Steem is the protocol) which has a set of underlying rules.
In the Steem protocol, to reach consensus, its algorithms follow a proof-of-stake (contrary to Bitcoin where there is a proof-of-value mechanism).
On top of the Steem protocol, several applications can be freely built. Those applications will be decentralized, as they will be based on a decentralized network in the first place.
In the Steem Blockchain context, Steemit is among the largest and most important (Steemit was the first application launched as a use case for the Steem Protocol).
That is also why here, I’m using Steem and Steemit interchangeably. However, Steem is the Protocol (defining the underlying core rules) and Steemit is one of the most important decentralized applications built on top of the Steem Blockchain.
How did Steem start? A brief history of Steemit
The company was co-founded by Ned Scott, CEO, and Daniel Larimer, CTO in January 2016. Both Ned Scott and Daniel Larimer were looking at ways to put into action the blockchain technologies for practical problems. The more they thought about it the more it made sense for them to use the blockchain to build up a community. In fact, as Ned Scott affirmed in an interview for coinreport.net:
“When the idea of Steem and Steemit really began to form we had been exploring several different blockchain-based business models. We were looking at micro insurance on the blockchain and a few other ideas, but ultimately, we kept coming back to the idea that the most useful and powerful thing to leverage around a cryptocurrency is a community.”
And he went on:
“Steem was born out of ideas about insurance and mutual aid: it was the idea that people would be able to help each other peer-to-peer if they were struggling to solve problems or needed assistance. It quickly grew into a much larger vision and Steemit was born as a place where individuals get rewarded by a community for posting and voting on content. That was back in January of this year.”
By April 2016, Steemit had launched an alpha testing, helped by more than 150 early adopters. As specified by Ned Scott in the same interview, the uniqueness of Steemit stands on the fact that everything that is done on the platform (posts, comments and votes) sit directly on the blockchain. Why is this important? This not only allows to manage things with a distributed system, where there is no central authority. It also should put an end to the old paradigm that took over the web in the last two decades, of a few tech giants that take over the world thanks to the data users give away for free.
What are the key principles behind Seemit? The three founding principles of Steem
Where platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Reddit get most of their value from the data created by its users without rewarding them. Steemit (also called Steem) instead tries to build its platform based on a few fundamental principles:
Everyone who contributes to a venture should receive pro-rata ownership, payment or debt from the venture.
All forms of capital are equally valuable: in short, either people of the community put cash or devote their time to grow the platform, they’re both considered as capital.
The community produces products to serve its members.
What does the Steem community do?
According to Steem White Paper, there are five primary values provided by its community:
A source of curated news and commentary.
A means to get high-quality answers to personalized questions.
A stable cryptocurrency pegged to the U.S. dollar.
Free payments.
Jobs providing above services to other members.
The Steem community starts from the assumption that with the incentives created by cryptocurrencies it is possible to bootstrap a social media platform like Steemit.
As further explained within the Steem White Paper (pg. 13):
“The vast majority of people have more free time than they do spare cash. Imagine the goal of bootstrapping a currency in a poor community with no actual cash but plenty of time. If people can earn money by working for one another then they will bootstrap value through mutual exchange facilitated by a fair accounting/currency system.”
And it continued:
“The tasks that can be entirely evaluated by an objective computer algorithm are limited in nature and generally speaking have limited positive external benefits…
…In order to give everyone an equal opportunity to get involved and earn the currency people must be given an opportunity to work. The challenge is how to judge the relative quality and quantity of work that individuals provide and to do so in a way that efficiently allocates rewards to millions of users. This requires the introduction of a scalable voting process. In particular it requires that authority to allocate funds must be as distributed and decentralized as possible.”
How does the Steem work?
As specified in Steem White Paper:
“The fundamental unit of account on the Steem platform is STEEM, a crypto currency token. Steem operates on the basis of one-STEEM, one-vote. Under this model, individuals who have contributed the most to the platform, as measured by their account balance, have the most influence over how contributions are scored. Furthermore, Steem only allows members to vote with STEEM when it is committed to a vesting schedule. Under this model, members have a financial incentive to vote in a way that maximises the long term value of their STEEM. Steem is designed around a relatively simple concept: everyone’s meaningful contribution to the community should be recognized for the value it adds. When people are recognized for their meaningful contributions, they continue contributing and the community grows. Any imbalance in the give and take within a community is unsustainable. Eventually the givers grow tired of supporting the takers and disengage from the community”
What are the Steem currencies? The Steem (STEEM), Steem Power (SP) and Steem Dollars (SBD) explained
To allow the Steemit community to be built on top of incentives that will enable its growth in the long-run, there are three main currencies. Each of those currencies serves a different purpose:
The Steem (STEEM): The social media cryptocurrency
The STEEM is the cryptocurrency of the social media platform. In other words, this is the unit of exchange based on the blockchain that can be easily exchanged on the market. Of course, its value can change quite quickly. Steem was valued at $19 cents as of June 2020.
The Steem Power (SP): The stock option of the Steem community
Stock options for startups are an effective tool to fuel their growth by giving ownership to employees; to create a strong incentive for growth. From the Steem community the equivalent of the stock options is the Steem Power currency. In fact, the users are rewarded for their activity on Steemit through Steem Power. This is a currency that follows a thirteen-week vesting schedule before. In short, those amounts cannot be easily traded on cryptocurrency exchanges. In short, the more SP you have, the more you can influence the reward system over the platform. And it is reinforced by the language used in converting a Steem in SP and vice-versa:
Converting a Steem in Steem Power (SP) is called powering up. This is because you stop being a speculator and become part of the community. Thus an active participant in building up the community
Converting a SP in Steem is called powering down. That’s because you are no longer a community member and will receive the payment of your currency in thirteen weeks. In fact, the week after you “power down” you will receive the total amount in the course of the thirteen weeks vesting schedule
As we’ve seen the Steem and Steem Power have two specific aims. The Steem is the cryptocurrency that has more speculative logic. The Steem Power instead is the currency with wich Steemit members are paid with. When you convert a Steem to a SP you become an active member of the community. Thus, you’re “powered-up.” Vice Versa by converting the SP in Steem you become a speculator, thus you’re “powered-down.” There is also another critical aspect of the Steem Power. This gives as we will see the power to its holders to elect a group of people, called “witnesses” in charge of publishing price feeds.
The Steem Dollars (SBD): The convertible notes of the Steem community
The Steem Dollars main aim is stability. In fact, the Steem dollars work as convertible notes. In fact, where startups use convertible notes as short-term debt instruments that allow startups to finance their operations by giving back ownership at a rate determined at the next funding round. The Steem Community leverages on Steem Dollars.
As specified in the Steem White Paper, the SBD:
“A blockchain based token can be viewed as ownership in the community whereas a convertible note can be viewed as a debt denominated in any other commodity or currency. The terms of the convertible note allow the holder to convert to the backing token with a minimum notice at the fair market price of the token. Creating token-convertible-dollars enables blockchains to grow their network effect while maximizing the return for token holders.”
The Price Feed, the witnesses and the anti-fraud mechanism of the Steem community
The price feed is the mechanism that allows a group of elected people to set the price of the Steem Dollars. In fact, to maintain parity with the dollar, it cannot be left free to fluctuations, but interest payments need to be made and withdrawn accordingly. As specified in the White Paper:
“SP holders elect individuals, called witnesses, to publish price feeds. The elected witnesses are presumably trusted by those who have a vested interest in the quality of the feed. By paying those who are elected, Steem creates market competition to earn the right to produce feeds. The more the feed producers are paid the more they have to lose by publishing false information.”
As defined in the White Paper:
“The primary concern of Steem feed producers is to maintain a stable one-to-one conversion between SBD and the U.S. Dollar (USD). Any time SBD is consistently trading above $1.00 USD interest payments must be stopped.”
How does Steemit Payout work?
When you produce content that gets upvotes and shares, you will automatically accumulate rewards. Those rewards will be paid out as it follows:
50% SBD
50% SP
The Steem Power (SP) currency can be converted in Steem (power down). If kept this gives its holder increasing voting power and influence over the platform. The Steem Dollars (SBD) give its holders an immediate and more stable currency that can be exchanged on the market.
However when you post something you have three options:
Power up 100%: you will only get rewarded with Steem Power currency
Default 50%/50%: you would get paid half in SP and half in SBD
Decline payout: in this scenario, your payout will be distributed to users
Steemit leverages on Zipf’s Law. That is, “if there are a million items, then the most popular 100 will contribute a third of the total value, the next 10,000 another third, and the remaining 989,900 the final third. The payout distribution is to offer large bounties for good content while still rewarding smaller players for their long-tail contribution.”
Why?
As specified in the White Paper:
“The economic effect of this is similar to a lottery where people overestimate their probability of getting votes and thus do more work than the expected value of their reward and thereby maximize the total amount of work performed in service of the community. The fact that everyone ‘wins something’ plays on the same psychology that casinos use to keep people gambling. In other words, small rewards help reinforce the idea that it is possible to earn bigger rewards.”
Forks, protocol wars and the rise of Blockchain Capitalism
Whether or not Steemit will work out, it’s hard to say. And as of now, as we’ll see, there are many things going on that moved away the Steem from its original mission. But I believe this case study is interesting because it shows how the Blockchain can be applied to publishing, and social media.
The fundamental idea behind the Steem blockchain is powerful. It’s about enabling the platform to be sustained by the community, at a decentralised level, both from a content generation standpoint and an investment perspective (Steemit users can both get rewarded with Steem currency and invest in the platform by being the Steem cryptocurrency.
In February 14 2020, the Tron Foundation announced it had acquired Steemit, the decentralized social media platform which at the time had over 10,000 daily active users. In the first two years, Steemit did gain traction, yet by 2018, the main decentralized application built on top of the Steem blockchain had to lay off more than 70% of its staff. Lack of financial resources might have been one of the causes that brought to the deal with Tron.
Yet, the community didn’t take this well, and it reacted. Justin Sun, founder of Tron in an open letter addressed the concerns of the Steemit community but that didn’t help. The community, fearing that the new take over would transform Steemit into just another centralized app. The community reacted, trying to take control of the decentralized app.
That became a real war between centralization on the blockchain and pure decentralization. The community managed to fork the protocol and to create a new one called Hive, which later on outperformed the Steem itself. While this story still goes on it’s interesting to notice this power struggle between who tried to take over the app and the community.
This sort of dynamic, probably new to corporations, might probably be the new normal in the Blockchain era, that might help build a new form of capitalism.