Hi everyone, I’m @brianwong. First of all thank you to my friend @rajithpriyasad for inviting me to participate in the competition organized by @cryptoacademy SEC S18-W1 || Master the market through technical analysis. I will write down my personal understanding and thoughts in the next article, I hope you all like it.
As financial markets become increasingly complex and volatile, the ability to understand and interpret market data through technical analysis has become essential for any trader who wishes to excel.
This focus on technical trading grew out of a recognition of our community's growing needs and interests for in-depth, practical skills in this area. Many of our members have expressed a desire to improve their ability to navigate the markets not only to improve their personal trading performance but also to enrich their understanding of the financial mechanisms that influence our economies and investments on a daily basis.
First, what is the importance of technical knowledge in trading?
Technical knowledge is of great importance in trading as it helps traders make more informed decisions, reduce risk and increase profit potential. Here are a few key aspects of technical knowledge in trading:
- Market analysis
Technical Analysis: Predicting price movements through charts and technical indicators. Traders can use tools such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, and more to identify trends, reversals, and overbought and oversold conditions.
Basic analysis: Understand the company's financial status, economic indicators, market sentiment, etc., to determine the intrinsic value and future performance of assets. - Risk management
Stop loss and take profit settings: Technical knowledge helps traders set reasonable stop loss and take profit points to control losses and lock in profits.
Position Management: Learn how to diversify and manage position size to avoid excessive risk exposure. - Strategy development and optimization
Algorithmic Trading: Writing and optimizing trading algorithms to automate trading strategies. This requires programming knowledge and a deep understanding of market mechanisms.
Strategy testing and backtesting: Use historical data to test and optimize trading strategies and evaluate their performance under different market conditions. - Market tools and platforms
Use of trading platforms: Proficient in the use of various trading platforms, including order types, chart analysis tools and trading interfaces.
Real-time data and news: Get and analyze market data and news in a timely manner to understand market dynamics and potential price drivers. - Psychology and discipline
Psychological analysis: Understand changes in market psychology and emotions, and avoid emotional trading and irrational decisions.
Trading discipline: Technical knowledge helps traders formulate and adhere to trading plans and avoid blindly following trends and impulsive trading. - Regulations and Compliance
Understand market regulations: Be familiar with the laws and regulations of the trading market to ensure compliance with trading behavior.
Avoid market manipulation and fraud: Technical knowledge can help identify and avoid potential market manipulation and fraud. - Continuously learn and update
Technological progress and market changes: Financial markets and trading technology continue to develop, and traders need to continue to learn new technologies and methods to maintain a competitive advantage.
Industry information and research: Continuously update your knowledge base by reading industry reports, attending seminars and training courses.
Practical application cases
Quantitative trading: Use mathematical models and algorithms to conduct high-frequency trading to quickly capture tiny price fluctuations in the market.
Hedge funds: Use complex trading strategies including arbitrage, hedging and leverage to pursue high returns.
Individual investors: Use technical analysis tools to formulate trading strategies and conduct transactions in stocks, futures, foreign exchange and other markets.
To sum up, technical knowledge is not just an auxiliary tool in trading, but a core element for successful trading. It can help traders analyze the market more accurately, manage risks, develop effective trading strategies, and stay competitive in the changing market environment.
Full analysis of candle chart patterns:
Candlestick chart is a chart that every expert in stock trading and foreign exchange trading must know.
Depending on the time period of the chart, each candle may represent a week, day, or minute. . . .
The role of candle charts in trend analysis
Traders can look at line charts to conduct buying and selling transactions. Generally, mobile apps have line charts.
But looking at the line chart doesn't reveal much. To put it simply, you don't even know where the bottom is when buying the bottom. . . .
If we want to analyze the next trend of prices, we can see many things through candle charts, including price changes, where there is resistance, where there is a trend, where the limelight has passed, and where there are small emotions. . .
Green candles show rising prices,
Therefore, the opening price is at the bottom of the real body and the closing price is at the top.
Red candles show falling prices,
Therefore, the opening price is at the top of the body and the closing price is at the bottom.
Each candle consists of a body and a wick.
The body of the candle tells you what the open and close prices were during the time frame of the candle.
If the chart is a 5-minute chart, then each candle represents 5 minutes, the starting price at 5 minutes, and the starting price after 5 minutes.
Each candle represents a segmented time period. Reflects price changes for trades executed during that specific time period.
The lines extending from the top and bottom of the body are the wicks
These represent the highest and lowest prices during this time period,
Both sides of the wick, upper shadow line, lower shadow line
It is a line that stands out from the main body of the candle. In trading, you will find that the upper shadow line and lower shadow line will become longer or shorter as the trading volume changes. It reflects the immediate trading sentiment.
What do candles tell us?
Over time, each candle can reveal more than just price movement. Experienced traders look for patterns to gauge market sentiment and predict where the market may go next.
For example, a long wick at the bottom of a candle could mean that a lot of traders were buying when the price was falling, which could be a sign of an uptick.
A long wick at the top of a converse candle may indicate that traders are selling and is a signal of heavy selling.
If the main body occupies almost the entire candle and the wicks on either side are very short, it may indicate strong bullish sentiment (green candle) or strong bearish sentiment (red candle)
Next, let’s talk about defining chart patterns and distinguishing between continuation patterns and reversal patterns. How to set effective stop loss orders using chart patterns?
Define chart mode
Chart patterns are graphics and formations used in technical analysis to predict market price movements. These patterns analyze historical price data to identify specific patterns and thereby predict the direction of future price changes. There are two main categories of chart patterns: continuation patterns and reversal patterns.
The difference between continuation mode and reversal mode
Continuation Patterns
Definition: A continuation pattern usually occurs in the middle of a price trend, indicating that the price will continue to develop in the original trend direction after a brief consolidation or correction.
Common types:
Flag: After the price rises or falls by a small flagpole, it enters a brief rectangular or parallelogram area and then continues the original trend.
Triangle: including symmetrical triangle, ascending triangle and descending triangle. The price fluctuated in a gradually converging area and finally broke through the triangle boundary to continue the original trend.
Wedge: Similar to a triangle, but both sides of the wedge are sloping in the same direction, and the price eventually breaks out in the direction of the original trend.
Reversal Patterns
Definition: A reversal pattern occurs at the top or bottom of a trend and indicates that the price trend is about to reverse direction.
Common types:
Head and Shoulders Top and Head and Shoulders Bottom: include a higher peak (or trough) as the head, lower peaks (or troughs) on both sides as shoulders, and price breakthrough After the neckline, the trend reverses.
Double Top and Double Bottom: After the price reaches the top or bottom at the same level twice, it forms an M-shape or W-shape. After breaking through the neckline, the trend reverses.
Triple Top and Triple Bottom: The price tops or bottoms three times at similar levels, forming three peaks or three troughs. After the breakthrough, the trend reverses.
Use Chart Patterns to Set Effective Stop Loss Orders
To better manage risk in trading, chart patterns can be used to set effective stop-loss orders. Here are some specific methods:
Determine stop loss position based on pattern shape
Continuous mode:
Flag: Place a stop-loss order below (uptrend) or above (downtrend) the flag. If price breaks out of the flag pattern but fails to maintain it, it usually signals a possible reversal.
Triangle: Place a stop-loss order outside the opposite boundary of the triangle to prevent false breakouts.
Wedge: Place a stop loss order outside the opposite boundary of the wedge.
Inversion mode:
Head and Shoulders Top/Bottom: Place a stop loss order slightly below (Head and Shoulders Top) or slightly above (Head and Shoulders Bottom) the right shoulder of the Head and Shoulders pattern to prevent the trend from truly reversing.
Double Top/Bottom: Place a stop loss order below the second high of a double top (double top) or above the second low of a double bottom (double bottom).
Triple Top/Bottom: Place a stop-loss order below the third high of a triple top (triple top) or above the third low of a triple bottom (triple bottom).
Set an appropriate stop loss distance
ATR (Average True Range): Use the ATR indicator to set the stop loss distance and adjust the stop loss point according to market volatility. Usually, the stop loss distance can be set to 1-2 times the ATR.
Percentage method: According to the risk management principles of the trading account, set a fixed stop loss percentage (such as 2% of account funds), and calculate the corresponding price distance as the stop loss point.
Dynamically adjust stop loss orders
As the price moves in the desired direction, stop-loss orders can be gradually moved up (uptrend) or down (downtrend) to lock in some profits and reduce risk.
Setting effective stop-loss orders through chart patterns can better protect traders' funds, reduce losses, and ensure maximum profits when the trend is clear.
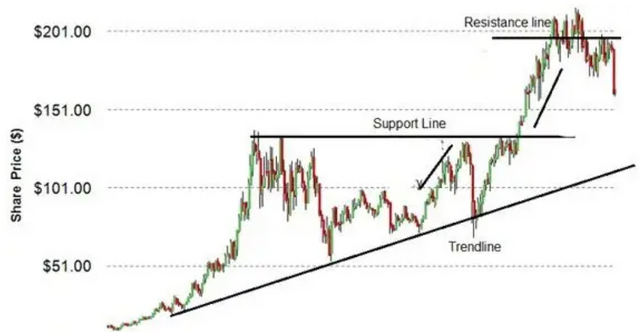
What is Trading View? How to use it to apply technical indicators to live trading? Describe the relationship between support and resistance levels and how technical indicators help understand these concepts.
What is TradingView?
TradingView is a popular online chart analysis and trading platform that provides traders and investors with powerful charting tools and technical indicators to analyze the market and make trading decisions. It supports a variety of financial markets, including stocks, forex, cryptocurrencies, futures, indices, and more. Key features of TradingView include:
Advanced Charting Tools: Provides a variety of chart types and drawing tools for technical analysis.
Technical indicators: A large number of built-in technical indicators, such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, etc., and allow users to create custom indicators.
Social network functionality: Users can share trading ideas, strategies and charts, and interact with other traders.
Live Market Data: Provides real-time data and news updates on a variety of markets.
Trading Integration: Integrates with multiple online brokers, allowing users to trade directly through the platform.
How to apply technical indicators to real-time trading using TradingView?
Create an account and log in: Visit TradingView’s official website (www.tradingview.com), create an account and log in.
Select a market and asset: Enter the market or asset you're interested in (e.g. ticker, currency pair, cryptocurrency, etc.) in the search bar and click Select.
Open a chart: Click "Full-featured Chart" to open a detailed chart for the asset.
Add technical indicators:
In the toolbar at the top of the chart, click the "Indicators" button.
Select the technical indicator you want to add from the drop-down menu, or use the search function to find a specific indicator.
Once the indicator is selected, it will be automatically applied to the chart.
Adjust indicator parameters: Click the name of the added technical indicator to open the parameter setting window and adjust the parameters according to your needs.
Draw support and resistance levels: Use drawing tools (e.g. horizontal lines, trend lines) to manually mark support and resistance levels that you think are important.
Analyze charts and make trading decisions: Analyze the market using technical indicators and chart patterns to make buy, sell, or hold decisions.
Direct trading: If your account is integrated with a supported broker, you can place trades directly through TradingView.
The relationship between support and resistance levels
Support: This is the level at which prices tend to stop and rebound during a decline. This is usually because there is strong buying interest at that price level, forming a "floor."
Resistance: This is the level at which prices tend to stop and fall back on their way up. This is usually because there is strong selling interest at that price level, creating a "ceiling."
The relationship between support and resistance levels can help traders understand the price behavior of the market. When price approaches support, traders may consider buying in anticipation of a rebound. Likewise, when price approaches resistance, traders may consider selling in anticipation of a pullback.
How Technical Indicators Help Understand Support and Resistance Levels
Technical indicators can provide additional information to help confirm the validity of support and resistance levels and predict future price movements. The following are several common technical indicators and their applications:
Moving Averages:
Application: Moving averages can smooth price data and help identify support and resistance. Prices often bounce or fall back near the moving average.
Example: The 50-day or 200-day moving average is often considered an important support or resistance level.
Relative Strength Index (RSI):
Application: RSI can identify overbought or oversold conditions. Near support, if the RSI shows oversold, it may indicate an opportunity for a rebound; near resistance, if the RSI indicates overbought, it may indicate the risk of a pullback.
Example: RSI below 30 indicates oversold and above 70 indicates overbought.
Bollinger Bands:
Application: The upper and lower Bollinger Bands can serve as dynamic support and resistance. The price may fall back when it hits the upper track (resistance), and it may rebound when it hits the lower track (support).
Example: Narrowing Bollinger Bands may signal impending large moves, and price breaks above Bollinger Bands are often accompanied by a continuation of the trend.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence):
Application: MACD indicator crossovers and divergences can help confirm the validity of support and resistance levels. A bullish MACD crossover near support could signal a rebound, while a bearish MACD crossover near resistance could signal a pullback.
Example: A MACD histogram turning from negative to positive may signal a price rebound.
By using TradingView and technical indicators, traders can better understand and utilize support and resistance levels to develop more effective trading strategies and risk management programs.
Outline pivot points and discuss their calculation and importance in trading. Explains how to configure and trade with pivot points, including strategies for trading against pivot points.
Overview of Pivot Points
Pivot points are a technical analysis tool used to determine potential support and resistance levels. They are typically used in short-term trading, such as day trading, to help traders predict market turning points. Pivot points and their associated support and resistance levels are calculated based on the previous day's high, low, and close prices.
Calculation of Pivot Points
Pivot points and their related support and resistance levels are calculated using the following formulas:
Pivot Point (P):
[
P = \frac{(H + L + C)}{3}
]- ( H ) = Previous day's high
- ( L ) = Previous day's low
- ( C ) = Previous day's close
Support and Resistance Levels:
- First Support (S1):
[
S1 = 2P - H
] - First Resistance (R1):
[
R1 = 2P - L
] - Second Support (S2):
[
S2 = P - (H - L)
] - Second Resistance (R2):
[
R2 = P + (H - L)
] - Third Support (S3):
[
S3 = L - 2(H - P)
] - Third Resistance (R3):
[
R3 = H + 2(P - L)
]
- First Support (S1):
These levels can be calculated on different time frames (e.g., daily, weekly, or monthly) to suit different traders' needs.
Importance of Pivot Points in Trading
- Market Sentiment Indicator**: Pivot points reflect shifts in market sentiment, indicating potential reversals or breakouts when prices approach these points.
- Support and Resistance Identification**: Pivot points and their related support and resistance levels serve as key reference points, helping traders identify potential buy and sell areas.
- Strategy Development**: Pivot points provide clear entry and exit points, helping traders develop more precise trading plans.
- Risk Management**: Pivot points can help set stop-loss and take-profit levels, controlling trading risks.
How to Configure and Use Pivot Points in Trading
Configuring Pivot Points:
- Use the pivot point indicator provided by trading platforms (e.g., TradingView). Most platforms support automatic calculation and plotting of pivot points and their support and resistance levels.
- Manually calculate pivot points by using the formulas and inputting the previous day’s high, low, and close prices.
Using Pivot Points in Trading:
- Reversal Trading Strategy:
- When the price approaches or touches support levels (S1, S2, S3), consider buying, expecting a rebound.
- When the price approaches or touches resistance levels (R1, R2, R3), consider selling, expecting a pullback.
- Breakout Trading Strategy:
- When the price breaks above the pivot point (P) and continues higher, consider going long, expecting further price increases.
- When the price breaks below the pivot point (P) and continues lower, consider going short, expecting further price decreases.
- Range Trading Strategy:
- Utilize these key levels for high and low trades when the price fluctuates between the pivot point and support/resistance levels.
- Reversal Trading Strategy:
Pivot Point Reversal Trading Strategy
Determine Trade Direction**: Observe the price behavior around the pivot point (P) at market opening. If the price approaches or touches a support level (e.g., S1) and shows a reversal signal, consider buying. Similarly, if the price approaches or touches a resistance level (e.g., R1) and shows a reversal signal, consider selling.
Confirm Reversal Signals: Combine other technical indicators (e.g., RSI, MACD, moving averages) to confirm reversal signals. For instance, if the price is near a support level and the RSI shows oversold conditions, it can further confirm a buy signal.
Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit: When trading near support or resistance levels, set appropriate stop-loss points (e.g., slightly below the support level or above the resistance level) to prevent sudden market fluctuations. Also, set reasonable take-profit points (e.g., near the next level of support or resistance) to lock in profits.
Monitor and Adjust: After executing the trade, continuously monitor the price changes and adjust stop-loss and take-profit points based on market conditions to ensure risk control.
Example Trade
Assume the price approaches the pivot point S1 in intraday trading and the RSI shows an oversold signal:
Buy Signal:
- The price approaches S1 and shows a reversal signal (e.g., long lower shadow or hammer candlestick).
- RSI is below 30, indicating oversold conditions.
Execute Trade:
- Buy near the S1 level.
- Set a stop-loss order slightly below S2 to prevent further price drops.
- Set a take-profit order near the pivot point (P) or resistance level R1.
Monitor and Adjust:
- As the price rebounds, gradually move the stop-loss point up to lock in partial profits.
- If the price approaches R1 and shows weakness, consider closing the position to lock in full profits.
Through the above strategies, traders can utilize pivot points and other technical indicators to effectively conduct contrarian trading and risk management.
Finally, thank you all for reading, I hope you can like and support me. I will also invite my friends
@trafalgar @wilhb81 @cheva came to participate in this competition, thank you
Your explanation of technical analysis and pivot points is really clear and helpful. It would have given more comprehensive look , if certain charts would have been added.
Thanks for sharing your insights!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
OK, thank you for your suggestion
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
As an experienced trader and a member of this crypto academy I'd advice you to add graphical representation in the form of charts in your assignment posts. It makes it easier to understand. Best of luck
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hello dear friend you wrote so well and I must say I appreciate such hardworking content despite the fact that you have a smaller rep and you might be new to the platform. But I must say you did so well and I didn't expect such hardworking content. Please continue creating such high quality content but also you must know that it advisable to apply some markdowns to make your article look attractive and well co-ordinated.
Meanwhile you can comment on my article through the link below https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@starrchris/sec-s18-w1-or-or-mastering-the-markets-with-technical-analysis
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
As you said, I am a new member, I will publish every post seriously
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Has abarcado todos lo puntos del concurso y detallado la teoría, se nota el empeño en transmitir los conocimientos y aportar en un tema tan importante.
Te deseo mucho éxito y bendiciones.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
@brianwong Understanding market data through technical analysis is crucial for traders who want to succeed in todays complex financial world. As markets become more unpredictable our community needs practical skills in technical trading. This knowledge helps us trade better and understand how financial systems affect our investments. Good luck to everyone in the contest
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Good luck to you too
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
TEAM 1
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted through steemcurator04. We support quality posts, good comments anywhere, and any tags.Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
The future of Gogo serial will be determined by how it handles copyright issues and whether it can transition to a viable business model by obtaining appropriate licensing arrangements.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit