Yesterday I go through the lecture taught by our respected professor @fredquantum which is all about Dark Pools in Cryptocurrency and here is my homework post in this regard, so let's begin with it without wasting much time;
.jpg)

1. Discuss Dark Pools in Cryptocurrency in your own words. How does dark pool works?

Dark Pools
As we all know, there is transparency, security, scalability, and reliability in cryptocurrency. People nowadays desire some privacy as well as more scalability, and some want a place where they may buy and sell assets without interfering with market prices. So, at that time, the Mimblwimble Protocol was created, which solved the privacy and scalability problems. Along with that, Dark Pools emerged to address the issue of buying and selling without being affected by slippage.
The idea of dark pools is not new. Long before the introduction of cryptocurrency, dark pools were in use. A dark pool is essentially a private place or platform for conducting financial transactions away from the general public's sight. It was just a matter of time until the concept of dark pools was brought into the crypto space due to their anonymity feature.
Crypto dark pools are essentially alternative private exchange platforms for swapping crypto assets from the main exchange venue. These Dark pools allow traders to place huge crypto orders while staying anonymous to the general public. In essence, we can think of it as a distinct exchange platform for whales and big participants in the cryptocurrency market.
How Dark Pools Works
Most crypto dark pools function by allowing traders to place large limit orders. Limit orders are orders that the trader places at a predefined price. Limit orders would normally appear on the exchange's public order book; however, dark pool orders do not appear on the public order book. In this instance, the order book is considered to be distinct and invisible. This protects whales' intentions from the general public, preventing people from making fast trading decisions that could disrupt the market. As a result, whale orders would be filled at a reduced cost.
When traders place these large orders, they are matched to orders that are priced the same. Because massive amounts of the asset are bought and sold, the placing and matching of these orders is referred to as Block Trading. Because the dark pool is intended for larger transactions, there is always a minimum amount required to place trades. Slippage is prevented since orders are filled at a specified price. Furthermore, while using dark pools, traders can only see their own orders and not the orders of others in the pool.
So nobody can see your order in the Dark Pool. Furthermore, the market's order book is not visible to outsiders, allowing traders to trade anonymously. And orders in the Dark pool will only be matched with orders in the Dark pool that requested the same fixed price.

2. Discuss any crypto exchange that offers a dark pool. How does its dark pool work?

Kraken Dark Pool
Kraken is a renowned exchange that provides the dark pool service. Kraken is a cryptocurrency exchange that was launched in 2011 in the United States. The exchange is credited with being the first to provide the dark pool service in 2016. The Dark Pool began with only Ethereum, but Kraken plans to create a Bitcoin dark pool in 2021.
Traders must meet specific requirements in order to place orders in Kraken's Dark pool, which I will discuss in the next question. If all of the requirements are completed, the trader can post a limit order on the Kraken dark pool platform for a charge. This limit order is then matched with others at the same price level. Market orders are not allowed since there is no order book in which traders can monitor the current price of the asset, and these orders are prone to slippage. Because the trade is not recorded in the order book, the process of matching these limit orders is known as crossing or cross trading.
Due to its anonymity and the fact that trading fees are the same for each pair, it is impossible to determine whether a trader is a market maker or a market taker.

3. What are the supported assets on the dark pool mentioned in (2) above? What are the requirements for getting involved in dark pool trading on the platform? Is there any fee attracted? Explain.

Kraken Dark Pool's Supported Assets
As previously stated, the assets now supported by the Kraken Dark pool include Bitcoin and Ethereum. These assets' pairs are as follows:
BTC Pairs:
- BTC/CAD
- BTC/EUR
- BTC/GBP
- BTC/JPY
- BTC/USD
ETH Pairs:
- ETH/CAD
- ETH/EUR
- ETH/GBP
- ETH/JPY
- ETH/USD
BTC And ETH Pair:
- BTC/ETH
Requirements to get involved in Kraken dark pool
These are the prerequisites for participating in the dark pool, according to Kraken;
- On the exchange, users must have been authenticated up to the Pro Level.
- Users can only place limit orders because market orders are not permitted.
- A BTC pair order requires a minimum deposit of about $100k.
- The minimum order value for an ETH pair is around $50k.
Is there any fee attracted?
Yes, there is a fee associated with making a trade on the Kraken dark pool. Fees in Kraken Dark Pool are typically based on your most recent 30-day trading volume. The lower the fees will be, the greater the volume. However, the fees typically range from 0.20 percent to 0.36 percent, which are in addition to the expenses charged for a standard limit order.

4. For the chosen dark pool, give a brief illustration of how to perform block trading on the platform. (Screenshots required).

To trade blocks on the Kraken Dark Pool platform, follow these steps:
- So, for the first and foremost, we'll have to visit the Kraken.
- After visiting the above provided link, there we have to set up an account.
- We will have to verify ourselves after creating an account. There are three phases in that Beginning where we must provide our name and address. Then there's the Intermediate level: We must present our ID as well as a bank statement. And, as shown in Fig. 2, I am an Intermediate verifies, and then there is Pro Verified, for which we must need to fund our account in order to apply for Pro Verified.
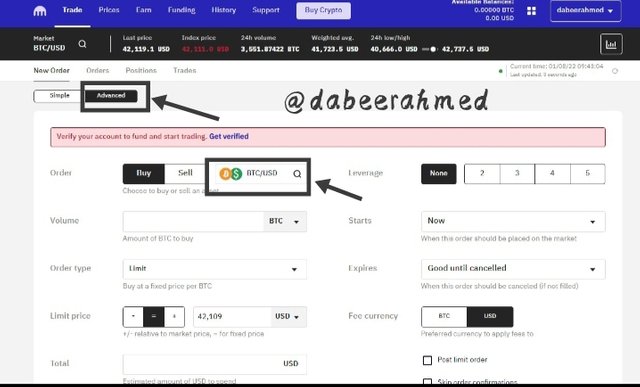
- Following that, we will click on trade, then on Advanced, and finally on the assets search option to navigate to Dark Pool trade (as shown in fig. 4). However, as we all know, in order to participate in Dark Pool, we must be Pro Verified.
Note: All the screenshots of above steps are provided below;

5. What's your understanding of the Decentralized dark pool? What do you understand by Zero-Knowledge Proofs?.

Decentralized Dark Pool
A Decentralized dark pool is, in principle, the same concept as a regular centralized exchange dark pool, with a few practical modifications. A decentralized dark pool allows traders to confidentially place large-scale trades without the interference of a third party. This means that orders placed and performed through a decentralized dark pool are not only unknown to the general public, but also to any facilitator or middleman. As a result, decentralized dark pools are completely private.
Unlike conventional decentralised trading protocols, a decentralised dark pool does not rely on liquidity pools to complete deals. This sort of dark pool is based on Atomic swaps, which are peer-to-peer exchanges between blockchains. This function facilitates trades between a pair that would otherwise be illiquid because the trade is between two parties at a specified price. As a result, slippage and any market effect are prevented.
When you place an order, it is divided into much smaller pieces that are ready to be matched. Following that, other nodes receive these pieces and compete to match them. Matched parts are saved, but unmatched ones are ultimately matched until the order is complete. The fees linked with the transactions are given to the nodes that match these transactions.
Decentralized dark pools can use zero-knowledge proof technologies in their processes for a greater level of authentication. I'll go into more detail about this later.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Micali, and Charles Rackoff first described Zero-Knowledge Proof in 1985 as a sort of encryption and verification protocol. It includes proving of a statement or piece of information without giving any further information about it. It ensures that information and communication are both secure and authentic.
The Zero-Knowledge Proof takes place between two people. The first is the prover, who possesses the information but must needs to prove it, and the second is the verifier, who verifies to see whether the prover actually has it.
Users can perform transactions on a decentralised dark pool using the Zero-Knowledge protocol without revealing balances, transaction prices, or transaction volumes. The nodes involved in matching orders can do so even if they are unaware of the details of the orders.

6. State one decentralized dark pool in cryptocurrency and discuss it. How does it work?

REN Decentralized Dark Pool
The Ren Protocol is a well-known project that provides a decentralised dark pool. Ren Protocol was founded in 2017 as the Republic protocol by Taiyang Zhang and Loong Wan, but was renamed Ren Protocol in 2019.
The Republic Protocol Whitepaper states that the Ren (Republic) protocol is a decentralised dark pool project that was one of the first to utilize atomic swaps in the Dark pool concept. When an order is placed in the Dark pool, it is broken down and dispersed to a network of Dark nodes via Shamir Secret Sharing. For the remainder of the process, this protocol launches two Ethereum smart contracts, The Registrar and The Judge.
After the order has been broken and spread across the darknodes, the Registrar prevents it from being reassembled by arranging the nodes in such a way that attempting to do so would be extremely difficult. The nodes then undertake a variety of computations in order to match the pieces with those of another order. The Judge uses a Zero Knowledge Proof to verify the computations' integrity without disclosing any information about them. After the fragments of two orders have been appropriately matched, an Atomic Swap for the crypto assets is launched.
According to my study, after Republic Protocol was rebranded as Ren Protocol, their attention switched to interoperability. There are currently no other projects that provide a decentralised dark pool in a proper manner.

7. Compare a crypto centralized exchange dark pool with a decentralized dark pool. What are the distinctive differences?

Differences Between Centralized Exchange Dark Pool and Decentralized Dark Pool
- To begin trading, a centralised exchange dark pool requires KYC verification, but a decentralised dark pool does not.
- The centralised exchange dark pool has no smart contracts, whereas the decentralised dark pool exchange has smart contracts.
- Before participating in a centralised dark pool, verification is required, whereas no verification is required in a decentralised dark pool.
- Dark pool centralised exchange Stop Limit orders are used to execute orders, whereas decentralised dark pool exchange orders are performed when an address is confirmed.
- A third party is involved in the centralised dark pool, while there is no third party involvement in the decentralised dark pool.
- There are slippage fees in centralised dark pools, but there are none in decentralised dark pools, but you to pay bridge fees.

8. Research any recent huge sale in any market in the crypto ecosystem and how it has affected the market. What difference would it have made if the dark pool was utilized for such sales?

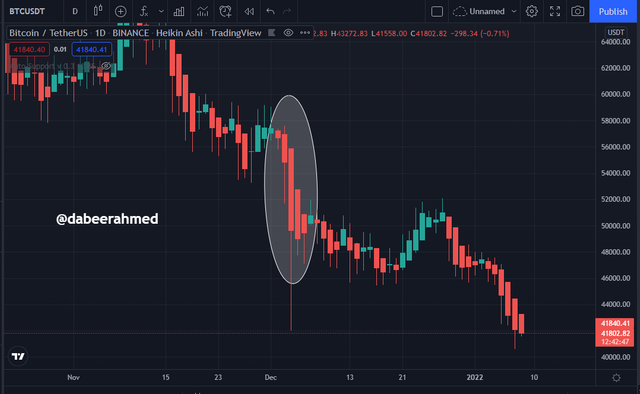
So, just a month ago, we saw a massive sale of Bitcoin in the crypto ecosystem, when on December 5th, 2021, $1 billion worth of Bitcoin was liquidated, and as a result, the entire crypto market was plundered. The price of Bitcoin dropped from $55 k to $41 k, which was a massive blow to the market. The chart of that massive is also provided below;
Screenshot taken from tradingview
What difference would it have made if the dark pool was utilized for such sales
So, if the liquidation that occurred on December 5th, 2021, which caused the market to collapse, had occurred on the Dark Pool, the change in the price of the asset would not have occurred, since this deal would have occurred anonymously with no market order to disclose. As a result, there would be no likelihood of the price decreasing.

9. In your own opinion, qualitatively discuss the impacts of trades carried out in the dark pool on the market price of an asset. (At least 150 words).

Normally, when huge orders come on the order book, traders react based on their emotions. Large purchase orders cause traders to acquire that asset, increasing its market capitalization and driving up its price. Large sell orders, on the other hand, force traders to sell that asset, draining money from its market cap and driving the price down. This is essentially an application of demand and supply, where if demand exceeds supply, the price rises, and vice versa if supply exceeds demand, the price falls.
When it comes to the dark pool, this effect does not occur. As previously stated, trades executed in the dark pool are not visible on the order book. This means that other traders will not respond on sentiment because they cannot observe such massive trades. In the end, there will be no substantial changes in the asset's price because demand and supply will be almost equal.
Furthermore, considering the large size of the trades done in dark pools, we would usually expect such trades to effect the price of the asset on their own. A massive sell deal of, say, 5000 BTC would vastly outmatch the smaller orders we see on exchange order books, which is generally meant to cause supply to exceed demand, causing the price to decrease. When using a dark pool, however, a large sell order is filled when it is matched with a buy order of the same magnitude. This balances the forces of supply and demand and hence has no effect on the price.

10. What are the advantages and disadvantages of Dark pool in Cryptocurrency?

Pros Of Dark pools in cryptocurrency
- Trading Volume is unavailable, preventing others from viewing the quantity of assets exchanged at any given time.
- Remove fear from other investors, hence removing fear of missing out or FUD from others.
- Orders are chosen at the discretion of the dealers.
- Transaction fees are lower when compared to other deals because there is less liquidity involved.
- Investors are given the right to privacy under the law.
Cons Of Dark pools in cryptocurrency
- Risky at times, which is why some dark pools advise traders to only trade with money they can afford to lose.
- Anonymous trading results in some fraudulent act being pushed around the exchange.
- No identification, principally the decentralised dark pool since the exchange allows decentralisation, which means large fraud could be carried out without anyone noticing.
- There is a lack of transparency in it because the order book is invisible.

Conclusion
Many new developments and technical booms are occurring on a daily basis, and solutions to difficulties are also available. Recent advancements in the crypto business sectors have resulted in the many good outcomes, including faster transactions, increased market competition, and increased functional productivity.
The dark pool is highly beneficial, as seen by its successful implementation in the financial markets. Despite the fact that the technology has proven to be valuable, it is still not very functional in the crypto field. I feel that a handful of improvements can be done to make the concept completely functional in the crypto space. Given that bitcoins have the anonymity function, this dark pool concept would significantly improve this characteristic.

Cc: @fredquantum
Regards, @dabeerahmed