1. In your own words, explain mining and block reward
A brief overview of mining
Mining is a concept in cryptocurrency that was borrowed from the industrial mining of gold, digging for oil, and other mineral resources alike because of the process of its acquisition.
Cryptocurrency mining can be simply defined as the process of bringing more cryptocurrency into circulation, and it is also a critical component of the maintenance and development of the blockchain ledger.
Gold and oil were initially close to the earth's crust, as miners could easily mine them without much effort or sophisticated tools. Miners earlier in the days were seen using shovels and baskets in water to mine for gold. But with the gradual scarcity of gold and more competition in the market, there became the need for more sophisticated tools; hence the reason for greater machinery and offshore oil rigs in the case of oil drilling: putting off miners with regular and less sophisticated tools.
Machines such as the ASCIs- for mining bitcoin can be likened to the large oil rigs built offshore while the regular computers initially used for bitcoin mining can be likened to crude equipment such as the shovel, hoe, and basket used for digging up oil
Crypto mining
Similar to the process discussed above, crypto mining, which is the mining of cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin ensures that cryptocurrencies are in circulation by using relatively more dedicated machines with greater computing power across time to build more secured blocks, which in turn rewards miners with these bitcoins. A block is the verification of bitcoin transaction worth 1 Mb. This convention is meant to keep bitcoin users honest and was conceived by Bitcoin founder, Satoshi Nakamoto. By verifying transactions, miners are helping to prevent the double-spending problem. Double spending is a scenario in which a bitcoin owner illicitly spends the same bitcoin twice.
Though Bitcoin mining ensures that there is more bitcoin in circulation, it is essentially centered on security.
For one to create these, they have to break the code or see the loophole of the existing block. Existing blocks are worked upon to create a more secure one. The security is created out of what is called a hash. Hashes are hexadecimal that serve as the identification for the new block. They are computed at a different rate in the quest to find the right hash. These hashes relate to the previous block but are more secured than it and are also used as the basis for future computation. I see it as an improvement upon existing technology. Like it takes tremendous skill and effort to improve an already high tech achievement, so also it is in the case of mining cryptocurrency: where there are already very secured blocks that must be decoded for another one to come through, hence the need for more electricity and higher computing power. China, as of 2018 was considered the greatest mining pool because it supplies cheap electricity and computational power.
The circle of crypto mining starts with security, then reward, and invariably, circulation.
Two basic functions of miners
- 1. Acts as agents of circulation of bitcoin
- 2. Responsible for coming up with the right hashes for a more secured blockchain
The blockchain is a fixed distributed digital ledger that is open to the general public. The bitcoin blockchain, which is the dominating crypto blockchain, is a product of mining. Miners are responsible for the auditing of transactions, making sure they are updated. This, they do by showing what is called Proof-of-work for finding the next right hash.
Miners do go through the hassle of mining for nothing. The brilliance of bitcoin mining is that there is a reward for whoever makes the blockchain more secure. Miners are rewarded with new bitcoins, depending on the number of bitcoins that are payable to miners at the time. Time has seen the reward go down from 50 - 6.25 bitcoins. They are also rewarded with the transaction fees of those in that block. I believe that the transaction fees will likely increase over time to cover for the halving of rewards, so these miners stay incentivized to keep on mining. This may not be the case if the value of bitcoin continues to soar higher.
Miners in the bitcoin world are mining for something greater than gold because the demand for bitcoin, in the long run, will be much higher than the demand for gold. Everyone uses currencies but not everyone uses or needs gold. And since the price of any product is determined by the forces of demand and supply, the value of bitcoin is bound to continue to have high value because of limited supply, since mathematically, bitcoin will never exceed 21 million coins. This motivates miners to continue to render their computational input in exchange for high-value coins.

2. What do you understand by bitcoin halving?
Bitcoin halving is a situation where the reward given to miners for mining new blocks is divided into two. This implies that miners receive 50% fewer bitcoin for verifying transactions. Bitcoin halving occurs after every 210,000 blocks are formed roughly every four years-until the total supply of 21 million bitcoins has been generated.
Bitcoin halvings are important markers to investors and traders alike because they reduce the number of new bitcoins being generated by the network. The reason is that there would be a limited supply of new coins, which would most likely see an increase in the price of bitcoin: in response to the forces of demand and supply.
Bitcoin analysts project that the full 21 million allocations of bitcoin will be fulfilled by 2140. If this is the case we can determine how many bitcoin halvings are meant to occur if we calculate from its first halving in 2012 to the last predicted to happen around 2140.
See workings below
Inception of bitcoin = 2009
The interval between halvings = 4 years
Last predicted halving = 2140
Time-space between bitcoin inception to last predicted halving:
2140 - 2009 = 131
The number of occurrences of halving:
131 / 4 = 32.8
So far Bitcoin has experienced three halvings (2012, 2016, & 2020) that have seen its reward hit 6.25. Since the halving have occurred only three times, it would still for more times as shown in the calculation below
33 - 3 = 30 times. That is to say that the current reward of 6.25 will be halved for additional 30 times by the network.

3. What are the effects of the halving on miners?
This is a challenge for the bitcoin mining industry, which derives the lion's share of its income from these block rewards. This forces miners to adapt faster and more sophisticated computational technologies or risk being pushed out of the bitcoin mining industry because of high competition for fewer coins.
The sudden decline in the rewards for mining means that mining is suddenly a lot less profitable. Except there is a big increase in bitcoin's price, bitcoin miners may temporarily stop investing in the mining process.
Miners are in the game for profit's sake and competition among miners keeps profit margins fairly steady over a long period. So if the rewards from bitcoin halving fall by half, that will ultimately mean that miners would be spending about half as much to produce these bitcoins. Electricity is one of the biggest costs of bitcoin mining, so halving the block should reduce the amount of electricity consumed by miners. This is good for miners since electricity use in bitcoin mining has always been considered outrageous.
The positive effect of halving on bitcoin miners is that the value of bitcoin always increases exponentially. Higher bitcoin prices push up the revenues of each block, thus the motivation for able miners to continue to invest in the mining process. The bigger mining pools are induced to keep on buying more hardware and increasing electricity output, even in the face of halving, because of an increase in bitcoin price.
I also think that continuous halving will see miner’s reluctance to release bitcoin into the exchange market: that is there may be an increase in bitcoin hoarding, as miners would want to ensure they maximize profit for their input from bitcoins by waiting to release coins when the value is very high.

4. What is the current block height on the Bitcoin blockchain? How many more blocks before the next halving?
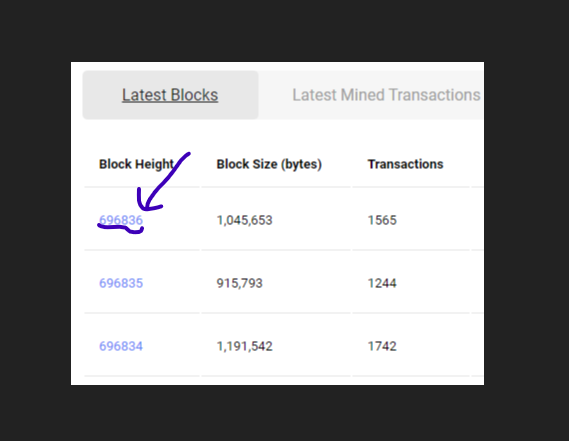
The screenshot above shows the block height of Bitcoin as of writing.
The current block height on the steem blockchain at the time of writing is 696,836 blocks
If Bitcoin halves every 210,000 blocks and the next halving would be the 4th. then:
Block height for the next halving = 210,000 x 4
= 840,000
Current block height = 696,836 blocks
∴ Number of Blocks until the next halving = 840,000 - 696,836
= 143,164 Blocks.
Therefore the blocks left until the next halving at the time of writing is 143,164 blocks

5. Do you think Steem’s inflation rate reduction can affect other coins? Why?
The decline in the inflation rate of steem would be insignificant when compared to other cryptocurrencies because its inflation rate decreases by 0.01% after every 250,000blocks that are mined.
Steem's current circulating supply is 387.85M STEEM out of a max supply of 348.80M STEEM. In terms of market cap, Steem is currently ranked 17 in the Proof-of-Stake sector.
Market capitalization is also an important factor of value than individual coin price, so with the current market capitalization of $ 219.21M, and market dominance of 0.01%, steem inflation reduction will not affect other coins, however, in the long run, factors such as adoption by masses, the utility of the coins, Value and perceived value of the project, costs of production and regulations could see steem's dominance and market cap increase over time, thus giving steem inflation reduction the lead that could affect other coins. I am just saying.
All things being equal, gradual scarcity of steem, and likely increase in value as provided for in the steem white paper would also see steem take an influential stand in the world of cryptocurrency.
From the brief analysis, I can say that steem has a profitable plan and a tendency for growth that could see its inflation reduction affect other coins in the farthest future but for the time being steem inflation reduction would not scratch the usage, price, or buying of other coins.

6. What is the current block height on the Steem blockchain? How many more blocks before the next 0.01% reduction?
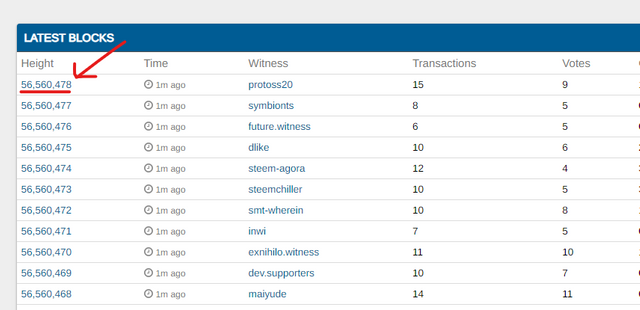
The screenshot above shows the block height of Steem as of writing.
The current block height on the steem blockchain is 56, 560, 478 blocks
If Steem inflation rate reduces by 0.01% every 250,000 blocks, and
Current block height = 56,560,478 blocks, then:
56,560,478 / 250,000 = 226.241
The number of steem reductions so far to the nearest whole number is 226.
Take the next whole number to calculate the block height for the next reduction:
Block height for next reduction = 227 x 250,000
= 56,750,000
∴ Number of blocks until next reduction = 56,750,000 - 56,560,478
=189,522 Blocks.
1 WHAT IS THE CURRENT VALUE OF BTC ON THE DAY YOU ARE PERFORMING THIS TASK? IF YOU MAKE A PURCHASE OF $2500, THEN
A. HOW MANY SATOSHI WOULD YOU HAVE?
B. WHAT IS THE VALUE OF A SATOSHI FOR THAT DAY?
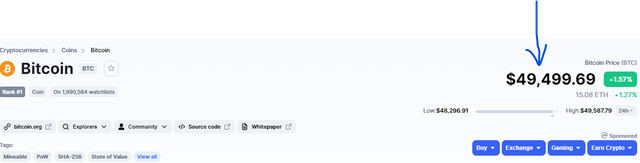
The current value of BTC on the day of writing is $49,499.69.
If I purchase $2500, then I would have;
SOLUTION
Let X be the number of BTC.
1 BTC–$49,499.69
X BTC–$2500
Cross multiplying, we have
X BTC= 2500/49,499.69
=0.0505053668012,
Approximately 0.0505BTC (3.s.f)
A.
Let Y be the number of satoshi
1satoshi = 1×10-8BTC
Y Satoshi= 0.0505BTC
cross multiplying,
Y= 0.0505 / 1×10-8
=5,050,000 Satoshi
If I purchase BTC worth of $2500, I would have 5,050,000 Satoshi
B.
As of the time of writing;
1satoshi = 1×10-8BTC
1 BTC = $49,499.69
So, 1satoshi = 1×10-8 × 49,499.69
1satoshi= $0.0004949969
Approximately $0.000494(3.s.f)
2 What is the current value of BNB on the day you are performing this task? If you purchase $30 then,
A . how many Jagers would you have?
B. what is the value of a Jager for that day?
(Show full working and correct to 3 s.f)
(1 jager = 0.00000001 BNB)

The value of BNB on the day I performed this task is $455.36.
If I purchase $30, I would have;
SOLUTION
Let X be the amount of BNB
1BNB = $455.36
X BNB= $30,
Cross multiplying;
X= 30/455.36
=0.06588BNB
Approximately 0.0659BNB (3.s.f)
A.
Let X be the number of Jagers.
1 Jager = 1×10-8BNB
X Jager = 0.0659BNB,
Then;
X= 0.0659/1×10-8
=6,590,000 Jagers.
From the above calculation, I would have 6,620,000 Jagers
B.
If 1 Jager=0.00000001BNB
1BNB= $455.36
Hence, 1jager = 0.00000001×455.36
=$0.0000045536
Approximately $0.00000455 (3.s.f)
Cryptocurrency has seen a great rise in the recent decades since the inception of bitcoin in 2009 by the anonymous Satoshi Nacomoto. Though it is argued by some that bitcoin is not the first cryptocurrency, it is certainly the first to have risen to prominence and to defiantly challenge the excesses of banks and fiat currencies because of its decentralized and less taxing system.
Bitcoin circulation lies solely on the mechanism of Bitcoin mining. Bitcoin mining has grown to attract huge investors while regulating the circulation and validating the transactions of bitcoin.
Steem on the other hand is a relatively new cryptocurrency when compared to bitcoin. Steem is an experiment designed to address challenges in the cryptocurrency and social media industries by combining the best aspects of both.
Thank you for reading
Cc:
@awesononso.