HOMEWORK QUESTIONS:
2a. What is the difference between PoS & DPoS?
2b. Advantages & Disadvantages?
2c. Name a few Blockchain projects which use the DPoS consensus mechanism and indicate the scaling capacity
INTRODUCTION
Blockchain is a decentralized system that is capable of compiling records of users transactions and information without the need or use of intermediaries or middlemen through a peer-to-peer process before verifying any transaction. The need for blockchain in the crypto space cannot be ignored because it is a cycle of blocks that contains transaction information on a network of computers.
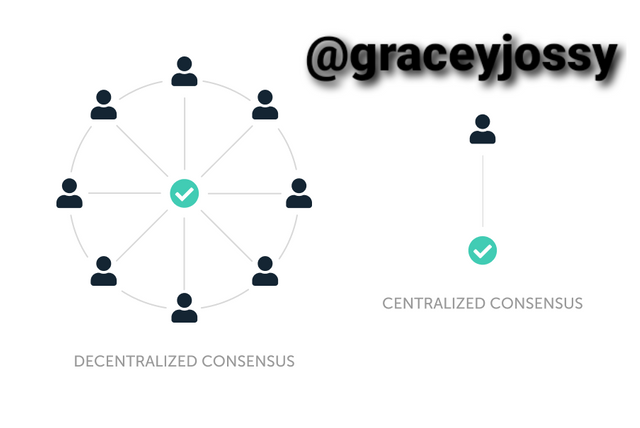
In a centralized network, decision making is dependent on the people in sovereignty, but in Blockchain, no authority controls the system (thus blockchain is decentralized and the decision is based on the consensus made by everybody). Therefore, Blockchain is a system that is devoid of corruption from a single source (middlemen, central authority).
Every individual has a say in governing the blockchain. Therefore, to make a decision, all the parties or people on the blockchain must come to a “consensus” or “agreement”, on what to be done and what not to be done on the blockchain. People on the blockchain system consensus through a method known as “consensus mechanism".
What then is a consensus mechanism?
Concerning blockchain, a consensus mechanism is a method that enables users or computers (nodes) to conduct and organize in a distributed manner. This mechanism secures that all the users or nodes operating on the network can agree on a single source of validity.
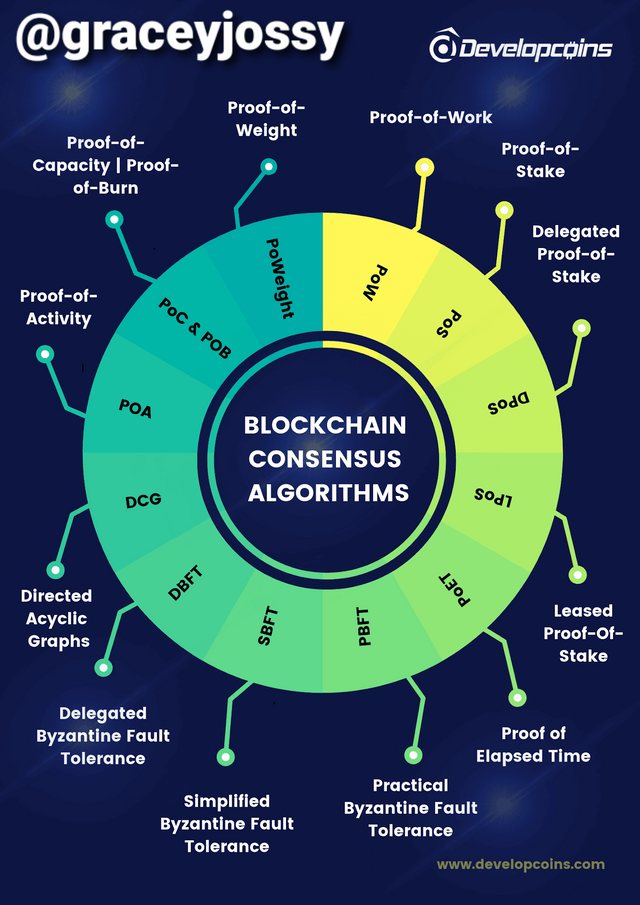
Blockchain uses different kinds of consensus mechanisms and they are as follows;
- Proof-of-work (PoW)
- Proof-of-stake (PoS)
- Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS)
- Proof-of-capacity (PoC)
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)/ Practical Byzantine fault tolerance (PBFT)
- Proof of Brain (PoB)
- Proof of Elapsed time (PoET) proof of authority (PoA)
- Proof of importance (PoI), proof of activity, direct acyclic graphs (DAGs)
- Etc.
Concerning the question above, in this article, I will be discussing just two of the different kinds of consensus mechanisms, which are; PoS and DPoS below.
What is PoS?
PoS is Proof of Stake, which is another means for confirmation of the transaction on the blockchain network of Cryptocurrency. The stake is the amount of coin in a wallet connected to the blockchain which provides a block validator freedom to a mint new block, proportional to the amount of his stake on the blockchain. Hereby allows to larger stalker an edge on the blockchain over others.
In the year 2011, PoS was initially proposed as a substitute to proof-of-work (PoW). The goal of reaching a consensus in the blockchain is the same in PoW and PoS, but the process of reaching the consensus is entirely different.
KEY TAKEAWAY
With Proof of Stake, your ability to mine new coins or verify transactions is not attached to your ability to solve those problematic puzzles we earlier talked about. Rather, it is directly linked to how many coins you hold.
In PoW your amount of stake determines your edge or level over others on the blockchain. Staking (locking up of coins) of a specific amount of the blockchain currency allows becoming a validator of transaction or an attester who bear witness of the validator before transactions are validated.
In the PoS system, staking is done by users at certain intervals, the system selects the node randomly the nodes to validate the next block or transaction. The selection is done based on the number of stakes, coinage, and randomization.
3 factors that determine selection in PoS as a validator
Amount or quantity of stake: The higher the stake, the greater or bigger the possibilities of being selected.
Coin age: Nodes or validators are selected based on how long their tokens have been staked or invested. Thus, the longer the age or duration of stake the higher the chance of being selected.
Randomization: validators are randomly selected based on the lowest hash value and the highest stake.
In PoS, miners are rewarded with cash from transaction fees whereas in PoW where miners are rewarded or paid with new coins.
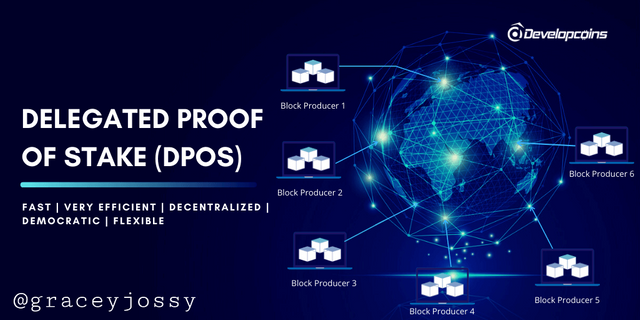
What is DPoS?
DPoS is Delegated Proof-of-Stake and was formulated in the year 2014 by Daniel Larimer – an American software developer and founder of Bitshares, EOSIO software and Steemit. PoS is a consensus mechanism that was designed as an alternative to both PoW and PoS to establish a technology-based democracy –done through the election process to avoid the centralization and deceitful use of the Blockchain. It's was made to avoid high energy demands, needs for machines with high nodes, and the lengthy period taken to process a transaction. Bitshares is the first DPoS that was created in the blockchain.
KEY TAKEAWAY
DPoS functions as a modified PoS consensus that relies on a group of delegates to verify blocks on behalf of all nodes in the network system, and it works using witness that is being selected by stakeholders on the base of one vote per share per witness through election process on the blockchain.
Witnesses are responsible for the creation or addition of new blocks to the blockchain. For example, on Steemit there are 21 witnesses governing the affairs of the blockchain and are responsible for transaction validation.
Administrators are called delegates in the blockchain system and they determine transactions fee, block sizes, witnesses pay, and block intervals of the Blockchain. The users in the blockchain elect to pilot the affairs of the blockchain and make key changes and are not in charge to create blocks and validation.
2a. What is the difference between PoS & DPoS?
The table shows the differences between PoS and DPos.
| NO. | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Decentralized | Semi-decentralised |
| 2. | Less scalable compared to DPoS | More scalable than PoS |
| 3. | Good for financial use | Suitable for social use e.g. Steemit. |
| 4. | Only those with high stakes and low hash value get the chance of being selected | Equal opportunity is granted to every user to be considered for election as a validator or a delegate. |
| 5. | Block builders are chosen in a deterministic way | Block builders or validators are selected or voted by the users. |
| 6. | Uses transaction fees | It doesn't use any transaction fee |
| 7. | There's no block reward. The miners are rewarded with funds from transaction fees | Validators are paid with staking rewards |
| 8. | Less flexible | more flexible. |
| 9. | Consensus is random | Consensus is a predetermined order based on the Delegate trust. |
2b. Advantages & Disadvantages of PoS and DPoS
The following are the advantages and disadvantages of PoS and DPoS respectively.
ADVANTAGES OF POS
PoS is highly secure as it prevents fraudulent activities because once detected, the node will lose its stakes.
Compared to PoW where miners invest so much to acquire computer hardware that consumes high electricity energy, Pos is affordable and easy to use.
PoS is fair in choosing validators and ensuring their payment.
DISADVANTAGES OF POSPoS works with the stalking of coins which gives users with the bigger stake the higher advantage on the blockchain hereby giving room for centralization in the blockchain.
The prize for the proof of stake is low as there's no prize for validation of transaction apart from the transaction fee which in most cases are small.
It's is difficult to stake and sell your coin and even staking has a period in which you cannot withdraw until this period Is over.
ADVANTAGES OF DPOSScalability and speed: It provides rapid processing of transactions than PoW and PoS. This is perhaps the most magnificent advantage: DPoS makes significance for many applications that require an increased level of scalability.
Better distribution of rewards: Theoretically, people will elect only those delegates who give them the most rewards, so everyone benefits, including a casual user. (This is what makes supporters say that DPoS is more decentralized than either PoS or PoW.)
Real-time voting security: Voters can instantly recognize malicious actions, and the malicious delegate can be voted out of the system.
Energy efficiency: DPoS consumes quite limited energy than PoW.
Less hardware: Participants don’t need expensive, technological equipment. A normal computer is powerful enough.
An incentive to “behave”: Block producers — delegates — can be voted out any time, so the possibility for loss of income and reputation gives a hedge against bad behaviour.
Flexibility: DPoS enables for a more creative and flexible approach to solving problems with either, in isolation, a recent Coinmonks piece explains, because DPoS unlinks the election of block producers from the block production itself. It gives a foundation for executing “interesting governance models in blockchain applications.”
DISADVANTAGES OF DPOSIt's easier to organize an attack: It’s easier to organize a “51 percent” attack because fewer people are in charge of keeping the network active.
The rich may get richer: People’s voting power is determined by how many tokens they have, meaning that people who own more tokens will exploit the network more than people who own very few.
Apathy can kill: Without an enormous number of engaged users, the network will not function as intended.
Delegates could form cartels: Delegates can organize into cartels by reducing the role of verification in a lesser number of hands. This makes it less decentralized, and it also makes it less resilient.
2c. Name a few Blockchain projects which use the DPoS consensus mechanism and indicate the scaling capacity
The scalability of a blockchain is the ability of a blockchain to boost its capacity to process more transactions per second. It can be defined as the boost in the transaction speed example is the number of transactions processed at a given period.

Source
Below are some examples of blockchain that uses the DPoS consensus mechanism with their scaling capacities.
Steem
It is a social media and content-based blockchain with a scaling capacity graded higher than Bitcoin and Etherium networks. In terms of scalability, Steem is among the rewards authors receive on the Steemit platform.
EOS
This blockchain was designed for public and private users, It does not make use of on-chain transaction costs. Daniel Larimer, the developer of steemit co-founded EOS. , it's scalability rate is 10,000 transactions per second (TPS) that makes it free and fast. EOS has a component that can handle more transactions from separate blockchains called inter-blockchain transfer.
Tron
Tron was formulated by a Chinese software developer called Justin Sun. Tron is integrated with the steemit blockchain system after a resolution was achieved in December 2020, and that is the sole reason why steemians are rewarded with Tron for using the steemit platform. Tron scalability rate is over 1,000 transactions per (TPS).
Bitshares
Bit share has a scalability rate of processing 100,000 transactions per second (TPS). It is a cryptocurrency used for stacking financial services, an example is an exchange and banking in a blockchain.
Worbli
Worbli is a cryptocurrency blockchain designed to facilitate business and transactions. It has a productive, honest, accessible and scalable financial system with a Scalability rate: 4, 000 TPS.
Nano
Nano was developed by Colin LeMaheiu in 2015 as the fastest blockchain with no transaction cost. The network has a scalability rate of over 1, 000 transactions per second.
Telos
it is an open finance network for building fast, scalable distributed applications with feeless transactions. It is the second most used blockchain cryptocurrency scalability of 10, 000 TPD and 0.5 seconds block time. Elections place every 2.5 seconds on the network. It is eco-friendly.
WAX
WAX means Worldwide eXchange (WAX), and it is a blockchain constructed to scale e-commerce transactions. It hosts e-sports and gaming. Scalability: blocks are produced every 0.5 seconds. WAX is the native currency of the Blockchain.
CONCLUSION
The consensus mechanism is a strategy used by the blockchain to bring about agreement, trust, and security. It is a collaborative and inclusive way of reaching an agreement over transactions and other affairs of blockchains.
DPoS is more like the PoS although it is not completely decentralized and it takes a different approach. In DPoS, the stakes do not validate the blocks, rather they choose representatives. Then these representatives validates each transaction. It is exceptionally efficient and is used by Steemit, EOS, and others.
In blockchains system, scalability is better in the DPoS consensus mechanism, than those that do not operate on the DPoS algorithm.
Special gratitude to my professors;
@sapwood
@awesononso
@reminiscence01
Thanks for reading through my homework.


Hello prof @sapwood @awesononso @reminiscence01
https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@graceyjossy/repost-steemit-crypto-academy-season-5-homework-post-for-task-6-different-types-of-consensus-mechanism-or-or-by-graceyjossy
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit