So, this is the ss of my assignment on which I got 7 marks but didn't get the vote on it.
Link of the assignment:-
Hey Steemit!
Here is my homework post for Professor @nane15. This is undoubtedly a great lesson, and I hope that you will enjoy reading this post.


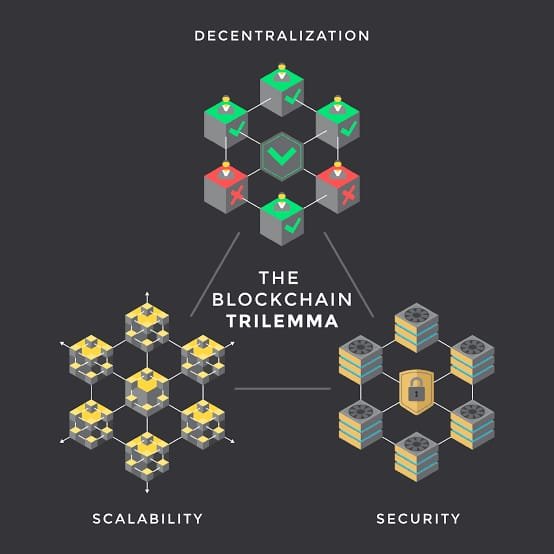
1.) Explain in your own words what the Blockchain Trilemma is.

Ahead of its time, the technology behind decentralized blockchain networks Such networks may potentially predict how they should operate and what purpose they should be used. Developers, on the other hand, find it challenging to create blockchains with all three of the recommended core properties.
The key aspects of blockchain technology should be scalability, decentralization, and security. However, given the notions we now have, it is tough to keep all features.
Even though networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum have dominated decentralization and security, they have not yet reached scalability. As a result of this problem, it is tough for them to obtain broad acceptance to the level where centralized systems would be entirely out of place.
Buterin, the community's most beloved developer, is at the vanguard of this enormous change, spearheaded by the best brains in the blockchain industry. Ethereum 2.0 can resolve the blockchain trilemma, as we'll explore in this essay.

The decentralized character of these networks creates significant hurdles, even though blockchain technology proves its effectiveness in several domains. To address one of these most pressing concerns, computer scientists invented the CAP theorem. Only decentralized data storage such as blockchain can provide consistency, availability, and partition tolerance, according to the CAP theorem (CAP). In today's distributed networks, this notion has evolved into a blockchain trilemma. Many people believe that public blockchains must make some tradeoff between security, decentralization, and scalability.
While central network infrastructures like VISA or the internet employ "client-server" interactions, public blockchain networks use "decentralized consensus" mechanisms. To do this, you'll have to keep track of an extensive, distributed network of nodes to establish agreement on data across a robust architecture while maintaining openness and open access for everyone. This is a scrimmage! There are only roughly seven transactions per second per Bitcoin, even though it is decentralized and secure (TPS). Few nodes in commercial blockchains like Hyperledger's Fabric can achieve consensus and handle large transaction volumes without compromising security. For a distributed ledger that is both quick and decentralized but also vulnerable, this level of hacker exposure is just not acceptable.
Blockchain technology's Holy Grail establishes a decentralized network with watertight security capable of handling internet-scale transaction throughput. A global community of enterprises, start-ups, and engineers is tackling the blockchain trilemma by focusing on Layer-1 and Layer-2 solutions. Layer 1 blockchain networks are those designed for speed, security, and scalability. Existing blockchain networks may benefit from advancements to Layer 2 technology and products that increase their capacity. Using blockchain technology and decentralized networks may become more common if the two levels are correctly matched.
We must first understand the blockchain trilemma before we can begin interpreting alternative solutions.
Trilemma: What Is It And Why Is It Important?
The blockchain trilemma is a term established by Vitalik Buterin to describe a trio of problems that blockchain developers face while creating new networks. One 'aspect' is sometimes sacrificed in favor of the other two, which is a common occurrence for inventors.
Decentralization:
Instead of being controlled by a single body, the network of blockchains distributes power evenly among all of its members.
Security:
The security of blockchain networks must be impenetrable to hostile actors.
Scalability:
Blockchains should handle many transactions and users without failing due to rising costs and transaction delays.
Achieving all three of these goals is considered an impossibility by some in the business, who believe it will never be done. Aspirational developers, on the other hand, feel that blockchain networks can achieve all three.

2.) Is the Blockchain Trilemma Really a Trilemma?

So far, blockchain technology has shown that it can alter our world, and new use cases are being developed every day. To achieve broad acceptance, blockchain technology must first overcome several difficulties.
Although the blockchain trilemma presents a difficulty to the technology's broad adoption, no legal rule forbids all three features from being attained concurrently.
Instead, the blockchain trilemma was established as a tool to define and better understand the issues confronting the development and adoption of blockchain technology and how they interrelate.
Developers are working hard to find solutions to the blockchain trilemma, and there have already been several successful suggestions and ideas on how to deal with it. However, progress has been made, and the trilemma still offers difficulty, but that doesn't mean it can't be resolved.

3.) Define the following concepts in your own words:
A. Decentralization
B. Scalability
C. Blockchain Security

.jpeg)
What Is Decentralization?
Blockchain technology is a driving factor behind several projects due to its focus on decentralization. Diverse industries may cut out intermediaries by using decentralized processes and technologies. Financial products can be removed from the financial system entirely if a decentralized finance platform (Defi) does this. Profits and control would then go directly to its users. Decentralized networks crowdsource consensus, which implies that no one entity can control or censor the data that transact across them. In some instances, however, achieving optimal decentralization may lead to decreased network performance. As more miners join the network to protect it, slower transaction speeds are a deterrent to broader adoption.
What Is Blockchain Security?
Reduce the number of nodes on any blockchain network geographically or decrease their total number for increased throughput. This can be done in two ways: However, this move toward more centralization makes PoW networks less safe. Fifty-one percentage of attacks are more possible on an open web with constrained nodal distribution because hackers can more easily amass hashing power. A network may be taken over by cybercriminals who use it to disrupt financial operations. The Ethereum Classic (ETC) blockchain, which is entirely unrelated to Ethereum, was subjected to three 51% attacks in August 2020, reorganizing over 4,000 blocks and allowing the attackers to alter data and double-spend ETC money, resulting in millions of dollars worth of network value being lost. Blockchain is impenetrable as a network because of its inherent security.
What Is Scalability?
Scaling a blockchain system involves achieving both high transactional throughput and room for future growth. To put it another way, the performance of blockchain technology will not be hindered if it is extensively utilized. An inability to scale a blockchain as popularity grows is called "scalability issues." While scaling is possible, the blockchain's trilemma suggests that security and decentralization are also viable options. If a blockchain network can develop in scale, it can compete with older, centralized systems with faster network settlement times and higher usability. Even though many blockchain platforms have achieved decentralization and security, today's leading decentralized networks still struggle to grow.
So, how can we overcome the blockchain trilemma and simultaneously achieve decentralization, security, and scalability?

1.) Based on your knowledge, explain at least two viable solutions to the challenges posed in the Blockchain Trilemma.


Solving The Blockchain Trilemma: Layer 1
When dealing with decentralized systems like Bitcoin, Litecoin, and decentralization, to refer to blockchain protocols as Layer 1. Many methods are now in development or in use that attempts to improve the scalability of blockchains.
- Improvements To The Consensus Protocol
Consensus is achieved using Proof of Work, which is widely used in popular blockchain networks like Bitcoin. PoW is safe, but it is also time-consuming. Seven significant transactions seconds are the limit for Bitcoin. Many blockchain networks choose Proof-of-Stake as a result, with Ethereum 2.0's conversion to PoS consensus mechanism being one of the most prominent examples. PoS consensus leverages network stakes to establish validator status rather than requiring miners to solve complex cryptographic algorithms. Increased capacity of the Ethereum network is expected as well as improved security and decentralization.
- Sharding
Despite its experimental nature, sharding has become one of the most used Layer-1 scaling strategies in the blockchain industry. Through the process of sharding, transactions are divided up into smaller "shards." Because the network is treating these shards simultaneously, many transactions may be processed in parallel. It is also feasible to divide up the data such that each node has a copy of the current block, rather than having a copy of every last block on the network. Using cross-shard communication protocols, they trade information like addresses, accounts, and the general state of the web for the advantage of the mainchain. Shards are being examined by several essential blockchain protocols, including Ethereum 2.0, Zilliqa, Tezos, and Qtum.
Solving The Blockchain Trilemma: Layer 2 Solution
For the blockchain community, "Layer 2" is the network or technology that operates on top of an underlying blockchain protocol to boost that protocol's potential for scaling. When it comes to Bitcoin, the Lightning Network is a Layer-2 solution meant to speed up transactions, while Bitcoin itself is a Layer-1 system. Because of their success in addressing scalability concerns, layer-2 protocols for PoW networks are now widely used.
- A Chain Of Blockchains Nested Inside Each Other
There are several decentralized networks, but they are all based on an identical blockchain. A parent-child connection links the main chain's blockchains to its secondary and tertiary branches. Child chains receive work from their parent chains and return it to the parent chain once completed. There is no impact on network functions until it is essential to settle conflicts. For instance, the OMG Plasma project combines Layer-1 Ethereum on top of Layer-2 layered blockchain technology to create the OMG Plasma Blockchain The mainchain's processing burden is significantly decreased due to this model's scalability enhancement.
- Statesman's Channel In New York
Different methods of communicating between the blockchain and off-chain transactional channels using a state channel may enhance transaction volume and speed. State channels don't need instant confirmation from a miner. Intelligent contracts or multi-signature techniques are more suited for protecting a network-related resource. All of the "channel's" transitions and the final "state" are broadcast to the blockchain when a transaction or group of transactions is completed on a state channel. Bitcoin Lightning, Ethereum's Raiden network, and the Liquid Network are examples of state channels. Scalability comes at the expense of decentralization in the trilemma trade-off.

2.) Conclusion

Blockchain engineers must grapple with the trilemma of decentralisation, scalability, and governance. Bitcoin and Ethereum have already accomplished so much for the world. However, the trilemma must be overcome before blockchain can really improve the lives of everyone, not just those in our little group.
We have projects that employ PoS and sharding, but none of them has had the opportunity to show the world that they can handle a big user base. We will finally know that the blockchain trilemma is no longer a concern if Vitalik Buterin succeeds in making Ethereum the market's second-largest project by market cap.
It was a great lesson, and I appreciate the work of @nane15 Professor. Thank you!
@steemcurator02
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit