
INTRODUCTION

Blockchain technology where transaction data and signatures are stuffed in a storage space or block and added to a list of other storage spaces connected in series by hash values, is not the only distributed ledger technology around.
There is also a distributed ledger technology that arranges transactions using directed acyclic graphs, according to the time each transaction was carried out. This is known as hashgraph.
This post elaborates on this novel distributed ledger technology known as hashgraph.
OVERVIEW OF HASHGRAPH

Hashgraph is a distributed ledger technology that employs the use of directed acyclic graphs and time stamps to record and store transactions. This technology eliminates the role of miners and reduces validation time. Making it faster than blockchain, another distributed ledger technology.
Rather than mining, hashgraph uses the gossip about gossip protocol. Thus, all the nodes mist not be aware of a transaction as at when it is carried out, but they will eventually learn of the transaction through 'gossips'.
Hashgraph was developed by Leemon Baird, the co-founder of Swirlds and it uses the Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance consensus algorithm (aBFT) to protect itself from attacks.
GOSSIP ABOUT GOSSIP
This protocol is best explained with an example.
So let's consider 3 nodes, Anthony (A), Barbara (B), and Chris (C). Their timelines take the form of a straight line as time increases constantly at a fixed pace.
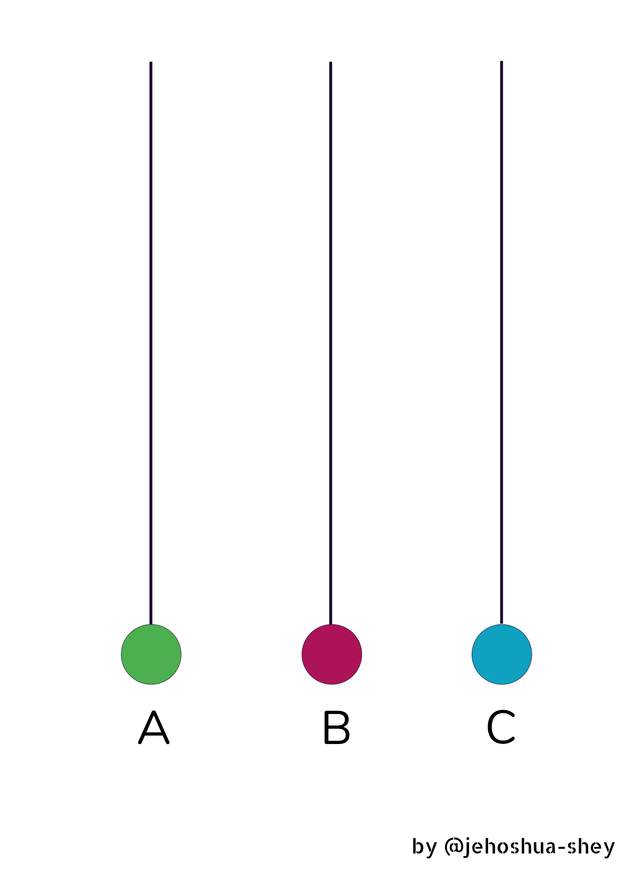
These all have initial events colored differently. This events are simply transaction data.
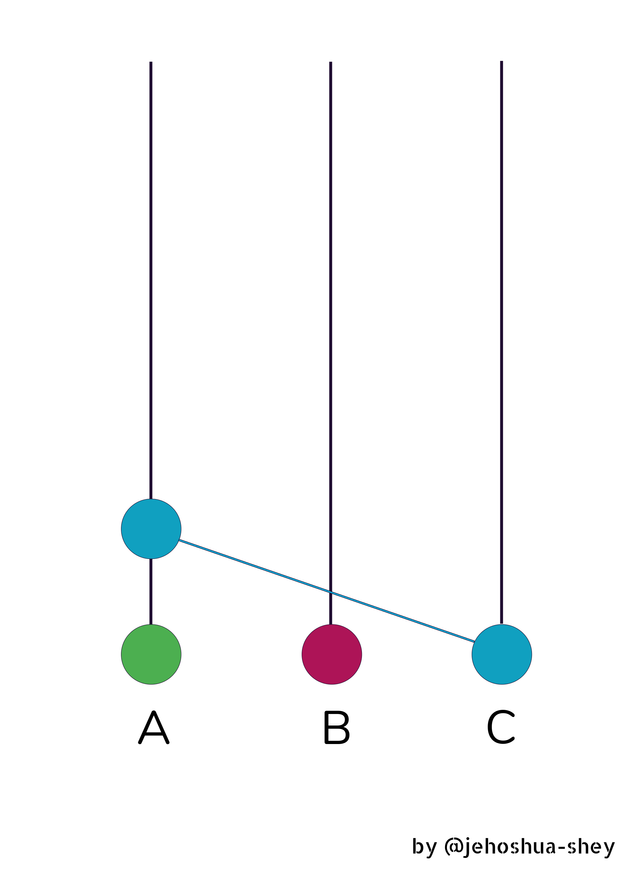
Now, Chris decides to share (or gossip) his event with Anthony. What happens is Chris updates Anthony on the transactions that he doesn't know about and through that, Anthony gets to learn something new.
So in this 'gossip', Anthony receives Chris' first event.
Now, Anthony wants to reciprocate and creates a body of information or another event (if you like). This one contains Anthony's first event and Chris's first event which Anthony learnt from Chris
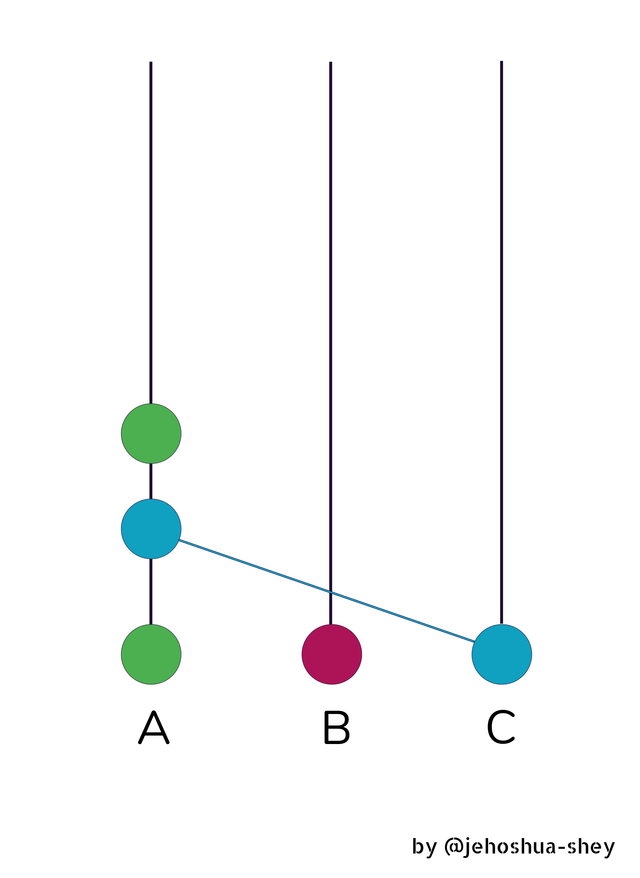
An events is simply data consisting of
The time the event is created,
The transactions to be sent
The hash of all the transactions being sent (ie. Chris's first event and Anthony's first event).
So, Anthony shares this newly created event with Chris
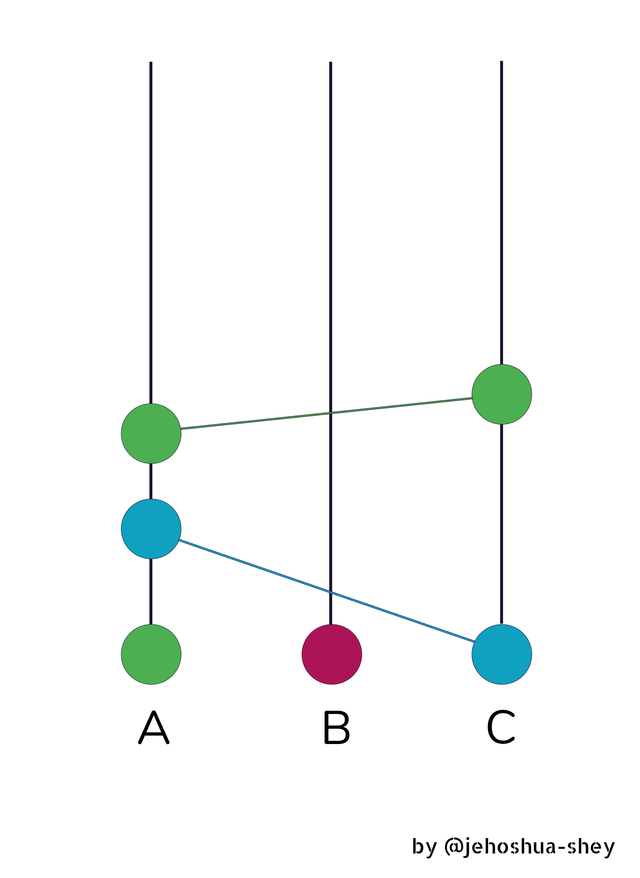
Now, Chris is updated on all his and Anthony's transaction.
Now, if this gossip goes on between all three of them, you would have a graph like this
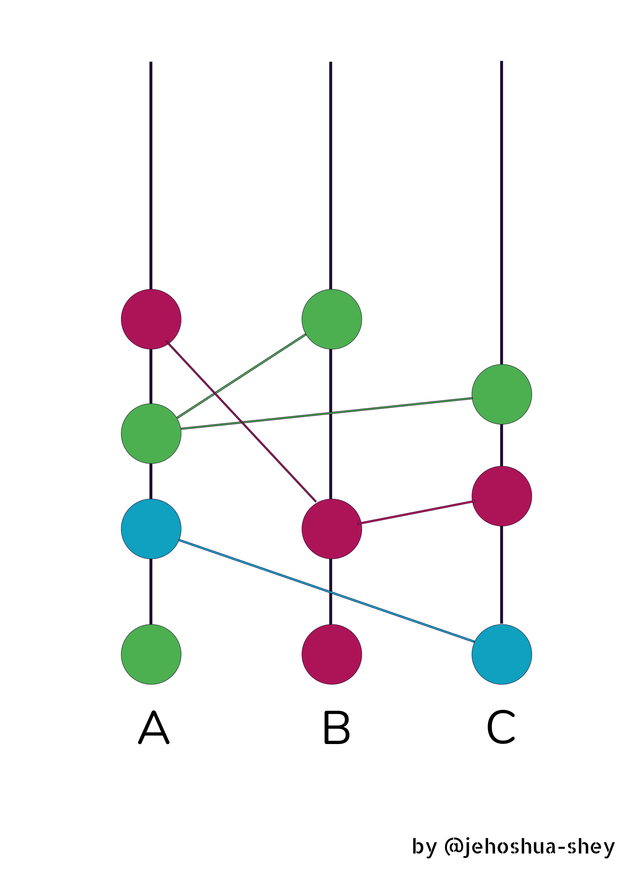
After gossiping for a while, there is the possibility that one or more of the nodes would have been updated on all the transactions that went on. This is the aim of the gossip about gossip protocol.
HASHGRAPH's BYZANTINE FAULT TOLERANCE

Byzantine faults are errors in the consensus caused by a node. A node could mistakenly or malicious send wrong information. It could also move to prevent a consensus from being reached on the network, except there is a counter measure to prevent this.
Well, hashgraph is Byzantine fault tolerant, meaning that it has that counter measure. Since the nodes go about 'gossiping' transactions between one another, it's very difficult if not impossible, for the node to convince all the nodes that a false information is true.
Let's consider a clear example
Note:
Each of the colored circles are events or transaction data
Each event on each of the straight lines contain the data of all the events below it.
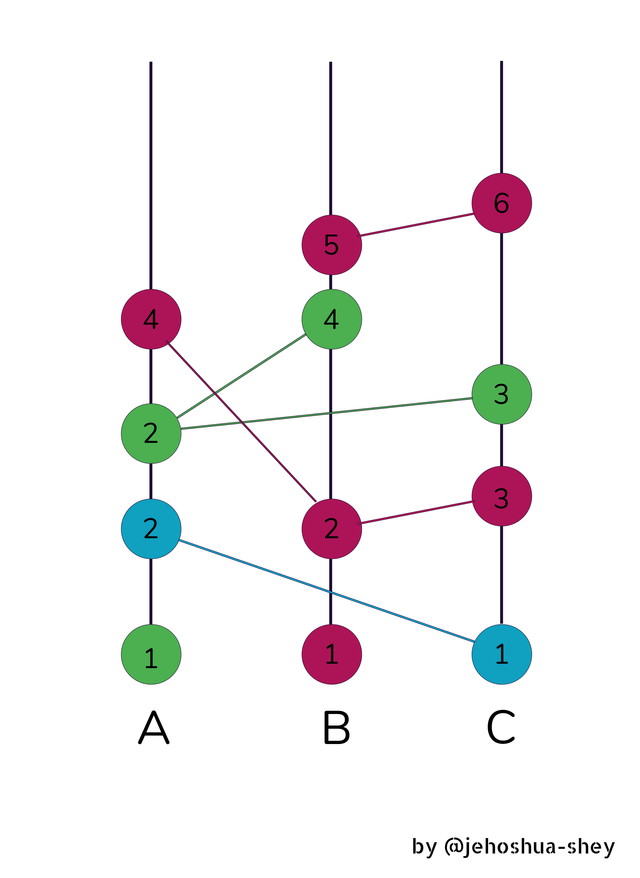
From the image above, Node A receives an event from C (C2), if Node A creates an event containing false information (ie. A2) and sends to Node B, Node B will eventually gossip with node C all the data she has including the false data from Node A which is supposed to contain data from Node C.
Now, Node C will recognize the false data from Node B, which she received from Node A. This is because that data should contain the data Node C initially sent to Node A. It's like someone lying to you about what you told someone else.
As Node C identifies the error, it will be addressed and Byzantine fault would be eliminated.
HASHGRAPH VS BLOCKCHAIN

Blockchain is in operation and has been tested diversely while hashgraph has barley made an entrance. From the concepts of both distributed ledger technologies however, we can draw some striking differences.
SPEED
Hashgraph is faster because of its gossip protocol which does not require the consent of all the miners to validate each transaction while blockchain technology utilizes miners to validate transactions especially in Proof of Work consensus.
FAIRNESS
On blockchains like bitcoin and ethereum, when the transactions initiated becomes much, miners choose which transaction to validate and this leads to increased fees. This is not the case on hashgraph as all transactions are validated as the technology does not allow transactions to be delayed or blocked.
SECURITY
Blockchain is secured but not like hashgraph which uses Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus (aBFT). With this, hashgraph is able to achieve consensus so long as more than 2/3 of the nodes are not malicious.
USAGE
Hashgraph is still an idea, it's yet to be tested in real life. There are doubts about its performance when it will be opened to the public. Blockchain on the other hand is not mew, it has had a lot of test and is still standing.
HASHGRAPH VS BLOCKCHAIN IN A VOTING PROCESS

Both have a valid case for their approaches to electronic voting. They are both capable of supporting it. However, there are reasons why hashgraph is better than blockchain
1. Scalability:
When you consider my country Nigeria for instance, we have a population of about 200 million people. At least, 50 million are eligible for voting and usually, voting is done within a day.
Current blockchain technology will struggle with that number of transactions in a day but hashgraph can cope with that.
2. Byzantine fault tolerant:
This feature ensures that consensus or an agreement is reached even if some nodes return false information or errors. Thus, the voting process on hashgraph is secure
3. Fairness:
I mentioned earlier how that hashgraph does not support delay or blocking of transaction but rather ensures that all transactions are validated. This will be very important in voting, where all the votes should count. On blockchain, increase in number of transactions can lead to abandonment/delay of some transactions.
HEDERA HASHGRAPH

Hedera hashgraph is the only publicly distributed ledger that uses hashgraph technology. It has a very user friendly website which is very easy to access.
The above image is all that can be found on the homepage. The menu is at the top right corner. Clicking on it drops down a menu list
You can learn about hedera's network by clicking here
If you're a developer and you want to find out about APIs and integrations, you simply click here
To find out about hedera's use cases, click here

Hedera has a native cryptocurrency called HBAR. If you want to know about it, click here
If you want to find out about governance on hedera, simply click here
Then if you want to learn about hedera, click on 'about' like in the image below
CONCLUSION

Distributed ledger technology is not only about blockchain, there is also the hashgraph, which though is new, has lots of potential and will solve lots of problems with blockchain of it succeeds. Hashgraph is faster, cheaper, and fairer than blockchain.
The only concern with hashgraph is that it is new and is yet to stand the test of time. It is also not decentralized yet so it is still very much theory.
If it succeeds however, it will correct so many lapses in blockchain, like scalability (to say the least).
Thanks for reading.
Cc:
@pelon53
Gracias por participar en Steemit Crypto Academy:
Información muy didáctica, pero en algunos caso no muy clara. Por ejemplo, cuando hay nodos maliciosos, para llegar a un consenso debe existir 2/3 de nodos válidos, y no más de 1/3 de nodos maliciosos.
Faltó información del protocolo Gossip, algunas ventajas y desventajas.
No le colocó el usuario a las captures de pantalla.
Espero seguir leyendo tus publicaciones.
Calificación: 7.2
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Sire why are they not curating us??
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Patience friend, there's a lot of curation work to do. Expiring posts are given precedence, so before your post expires, it'll be curated, hopefully.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit