
1. Explain the Blockchain CryptoGraphy and mention few names which are the Blockchain Platforms (Few names of the Blockchain Platforms)?
Everything security on blockchain is the result of Cryptographic functions. Outside blockchian, we have seen messages sent privately to people get leaked in the public space and this has led to serious problems in different levels. Cryptography is a system that secures the communication between two parties where outside parties are not able to access or understand the information carried in the message. Cryptography was coined from two ancient Greek terms; Kryptos meaning hidden and Graphien meaning write.
In Cryptography, we will come across terms like
- Encryption: this is the conversion of plain readable text to unreadable codes or language. This is done at the sender's end
- Decryption: this is decoding or conversion of the unreadable codes or language to plain readable text. This is done at the receiver's end
- Key: Acting like a password to access the message, this is the information required to decipher the message.
- Cipher: This is the cryptographic function that needs to be decrypted
Blockchain employs the Cryptography system to keep up with the security and data consistency on the blockchain network. Once data is entered on a block and it gets validated, changes cannot be made to it. In the blockchain space, cryptography is used to ensure security by developing unique keys for users and other tools like Hashing with the ideal purpose of ensuring safety of users transaction information and giving users some level of privacy .
Examples of Blockchain Platforms
a. Ethereum Blockchain
b. Tron Blockchain
c. Steem blockchain
d. Stellar Blockchain

2. Explain the Public Key CryptoGraphy.
The Public key is the unique key created using cryptographic functions (usually a mix of alphabets and numbers) that is shared publicly on the blockchain network. The Public key is only used to encrypt messages so the sender of the message will encrypt the message with the public key of the recipient. The recipient will only need his private key to decrypt the message and make meaning out of it. Because the message was encrypted with the recipient's public address, the private key of the recipient is the only key paired with that public key making it difficult for an outside party to decrypt and get access to the message.
The public key is generated using the private key and combined with hash functions ,a public wallet adress can be generated. This public adress can be seen and shared to everyone on the network and is used to send and receive funds on the network.

3. Explain the Private Key CryptoGraphy.
The Private key is one of the important keys users should keep very well. The private key just like the name implies should be kept privately by the user and should ot be shared with anybody because it is this key that gives you full control of your wallet and the assets you have in store. Remember when a message is sent, the recipient will need his/her private key to decipher the message i.e decrypting it from cipher text to plain text.
When a user creates a new wallet, the Blockchain wallet generates the private key and stores it for the user. This private key is what you will use to access the wallet and validate transactions in the form of digital signatures. Once you lost the private key, you refuse to gain access to your wallet and the assets you had in store so this key ought to be kept manually (written down) or saved somewhere safely.

4. Explain the Digital Signatures CryptoGraphy and what is Singing Of Transaction/Message?
Digital signature is a security tool used to validate and authenticate a message. The sender creates a digital signature using his private key and to decrypt the message, the public key of the signer will be needed.
The digital signature just like the traditional signature is to validate the message and the authenticity of the author.
The digital signature depends on two functions:
a. Sign : This is validating a transaction with your private key to produce a digital signature for the transaction.
b. Verify: this is verifying the message with your public key to check the message's authenticity
Signing a transaction is employing the sign function of digital signatures where the authenticity of a transaction is validated using the private key. Adding a signature to a transaction can be done manually but some wallets automatically generate signatures using the private keys of the user.

5. Explain what is Symmetric and Asymmetric cryptography?
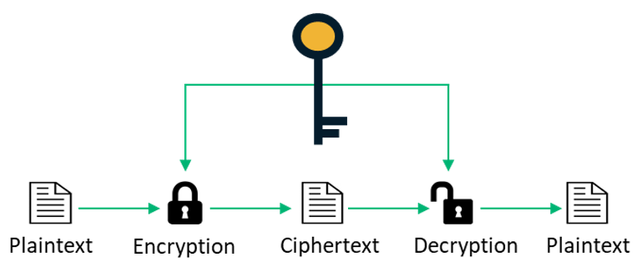
This is a type of cryptography where a single key called the secret key is used for both encryption and decryption of the message. The sender encrypts the message with this secret key and the receiver will have to use the same secret key to decrypt the message to make meaning out of it. In this case, outside parties who do not have access to the secret key cannot decipher the message.
Symmetric cryptography can be in 2 forms;
Block Symmetric cryptography; where a set legth of bits are encrypted in blocks and the data is stored in the system until the block is completed.
Stream Symmetric cryptography; Here the data is streamed as encryption continues and the data is not stored in the system.
Examples of Symmetric Cryptography
- DES (Data Encryption Standard)
- IDEA (International Data Encryption Algorithm)
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
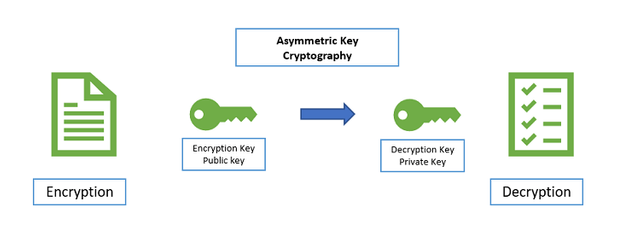
The Asymmetric key Cryptography unlike Symmetric cryptography uses 2 separate keys instead of one. Here both public key and private keys needed. The sender encrypts the message with the public key and the expected recipient can get access to the message using his private key. The public keys and private keys are paired so any outside party that tries to acces the message using another key aside the public key's paired private key will be unable to access the message. However, when the sender encrypts the message with hisprivate key, the public key of the sender is the only way to decrypt the message and this process authenticates the sender of the message.
The Asymmetric key Cryptography is what is employed in the blockchain and cryptocurrency space.
Examples of Asymmetric Cryptography
- Rivest Shamir Adleman (RSA)
- Digital Signature Standard (DSS)
- Elliptical Curve Cryptography (ECC)

6. How Blockchain Wallets CryptoGraphy works and explains the available types of Crypto Wallets.
Crypto wallets serve the same purpose the wallets we use in our every day life serve - a safe place to store. Crypto wallets store all your private keys which gives you some claim of ownership over the wallet and its assets. Crypto wallets also enable users to send and receive funds using a unique wallet address generated using cryptographic functions.
There are 2 keys linked to a wallet:
a. Private key; This key is to be kept secretly and can be used to access the wallet. When this key is lost, the user loses everything.
b. Public key: This key is shared on the blockchain and combined with other hash functions a wallet address is generated.
The Wallet address is the address used to send and receive funds from other adress. The wallet address is shared to the public but it poses no risk of theft or loss of asset for users because the private key still secures the wallet.
Types of Crypto wallets
Crypto wallets can be categorized into 2
Hot wallets: These are wallets that can only be accessed using the internet. Crypto assets are stored on a server on the internet and most of this wallets facilitate the sending and receiving of crypto assets.
Cold wallets: These wallets need no internet to access. The keys are stored offline and the risk of hack is less as compared to hot wallets.

7. What is the Merkle trees and What its importance in blockchain?
Merkle Tree is one of the important component of a blockchain network that sets out the various transactions and their corresponding hashes in a block. The Merkle Tree helps in the easy verification of tyhe data recorded in the block. Also called the Hash tree, the structure indeed looks like a tree with the leaf component being the lowest node and the root hash, the highest node made up of the combination of all the transactions in the block.
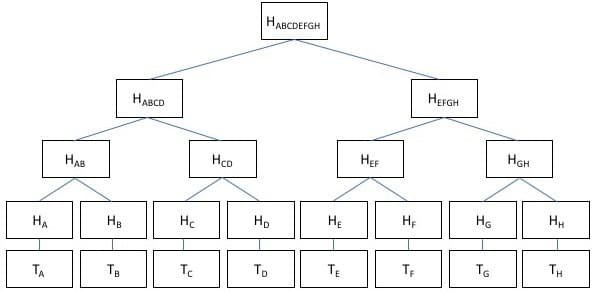
The Merkle tree is built by pairing the hashes of two nodes continuously until the root hash is generated. The Merkle Tree is built from bottom to top and when the number of transactions are not even, the last hash will be duplicated to make the number even.
Importance of Merkle Tree in Blockchain
- Transaction validation is faster as there is no need to go through all the transactions recorded in the block.
- Data integrity is ensured as a single alteration made to any transaction will ne identified because the root hash will be invalid.
- Transactions in the block can be verified easily without having to download the entire block.

8. Practical + Theory, do some practical research explain the functionality of Key, Signature, Transaction, Blockchain with proper screenshots of yours practical.
I will perform this part of the task using Blockchain Demo.
Keys
Like earlier said, the public keys and private keys are paired together in the sense that a private key has a corresponding public key.
I will illustrate this using the Blockchain Demo.
.png)
From the image above, the Random button was used to generate the Private key: 96264988020832713493864284997389439510519088540742009701511763342518329563053
The correspondig Public key for this private key is : 0498379ba3406ce3cea8cc622535918ba21d9c3c12b51f9d5630c9ad570859a55a2de1f1bd12a0cfda25bc6892de81dbdba880c5f956e663e40e96c62098e96c7c
Now, I enter my own Private key: 9871234
.png)
The Public key generated for this private as shown in the image above is: 043d1fd229012a135404c7d5723e4359aee8b103d49973b01533e50dc58aca4e453ed2ef525d931e8539d4807a3092ea7aeab58075854d2a9bc33e0e9279120f66
This illustration has proven that every private key has a unique corresponding public key that is why when a message is encrypted with a private key, it will take only its corresponding public key to decrypt the message.
Digital signatures
Digital signatures are used to validate the authenticity of a message and verify if its from the expected sender. Below is
an illustration of how we can add digital signatures to a message.
.png)
I enter my message: Steemit
Private Key: 9871234
The unique digital signature generated is: 3046022100ca2f3a2a894ed473b879464386d82b2a164a8ca598920404df364c65116fba9502210082c423187f1f540ec44e57dd10de7f0a3e697dc149593802ede1b8f7913185b6
This is the sign function of the digital signature.
Now, let's look at the verify function.
The verify function is to verify the authenticity of the sender and the validity of the transaction. Once the signature corresponds with the Public key, the dialog box goes green as seen below:
.png)
Transactions
Now, we will look at how the sender encrypts a message or transaction using the public keys. The recipient will be able to decrypt the message because he has a corresponding private key.
The sign option adds a digital signature to the message.
.png)
Now we move on to verify the transaction. The entire box goes green, meaning the transaction is valid.
.png)
Blockchain
Here, we will look at how blocks are added to a blockchain and how any attempt to alter the information of the block invalidates the block.
Taking Block 5
This is how the block looks like before I try making modifications to the details in the block. Everything looks right
.png)
Now I make changes to the first transaction in the block where I change the figure from 7 to 14.
.png)
The block goes red, indicating an invalid transaction in the block. The signature also goes red to indicate that the new transaction or message is not from the right sender.
The block can be re-mined where a new nonce will be computed for the transaction to make it valid but the digital signature will remain red to indicate that the message has been altered and was not done by the sender.
.png)
Conclusion
Cryptography has beefed up security in the blockchain space where very unique keys are being generated using cryptographic functions. Private keys and Public keys are paired together in the sense that any private key has its own unique corresponding public key.
We have also looked at how the Merkle tree is an important component of a blockchain that helps in the verification of a block easily.
The practical part of the work has also proven how private keys and public keys are linked and also how an attempted alteration to the details of a block invalidates the block.
Thanks for reading. Big credits Prof. @stream4u for this wonderful lecture. See you next season hopefully, it was a wonderful experience.