A hashgraph is a decentralized public distributed technology that offers a new consensus alternative to the blockchain developed by an American scientist called Lemon Baird in the mid 2010s and officially released in July 2017.
It is a third generation crptocurrency project that uses a gossip protocols to validate its transactions and not the use of miners unlike the blockchain. The gossip protocol is used to create a Directed Acyclic Graphic (DAG). The graph shows events that forms a record of how information is communicated. With the help of the DAG, the hashgraph is able to create an Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT). Presently, the hashgraph technology is patented and the only authorized ledger is called the Hedera Hashgraph. The native cryptocurrency of the Hedera Hashgraph system is known as HBAR.
Simply put, a hashgragh is a graph connected by cryptographic hashes that maintains detailed records of gossips such as who gossipped, to whom, in what order etc.
The gossip protocol enables the validation of transactions through the transfer of information between network nodes. An illustration of a gossip protocol is when a member of a group named Jacob randomly sends an information on a particular subject to another member named Kate and then go ahead to select a different member at random and relay the same information. Meanwhile, after Kate has received the information, she sends it to a different member of that same group and random. All members with the same information continue to randomly send it to others, due to this way, the members will all be aware if the information has been edited or a new information has been added. Like the name 'gossip' implies, information will quickly spread through the group.
The synchronization of information through the gossip protocol is called a gossip sync. Each member memorializes the gossip synch with an event which is composed of a timestamp, hashes, transactions and digital signature.
The Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) is the ability of a distributed network to achieve consensus in order to continually operate despite incorrect or malicious data by quickly rejecting them and validating each block or hash with the use of honest nodes which are constantly in communication with each other. Due to the constant communications between nodes, there is no need for multiple confirmations of transactions. The use of Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) guarantees the security of the data stored within the Hashgraph network by enabling the prevention of malicious people from manipulating and corrupting the system.
Differences Between Hashgraph and Blockchain
1. Data storage:
While the blockchain stores its data in blocks, the hashgraph stores data in a directed acyclic graph.
2. Security:
Both the blockchain and hashgraph are well secured and impossible to hack. While the blockchain’s digital blocks are tamper-proof due to its public distribution properties, the hashgraph uses Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) to secure its network.
3. Speed:
In blockchain, the transaction speed varies depending on the cryptocurrency, platform etc. Though it is considered fast when being compared to centralized banking system, the transaction speed of the hashgraph is relatively faster than the blockchain. While the blockchain offers a speed of 100 to10,000 transactions per second, the hashgraph offers a speed of 500,000 transactions per second with the use of gossip protocol.
4. Advantage:
In blockchain, the miners have more power and advantage when it comes to selecting orders to process, stopping a transaction etc. Miners are required to validate the transactions in a blockchain and this gives them an unfair advantage while the hashgraph randomly allocated nodes and ensure that no individual is affected due to the order of transactions with the use of timestamp.
5. Accessibility:
The blockchain is publicly used (open sourced) and therefore has multiple people actively using it while the hashgraph is a patented technology.
6. Development:
The blockchain has been in existence for decades and gets even more popular each day, it has been known to withstand the test of time and various cryptocurrencies which are continually being built on it. The hashgraph on the other hand is relatively new and is yet to be popular and adopted by various people.
7. Consensus Mechanism:
The blockchain uses various consensus algorithms such as proof of work ( POW), proof of stake (POS), proof of elapsed time etc depending on the cryptocurrency while the hashgraph does not require algorithms as it uses virtual voting to get network consensus.
8. Efficiency:
Whereas blockchain, uses a lot of time, effort and power in mining, Hashgraph creates events which makes it very efficient as it does not utilize much effort.
The properties of Hashgraph is based on theory due to the fact that it is patented and therefore not released to the public. Its potential and effectiveness will be verified once it is released to the public. As a result of this, one cannot help but choose the blockchain which is more accessible and proven time and again to be effective.
The inherit hashgraph is a decentralized public distributed ledger network based on the hashgrapgh algorithm. It is owned and managed by a governing council of global enterprises such as Swirlds, google,LG, IBM, FIS, Shinhan bank etc. Its official website Is https://hereda.com/
The drop box at the right side indicates the various services offered such as the network features which shows the services It offers such as the token services which offers the option to create your own native token whether fungible or non-fungible token and the consensus services which enables one to create any method of verifying and carrying out series of actions using the Hashgraph consensus protocol. It also gives information on how the Hedera works, live and historical data to explore the Hedera and the dashboard to view its network activities.
The HBAR features allows one to learn more about the native token of the Hedera Hashgraph which is called HBAR, create a Hedera account and trade the $HBAR.
The site also lists the organizations the owns and manages the Hedera
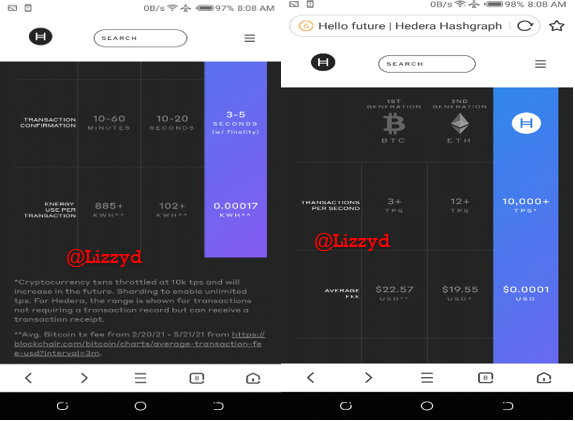
The website compares the 1st generation cryptocurrency (Bitcoin), 2nd generetion cryptocurrency (Ethereum) and the Hedera Hashgraph which is the 3rd generation cryptocurrency. It compares important facts such as the transaction per second, average fees, transaction confirmation and the energy used for every transaction.
The website is without a doubt self explanatory with a lot of awesome features given made available to the public.
Cc: @pelon53


Gracias por participar en Steemit Crypto Academy:
No cumple con las reglas emitidas por Steemiblog para esta semana, donde el SP debe ser igual a superior a 150.
Espero poder corregir tus tareas.
Calificación: No Apta, no cumple con los SP.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Dear Professor @pelon53, I have powered up my steem power to the required point. and I plead you kindly help re-check my post for scoring. Thank you so much sir.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Professor @pelon53 Kindly hell me recheck my post. I have powered up my steem. Thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Professor @pelon53.
Kindly help me recheck my post, I have powered up my steem. Thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Professor @pelon53....Kindly recheck my post, I have powered up my steem. Thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Buenas Tardes, usted debió revisar las reglas que dicen muy claro lo siguiente:
• Según los criterios determinados por el equipo de Steemit, no recibirás un voto por tu tarea si tu reputación no es superior a 50 y no cuentas con 150 SP o más.
Por lo tanto, en el momento de la revisión, usted no tenía los 150 SP.
Calificación: No Apta por no tener 150 SP al momento de la revisión.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit