It is with great pleasure to be a participant in this week assignment of professor @pelon53 which he taught about SIDECHAINS, I can say I understood the class and I have been able to give back base on my own understanding and the research I made. I stand corrected in any way as I might have come short in details of a particular question.


1.- Explain in detail the Sidechains with the use of ZK-Rollups.

For this discussion, the blockchain that is referenced is Ethereum because it is one of the networks experiencing scalability issues and it is also the network that deals with sidechains that make use of ZK-roll ups.
Ethereum blockchain is the second largest and the second most popular blockchain in the world. One of the reasons is that it was developed to solve some of the issues experienced by Bitcoin's blockchain and another reason is that it was the first to start the smart contracts industry. Due to these reasons, Ethereum's blockchain has been seen in increment in its use by enterprises that require automatic transactions which are based on certain rules. The adoption of smart contracts has brought immense flexibility for its wider enterprise application. This popularity has brought upon Ethereum's network a large number of transactions to be executed on the blockchain. These transactions have started testing the scalability problems of the network.

The core of the scalability issue is Ethereum's mode of operation also known as Proof-of-Work. This consensus mechanism allows Ethereum to process a block where transactions are stored to 7-15 transactions per second (tps). This is because every node has to verify each and every transaction that goes on in the network. And unless this problem is solved, the congestion of the transactions would lead to delays and high commissions for Ethereum users. Different solutions have been proposed by Ethereum's network which is categorized to on-chain scaling and off-chain scaling.
Looking at off-chain scaling, they are solutions that are deployed by Etherem's network but are different from Layer 1 main network (main net). That means no changes to the existing protocol in the Ethereum network are required. Some of them derive their security from the Layer 1 main net protocols, they are regarded as Layer 2 solutions. While some involve the creation of new chains and the security is not dependent on the Layer 1 main net protocol.
Also in the Layer 2 solutions, they are centered around servers or clusters of servers that are termed differently such as nodes, operators, validators, sequencers, and block producers. In loose terms, transactions are submitted to these Layer 2 nodes rather than being submitted into Layer 1 nodes. For some Layer 2 solutions, these transactions are batched together before being sent to Layer 1 for security. One of such solutions is a Roll-up.

A Roll-up is a means by which transactions are executed outside the Layer 1 main network and then the data derived is posted to Layer 1 so that it can be immersed in the consensus protocol of the main net. As the transaction data are then put in the Layer 1 blocks this ensures the security of the data. Roll-ups are the scalability option that is very popular in Ethereum's network. The mechanisms of Roll-ups are varied but generally, they group different transactions from Layer 2 chains (sidechains) and generate a cryptographic proof also called a SNARK which is sent to Layer 1 main net.
One of the varied Roll-up is called ZK Roll-up or Zero-Knowledge Roll-up. It is called zero-knowledge because it makes use of cryptographic proof where one party (the prover) can prove to another party (the verifier) that something is known without revealing the known information directly. This ZK proof is used to present data to Layer 1 main net which is then recorded on Ethereum's blockchain but in this case, there is no interaction because of the use of SNARK Proof. It is made up of two types of users namely, transactors and relayers.
The transactions are those that make transactions and broadcast them to the network, while the relayers are those that collect the large amounts of transactions seen and use them to create a Roll-up. The relayers are the ones to generate the SNARK proof. The SNARK is a cryptographic hash that shows the state of the blockchain. Anyone can become a relayer, but must first stake the bond that is required in a smart contract. This process is needed to remove the unforeseen bad actors.
Some of the benefits of ZK Roll-ups are:
- Low transaction costs.
- Fewer data contained for each transaction helps to increase throughput and scalability.
- No need for a fraud game verification like is found in Optimistic Roll-up, this can delay withdrawals by up to two weeks.
- The model used in computing the blocks is in parallel, and it encourages decentralization.
- Faster than other types of Roll-ups and scalability solutions.
The Layer 2 projects using ZK Roll-ups are Loopring, ZKSync, Hermez, StarkWare, ZKTubeAztec, Deversifi, and Curve.fi

2.- Explain the Liquid Network side chain


Liquid Network is a settlement network that operates as a sidechain to make Bitcoin transactions and the issuance of digital assets to be faster and more confidential. It is designed with improved efficiency to the cryptocurrency trading markets at its core. The Liquid Network which is also a sidechain is a blockchain that helps to process transactions between Bitcoin's main chain and its chain through a two-way peg. The amount of BTC that is flowing in the Liquidity network is always equal and verifiable to the number of Bitcoins that are locked on the Bitcoin main chain. Liquidity Network depends on Bitcoin but Bitcoin doesn't depend on the Liquidity network.
The Liquid tokens are used for faster Bitcoin transactions, improve the confidentiality of Bitcoin transactions, and to help issue new assets, trading, and for payment of transaction fees for any type of asset on Liquid.
Liquid Bitcoin (L-BTC) is a unique type of asset on the liquid network. It is backed by Bitcoin in the ratio 1:1 of the Bitcoin held in the mainchain. L-BTC is created when BTC is moved to the Liquid Network and then destroyed when BTC is moved out of the network. The process of moving BTC to Liquid Network is known as Peg-in, while the process of moving BTC out of Liquid Network is known as Peg-out.

No single member acts as a centralized entity.
The blocks on the Liquid network aren't mined like Bitcoin through the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism. The blocks are signed by 15 Liquid functionaries in a round-robin. So even though anyone can become a node and inspect the state of the network, it is the Liquid functionaries that perform actions such as the signing of transactions, generating new blocks, and making sure the BTC held by the network is secured.
Every transaction on Liquid Network incurs a fee, this fee is paid in Liquid Bitcoin (L-BTC). They work in a similar fashion to Bitcoin Network where transaction fees are paid in Bitcoins (BTC). One of the reasons why Liquid transaction has a fee is to stop the risk of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. This is a situation whereby a malicious user would send a large number of transactions to the network at zero cost to either fill up the block space and thus prevent other transactions from being completed.
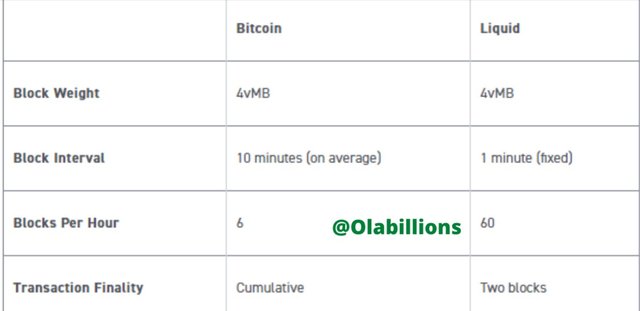
Liquid Network transaction capacity is almost the same as that experienced in Bitcoin blockchain, but it enables faster transactions due to higher block production frequency and two-block transaction finality. The transactions that are carried out on the Liquid Network are a little bit larger than the transactions found in Bitcoin Network because it uses a cryptographic feature called Confidential Transactions that helps to hide the type of asset and amount in the transaction shown in the Liquid blockchain from third parties. This makes it that the transactions in a Liquid block are fewer than a Bitcoin block. However Liquid network has a higher block producing frequency because it has a higher transaction per second (tps) than bitcoin.

3.- Describe the steps to connect the Metamask wallet and the Polygon network wallet. Show screenshots.

These are the steps that were taken to get to connect my MetaMask wallet with the Polygon Network wallet.
- Visit the Polygon address and then click on Use Polygon. It would bring out a list, on that list click on Polygon Wallet.
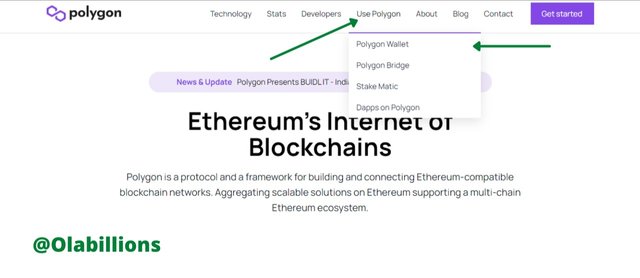
Source - On the next page that opens click on Polygon Wallet.

Source - On the next page click on MetaMask because that is what we are using to connect to Polygon's network.

Source - You would be asked to input your password, do that and click on UNLOCK.
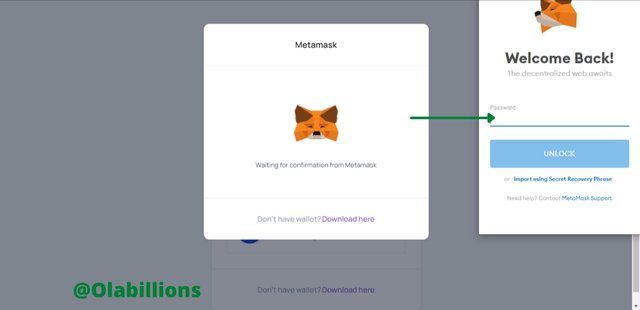
Source - Then a display would request your consent. Click on Sign.
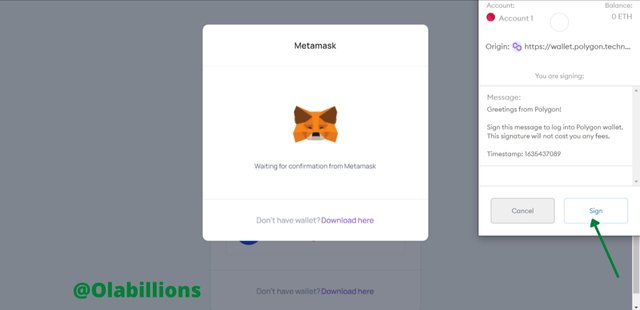
Source - Finally, you have connected your MetaMask wallet to Polygon Network. To be sure you can view the icon above and you would see Account.
Source

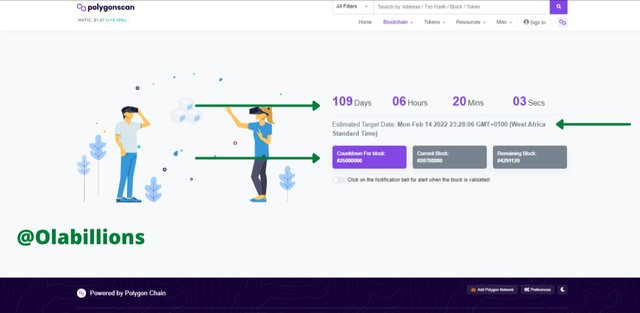
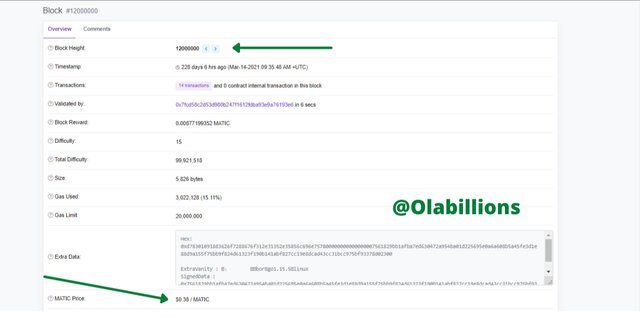
4.- According to the polygonscan block explorer, when will the block 25,000,000 be generated? Show screenshot. Explore the 12,000,000 block, at that time, what was the price of the Matic? Show screenshots.

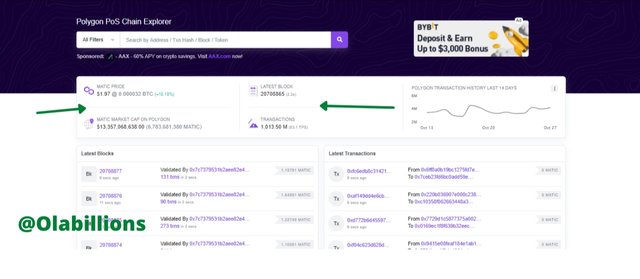
First I visited polygonscan for this exercise. On the home page, I saw some basic information on the explorer. The current price of MATIC was displayed and it stood at $1.97, while the latest block was at 20,708,865, the MATIC Market Cap was $13,357,068,638.00, and the Transactions recorded so far stood at 1,013.50 M.
Then I checked for when the 25,000,000 blocks would be generated. It stood at 109 days, 04 hours, 58 mins, and 48 sec. The estimated time given is Mon Feb 14, 2022, 23:26:37 GMT+0100 (West Africa Standard Time). This reminds me of Saint Valentine.
Then checking block 12,000,000, I was able to get the block with the details of the block. One of them is the price of MATIC at that time which was at $0.38.

Conclusion

ZK Roll-up is an important solution to the Ethereum blockchain simply because they help scale Ethereum's network. They also help to reduce the costs associated with operating on Ethereum's blockchain. Ethereum has proposed different scalability solutions to help Ethereum's network achieve high efficiency even during peak periods. ZK Rollup is one of them and is set to play an integral role in helping Ethereum's network scale.
Another phenomenon in the cryptocurrency space is Liquidity networks. It is a side chain that helps the main chain scale and also experience efficiency in their networks. One of such is Liquidity Network by Blockstream. Their focus is on Bitcoins and some other cryptocurrencies. They have created a platform that is accessible to any individual and it is all-encompassing.