Introduction
Greetings, Steemians!
It's a beautiful time to be back at the academy; it's now week six of season three, and I'm pleased to have been a part of it thus far. The concept of blockchain and how it is produced were explained in Professor @stream4u's class. It was an excellent lesson, and I will answer to the homework task in this article.
 Design made with Posterwall
Design made with Posterwall
What is Blockchain and What are the types of Blockchains / Explain in detail the types of Blockchain?
The term "blockchain" has been around for a while; it's one of the ground-breaking technologies that has resulted in a trustless system that is free of any suspicion. The technology behind Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, and other digital currencies. Blockchain is an online technology that records, stores, and secures data in a decentralized manner such that it cannot be altered or hacked after it has been recorded.
Furthermore, the blockchain is made up of digital records known as Blocks that are linked together in a chain structure to complete the blockchain. This block cannot be altered, hacked, or removed in any way.
When a transaction takes place, a copy of the transaction is created and distributed to all of the Blockchain's linked nodes. This is accomplished by the application of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
The time it takes for a block to be generated varies in each blockchain. For instance, the time taken to generates new block in the Bitcoin blockchain is 10mins, this block contain the transaction data/information stored inside the block, which will have a hash code. This hash is linked to the next block, and the next one too resulting in the formation of a blockchain.
The hash employs a one-way encryption mechanism, ensuring that if any information/data in a block on the chain is changed (because the block is connected to the next block), the chain will be disrupted and the blockchain would stop working. As a result, once data/information has been recorded, it is impossible to change any data in any block without affecting the other blocks.
The blockchain system consists of some key components, which are as follows:
The Blocks
This refers to the storage of the blockchain, the block contains a completed data of a transaction that has been confirmed and validated in the system, hence the data cannot be changed or altered after it has been saved. The decentralized aspect of the Blockchain is maintained by sending a copy of the new block data to all connecting nodes within the network. Data, which is information, Nonce, which is a 32-bit number, and Hash, which is a 256-bit alphanumeric figure, are the three important aspects of the block.
The Chain
Each block in a network has data (information), a hash, and a Nonce number. The chain is the hash that connects new blocks to previous blocks, revealing the block's position and keeping the blockchain orderly. Data recorded in a blockchain becomes more accessible as a result of this.
The Nodes
A node is a group of computers joined together for the fast running of the blockchain. In order to validate the transaction before adding a block to the chain, every connected node shares the data of new blocks with other nodes in the system. This protocol demonstrates the Blockchain's decentralized character.
The Miners
Miners are referred to the members of a blockchain network who are involved in the validation of new blocks on the network before they can be added to the chain. Mining varies by network; for example, Ethereum employs the Proof of Work consensus technique, which entails the use of high-powered computers to do complex mathematical computations in order to validate a block's hash, with the first miner to validate the block receiving a reward.

What are the types of Blockchains
With various sectors adopting blockchain technology, there is a large range of use cases based on the type of blockchain and the use case. Presently, there are four (4) types of blockchains;
Public Blockchain
In the cryptocurrency world, this is the type of blockchain is an open blockchain that lets anyone with an internet connection to connect to its network. The public blockchain makes use of distributed ledger technology, which means that all data is dispersed across all nodes linked to the network rather than being kept in one place. Because its data is dispersed to all nodes linked to the network, this blockchain variant avoids centralization and improves transparency. It's notable as it's open source, allowing anyone to participate as a node in the network for transaction validations or make changes.
The most well-known cryptocurrenciesBitcoin and Ethereum are typical examples of a public blockchain.
Advantages of Public Blockchain
Trustless: the public blockchain is Trustless, which means it does not require anyone to trust anyone before using it. Smart contracts must be dealt with in order for transactions to be completed.
Ease of Access: another advantage of a public blockchain is that it is entirely free and open to the whole public. The blockchain network can be used in a variety of corporate and organizational applications, including payments of salaries to the workers.
Transparency: transparency is another advantage of the public blockchain because it is open source and the information is not kept to a single place but rather distributed throughout the network, making it accessible to anybody, anywhere who is connected to the network.
Disadvantages of Public Blockchain
High cost of Mining and maintanance: mining on the public blockchain necessitates the use of powerful computers in order to keep up with the time it takes to create a new block. This results in higher electricity cost and the cost of setting up powerful computer. In addition, the cost of maintaining a public blockchain is high, and as the number of users grows, more network capacity is necessary for speedier data transfer.
51% attack: since there are no limitations on who may join the network, if the attackers were to gain control of 51% of the mining power, they would have an advantage over the available legitimate mining power, putting the network at danger and potentially causing massive losses.
Low Scalability: as the number of nodes connected to the blockchain network grows, the network experience low scalability and low transactions per seconds (TPS).
Private Blockchain
Private blockchain is a small scaled blockchain that requires permissions, which means that anyone who wants to access data on the network must first obtain permission from the central body. In this type of blockchain the block data/information is stored across connected nodes in order to keep correct information about the blockchain network; nevertheless, public access to nodes is not assured, as only authorized nodes can access and share from the full system's decentralized operations. As a result, only a small number of nodes are permitted to verify, validate, and broadcast transactions on the private blockchain.
This type of network is commonly found in businesses, financial institutions, and educational institutions, etc. This is typically created by a central body, and only authorized nodes in the network have access to the data stored there.
Advantages of Private Blockchain
High Transaction speed: due to it small-scale it increase the speed of transaction in the blockchain network.
Highly Secure: because of the complexity of its operations, it has a high level of security, ensuring that all nodes are sufficiently protected.
Disadvantages of Private Blockchain
Requires permission: the disadvantage of private blockchain is that it requires permission to access the information on the network
Lack Transparency: the data/information on the private blockchain cannot be accessible by everyone, hence it is not as transparent as the public blockchain, which makes all information available to everyone.
The Hybrid Blockchain
The hybrid blockchain combines the characteristics of both public and private blockchain. This type of blockchain is done by setting a private blockchain (permissioned) alongside a public blockchain (permissionless),
The data/information on this type of blockchain is not visible to the public, but it can be verified using smart contracts, ensuring that the information/data contained on it cannot be changed or altered. The connected nodes in the network have access to all data stored on the network, but their identities are hidden from other nodes unless they've conduct a transaction.
This type of blockchain can be employ in the medical field to stored medical information and this information can not be accessed by any random party, but the information can be accessed via smart contract.
Advantages of Hybrid Blockchain
Speed since the number of nodes are limited, this allows for fast verification of transactions, enhancing speed in processing of transactions.
Highly Secured: this is another advantages of this type of blockchain since there are few nodes on the blockchain
Highly Scalable: Hybrid blockchain is extremely scalable and can handle a large volume of requests at a low cost.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Blockchain
Lack Transparency: The lack of transparency in this blockchain is a disadvantage because only the connected nodes who have been granted permission to join the network may see the data stored on the blockchain.
Not fully Decentralized: another disadvantages is that because the hybrid blockchain isn't really decentralized, access restrictions exist inside the Blockchain network.
The Consortium Blockchain
The Consortium blockchain is comparable to a hybrid blockchain, which combines public and private blockchain characteristics. The main difference is that different groups collaborate to run the same blockchain, with the Connected node having access to the ledger. This makes it appear to be a Public blockchain because it is not controlled by a central body, and it is a permissioned blockchain, which means that only members of the groups involved can access it, making it appear to be a Private blockchain.
This type of blockchain can be employ in the Banking field, where different banks can combine together to run the same blockchain and deciding who will validate and confirm transactions.
Advantages of Consortium Blockchain
Speed: just like the hybrid blockchain, thd consortium blockchain is very fast, as it allow for easy data access and transaction verifications since the group can restrict the nodes in the network.
Highly Secured: Because the group participating can restrict other nodes in the network and control who can join the network, this blockchain type is highly secure.
Highly Scalable: Consortium blockchain is extremely scalable and can handle a large volume of requests at a low cost.
Disadvantages of Consortium Blockchain
Not fully Decentralized: another disadvantages is that there is access restrictions inside the blockchain network, as the group only decided who can access the data.
Lack Transparency: just like yrhe hybrid blockchain,the consortium blockchain lack transparency, since only the node allowed by the group can see the data stored on the blockchain network.

What are the benefits of blockchain?
The blockchain technology has brought many breakthroughs as these it has so many benefits. These benefits include;
Immutability: one of the benefits of Blockchain is that it preserves data originality; after all valid transactions have been completed on the blockchain, it cannot be edited, erased, or changed. Transactions are done in real-time, therefore each transaction has a time and date stamp, making it immutable. The rigidity of blockchains is improved as a result of this.
Enhanced Security: another benefit of blockchain is its increased security, immutability, and use of cryptographic technology to encrypt and secure data, not forgetting its decentralized nature, which distributes information to all accessible nodes in the blockchain and ensures strong security.
Elimination of Middleman: the Middleman is one of the obstructions in the traditional centralized system, which results in protracted delays or obstacles, as well as delays in completing a single transaction, the blockchain is built on a decentralized system that is it doesn't need any middleman to execute transactions
Reduced Costs: the cost of doing transactions on the blockchain is lower than in the traditional finance system since there is no middleman involved; therefore, there is no need to pay any additional fees as in the traditional finance system. This is a significant benefit of blockchain technology.
Decentralization: this is one of the major benefits of the blockchain, as the technology is notable for its decentralized nature, which allows each node in the network to participate freely without the need for a central authority.

Explain Blockchain Distributed ledger.
The Blockchain Distributed Ledger is the core of it's decentralization. This refers to the distribution of data throughout the blockchain network's connected nodes. In this instance, all legitimate nodes in the blockchain have unrestricted access to any new transaction that occurs in the system and have duplicate copies of it.
For example, if a node creates and validates a transaction, the distributed ledger protocol notices it and duplicates it before sending it to other connected nodes in the system. This data is saved permanently and cannot be hijacked or altered. this distributed aspect makes it highly difficult to be hacked by any malware or hacker, if hacker want to succeed in hacking it needs to compromised all associated nodes linked to the distributed ledger technology, which is theoretically impossible.
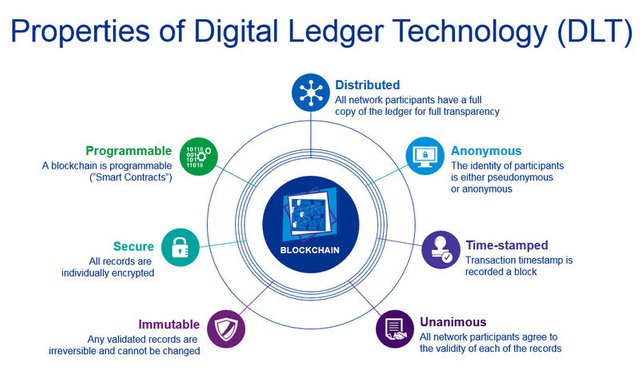
The properties of Blockchain Distributed Ledger;
Highly Secured: the use of hash cryptographic features in a distributed ledger makes it highly secured has it ensures the blocks are encrypted and validated by computing the equivalency of the nonce number.
Distributed: another properties of distributed ledger is that all information and data are duplicated and distributed to all available node of the network
Immutability: this is another properties of the distributed ledger has the time and date stamped of the transaction is made available to its users.
Programmable: the distributed ledger uses smart contracts and it works automatically, it can be customized or programmed to meet the needs of the user.
Unanimous: the blockchain distributed ledger made sure all connected nodes and participants' identities are hidden and kept confidential, enhancing the blockchain's security and the safety of its users.

What Is Blockchain Double Spending and how Bitcoin handles this problem?
Double spending is one of the major issues with cryptocurrencies, which occurs when the same crypto amount is utilized in multiple transactions. In other words, double spending occurs when a particular value of an asset is spent twice in the system, either as a result of an initiating attack on the blockchain or as a result of a transaction launched directly between buyers and sellers.
For example, when a transaction take place in an attack scenario, the money sent to receiving addresses is reversed to the sending address and thus used for further address transactions. Some are considering various attacks on the blockchain, but the 51% attack, in which a miner controls more than half of the network's mining capability, appears to be the most promising. And after this is done, a parallel blockchain chain is built in the blockchain, with faster block mining to make it more respectable in the ecosystem.
There are various types of double-spending attacks, such as:
Vector Attack 76: this type of double-spending attack take place as a result of a network problem. Hackers exploit it to steal users' funds or transmit false crypto assets to receivers.
Finney Attack: this type of double-spending take place when the recipient accepts a transaction without confirming it, as a result of a miner duplicating the transaction's details in other blocks and using them.
Race Attack: I will discuss in details about this type of double-spending in another section of this task.
How Bitcoin handles Blockchain Double Spending
The Bitcoin network employs a technology known as the distributed ledger technology to avoid the problem of double-spending. For easy illustration whenever transaction take place on the Bitcoin network, the transaction will remain unconfirmed, then miners (validator of the transaction) will proceed to verify and validate the transaction (made sure it contain no error) using a mechanism called hash algorithm, after which the transaction has been verified and validate, then it will be added to the blockchain's distributed ledger.
For instance, If an attacker issued a double-spending attack, the completed transaction will be verified and given to the receiver, while the unconfirmed transaction will be erased from the blockchain. Hence, the asset sent and the transaction information cannot be edited or altered after the transaction is added to the public ledger.
Another method that Bitcoin employs to address the issue of double spending is complete spending, in which a user cannot spend the UTXO in part. This method is used in the Electrum Bitcoin wallet; a user cannot partially spend the funds in the Bitcoin wallet; instead, they are automatically sent completely to create two outputs; after confirmation, the actual withdrawal goes to the destination wallet, while the remainder is diverted down to the user wallet via a Change address.
For example, In the case of an Ethereum wallet, if a user has a balance of 0.6 BTC and wants to send 0.4 BTC to a recipient, two outputs will be created: 0.4 BTC to the recipient address and 0.2 BTC to be sent back to the user wallet via the change addresses.

Practical + Theory, Visit Blockchain Demo and check section Blockchain, then explain in detail how Blocks Hashes Work in Blockchain, what will happen when any middle of the block gets changed, try to give screenshot for each possible details.
Hash
The use of a cryptographic hashing method to encrypt the details of a transaction and data recorded in a block is known as block Hashing. I'll demonstrate this method using a blockchain demo to help you understand it better. This would allow me to demonstrate the procedure for various blocks.
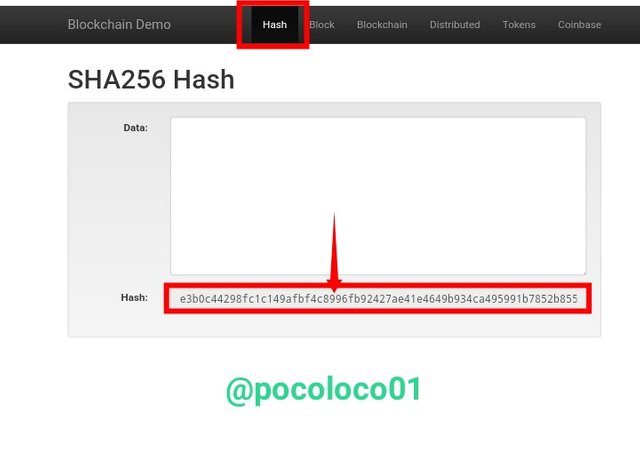 The Hash Section
The Hash Section
Above is the screenshot from the Blockchain demo page's "Hash" section, showing a randomly generated hash with no data input, and we got the hash Below
"e3b0c44298fc1c149afbf4c8996fb92427ae41e4649b934ca495991b7852b855".
Now let input the data and see what the output Hash will look like
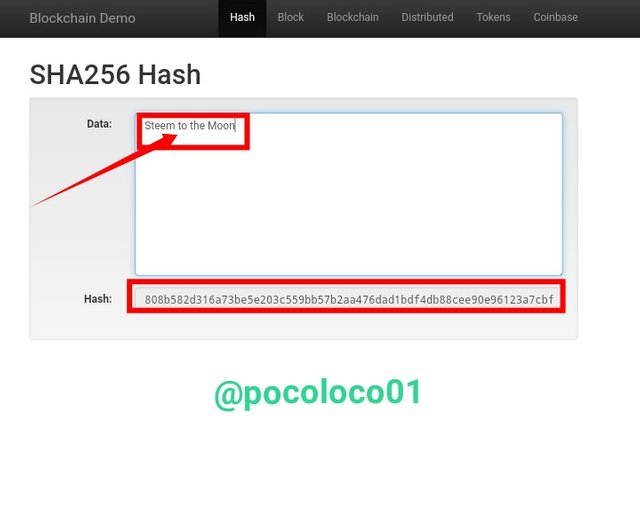 Input Data
Input Data
Above is the screenshot from the Blockchain demo page's "Hash" section, showing the result of the generated hash for the data input "Steem to the Moon", and we got the hash below
"808b582d316a73be5e203c559bb57b2aa476dad1bdf4db88cee90e96123a7cbf".
Now I will input a bigger data, and see what the output Hash will bring out.
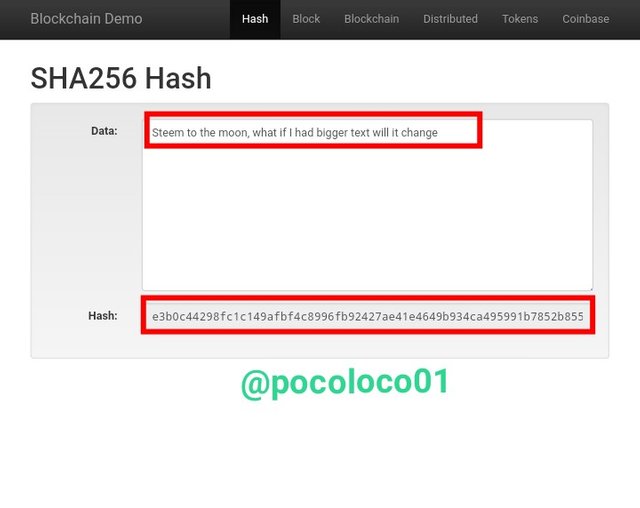 Input bigger Data
Input bigger Data
Above is the screenshot from the Blockchain demo page's "Hash" section, showing the result of the generated hash for inputting a bigger data, I inputted "Steem to the moon, what if I add bigger text will it change", the length of the Hash is still the same below is the hash generated
"8c8b7d6b03bef59d65d78c7505ec0240244803d8bc6f718618d1f5005578e66a"
From the illustration above, I observed that anytime I try to change the data, no matter how big the data inputted is, the Hash will change but the length of the Hash will still be the same.
Blockchain
Now, let's go to the blockchain area of the Blockchain Demo, I will be exploring this area of the Blockchain Demo below.
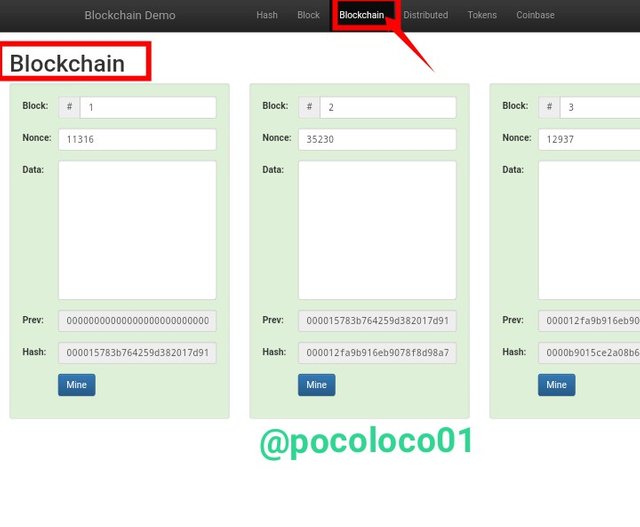 Blockchain Section
Blockchain Section
From the above screenshot, this is the page you'll see if you go to the "Blockchain" section; as you can see, there are three different blocks on the blockchain, each with its own block number, Nonce, and Hash. These blocks are connected on the blockchain by adding the previous block's Hash generated to the newly produced block.
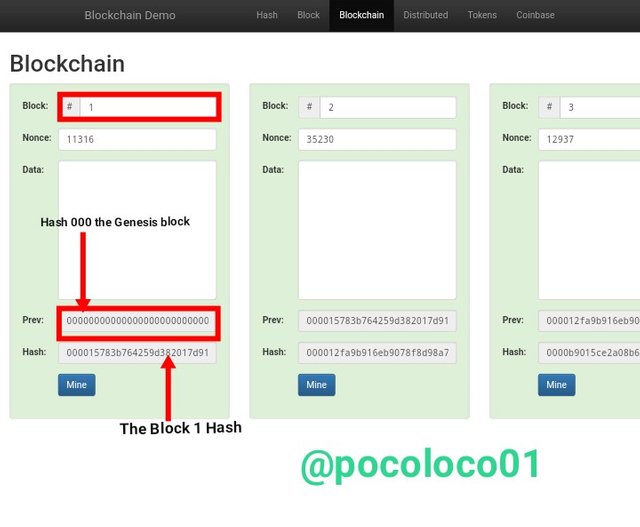 The block 1
The block 1
From the above screenshot, it can be seen that Block 1 has a previous hash of 0000 and a hash of *"000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf."
This is due to the fact that it is the first block on the Bitcoin Blockchain, known as the Genesis Block.
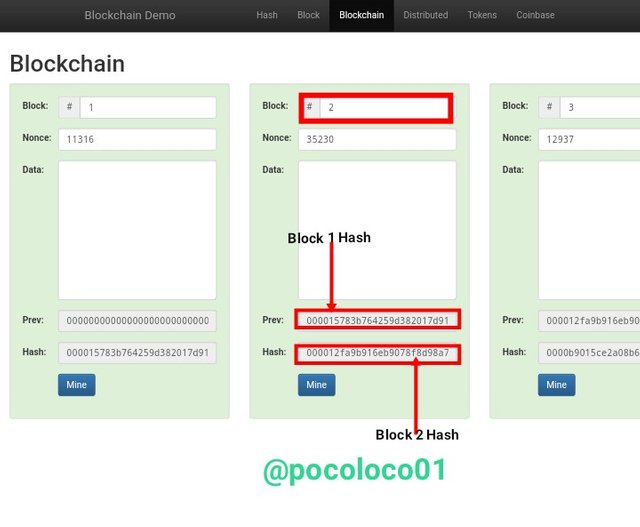 Block 2
Block 2
Looking at block 2, the previous hash was block 1 hash "000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf", that is block 2 is directly linked to block 1.
The same may be said about blocks 3, its previous hash is block 2 hash "0000b9015ce2a08b61216ba5a0778545bf4ddd7ceb7bbd85dd8062b29a9140bf", same goes to block 4 as the previous hash is block 3 hash.
This theory mean all blocks are linked to the previous block to form a blockchain.
Adding Data
I'll take account of the Hash numbers for each of the blocks while doing so. However, I will change the data of block 1, just by doing this the hash changed instanly
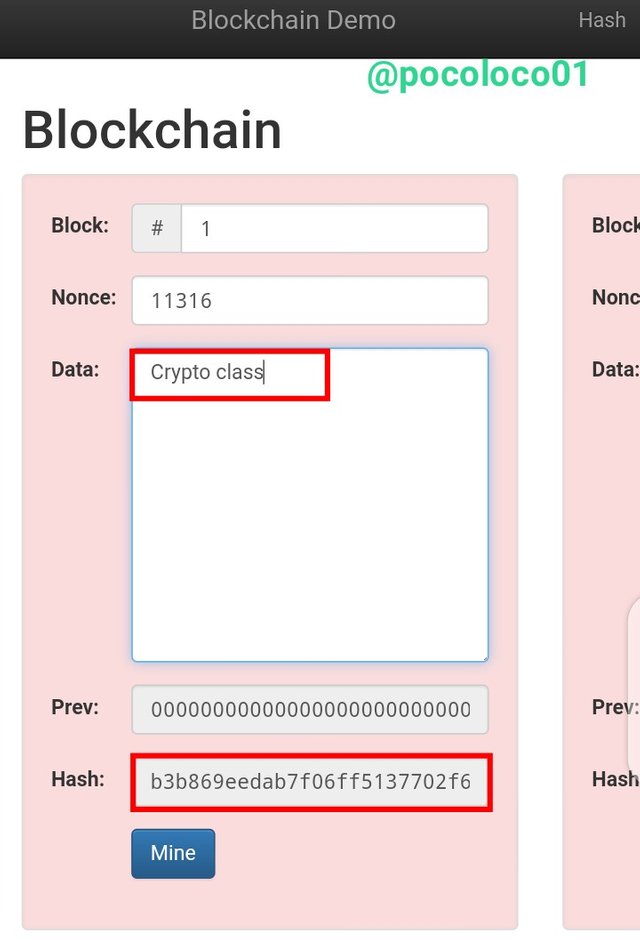 Change the Data
Change the Data
From the screenshot above, I entered "Crypto class" for the data of block 1, the colour changed to red which means an Invalid block, also the hash number changed but didn't start with zeros and this mean the block isn't valid
This is the Hash; "b3b869eedab7f06ff5137702f6373c86895c492366165178352b7f1041801981"
As you can see in the illustration above, I changed the data, but the Nonce number remained the same, indicating that re-mining was required to validate a block with a changed data. In order to mine a block, the Nonce must be linked to a unique hash number and the hash generated must start with zeros. To mine the block successfully, we'll still need a correct Nonce.
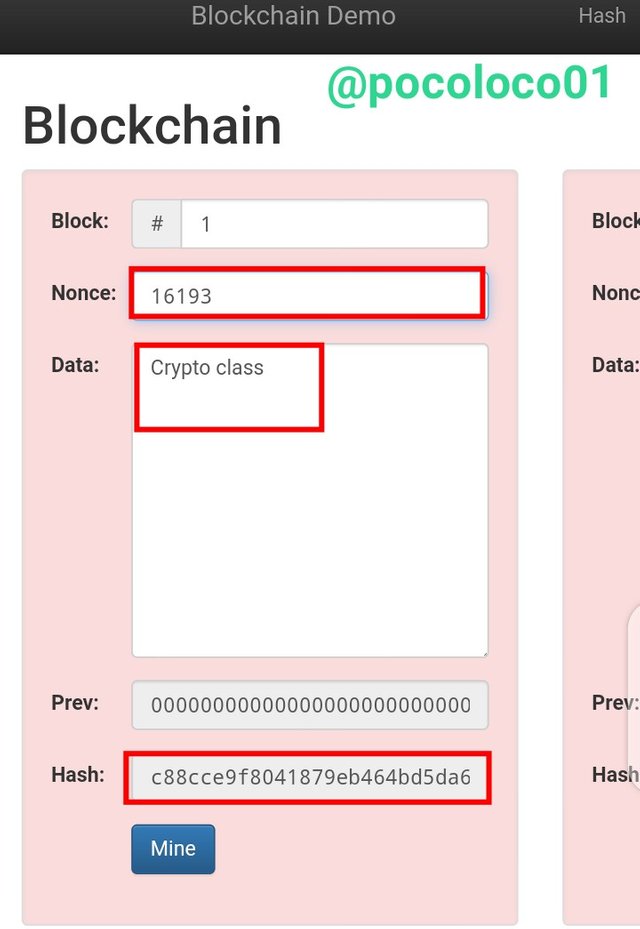 Change Nonce
Change Nonce
So now I try to change the Nonce, I changed the Nonce to 16193 and the colour is still red, that is the block is still invalid since the Hash produced didn't start with zeros.
This is the Hash; "c88cce9f8041879eb464bd5da61a0c462adf49d7db650a76e1d07d699550992a".
From the illustration above, even after changing the Nonce I still didn't generate a valid Hash, as stated earlier to generate a valid block the Nonce must be corrected and linked to a unique hash number and the hash generated must start with zeros.
Mining the Block
Mining refers to the process of validating transactions on the blockchain network this is done using a very powerful computer, these computer solved the mathematical problem to determine the correct Nonce thus validating the block. Not forgetting the Hash of a valid block starts with zeros.
Now taking this to the Blockchain Demo, to get the correct Nonce by changing the Nonce it will take a lot of time, to avoid this,I clicked on Mine, and let's see the result.
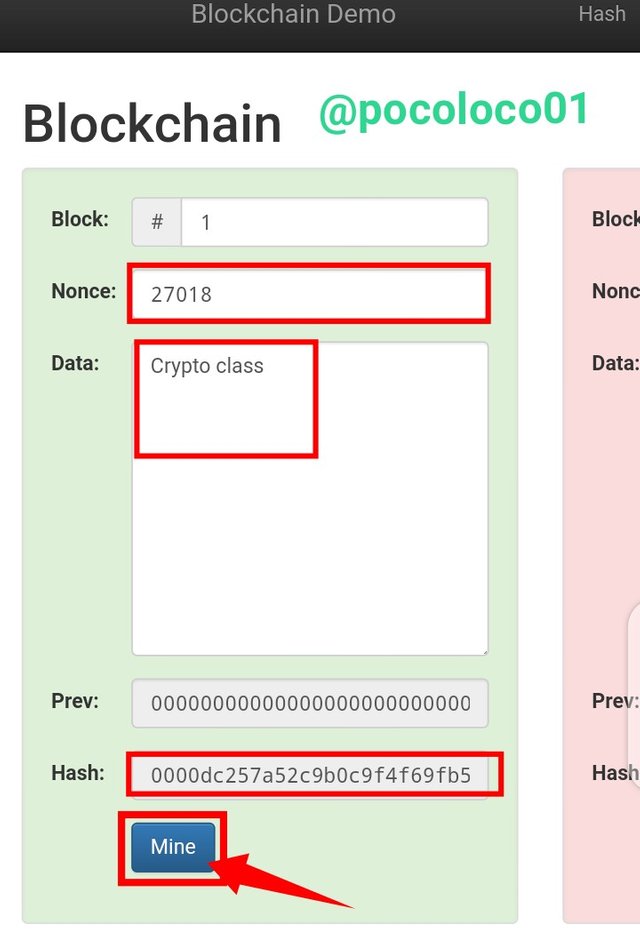 Mine the Block
Mine the Block
By clicking on Mine, I was able to generate a valid Hash, for the "Crypto class" the data I inputted for block 1, also the Nonce 27018 and a Hash "0000dc257a52c9b0c9f4f69fb5cdf925ffeb97410970971fd817e39b1471931a" with green color that is the block is considered valid as the Hash starts with zeros.

What Is Race Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Finney Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Vector76 Attack in blockchain?
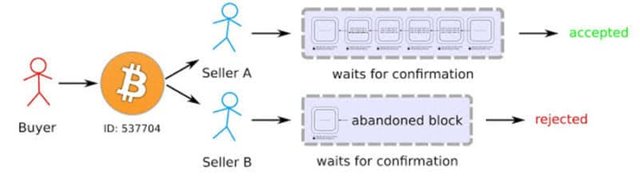
Race attack is a type of double-spending, when an attacker transfers the same token to multiple users within a blockchain using different nodes. This form of attack is most common in buyer-seller transactions, and it is carried out quickly with the goal of purchasing numerous assets with a single token.
Typically, this form of attack is successful. If the attacker initial this attack, the miner will validate one of the transactions and won't validate the others, erasing the invalid transactions from the blockchain. As a result of the double spending attack, the recipient, who must have received an invalid transaction and asset release, has suffered a loss.
Let me illustrate further using an example, if an attacker wanted to buy an asset from two (2) different users, he then send 0.1 BTC to the two (2) user within the blockchain using , the user that released his/her asset without confirming the transaction will be the victim of this attack. If one of the user receives 0.1 BTC , he or she can release the asset to the attacker and the second transaction to the other user will be considered invalid and will be erased.
It's critical to be mindful of such attacks; if you're in a deal with someone, the best method to avoid this type of attack is to wait for confirmation before releasing the asset to the other person.

Limitations/disadvantages of Blockchain
There's nothing perfect, as long as the blockchain has some advantages, there are some disadvantages also.
The Cost Maintenance: the cost of mining and maintaining the process is very high, setting up mining requires a powerful computer, and to maintain these powerful computer is very high not forgetting the energy consuming all this requires a lot of money.
High Transaction Fee: another disadvantages of the blockchain is the the high fee involved in transacting, In the Ethereum blockchain for instance, the transaction fee is very high, performing Transaction on this blockchain is costly irrespective of the amount you want to transfer you need to pay high gas fee.
Scalability: this is one of the disadvantage of blockchain, this issue is seen in some blockchain has the number of participants increased the process of handling numerous transactions will be slow making the the blockchain less scalable.
Irreversibility: the unchangeable property of blockchain precludes data from being changed or altered after it has been recorded. This could be a disadvantage if, for example, a user sends funds to the wrong address due to an error or a lack of patience, since data once recorded in the system is immutable the fund cannot reversed.
Performing Crimes: due to the blockchain's decentralized nature, users can easily transact without the use of an intermediary and without the requirement for KYC verification. This is another downside of the blockchain, as criminals utilize it to conduct illegal transactions such as buying drugs and weapons.

Conclusion
Since its inception, blockchain technology has ushered in a slew of new developments around the globe. Being the basis for the security of cryptocurrencies and their networks.
The blockchain technology is completely decentralized, and the data stored on the blockchain is immutable once it is written it cannot be changed or altered this has added an extra layer of security.
Other notable qualities of the technology, includes decentralization, transparency, and open-source, have been added to its benefits. Despite this, blockchains have some disadvantages or restrictions, such as scalability and slower transactions, but we must keep in mind that this technology is still in its early stages, and many advancements are taking place on the blockchain.
Special appreciation to professor @stream4u for this enlightening lecture.
Hi @pocoloco01
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 8/10
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit