Hello Steemians, I welcome you all to another week in the Steemit Crypto Academy. Today's lesson was delivered by professor @stream4u on "Blockchain". In this post, I will be performing the homework task given at the end of the lesson.


Blockchain
Blockchain can be defined simply to be a string of information or data stored electronically in a database. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology and every node of that network has a copy of the ledger and all information and activities done on the ledger is verified by the connected nodes.
Blockchain is made up of blocks these blocks contain information, transactions data like a digital ledger but in a decentralized system so everyone has access to it, and these blocks are interconnected with similar blocks.
Data stored in a blockchain are secured due to the Hash function that only generates strings of alphanumeric characters instead of the original data and making it very difficult to get the original data from this hash.
Blockchain is the system on which cryptocurrencies are built, the blockchain is set up in 3 parts namely;
Blocks
Blocks can be said to be digital files that hold or contains transactional data of a network, the data stored on these blocks are encrypted and permanently stored and can't be reversed, only copies of this data are sent out to nodes making it a transparent system.
Blocks of different blockchains differ in many aspects like scalability (block size), creation time, etc. But all blocks have some similarities like
- There is data stored on the block
- 32-bit number called a nonce this nonce is generated with a new block.
- A hash is a string of alphanumeric characters that is unique to each block but carries the hash from the previous block to maintain the blockchain.
Nodes
Nodes are computers that mine, update, and validate new blocks. The blockchain system is decentralized hence every and anyone can be a part of it, so all connected nodes get a copy of all transactions done on the blockchain as well as validates all new blocks.
Miners
Miners are individuals in the blockchain network that validate transactions and mine new blocks to the blockchain. Miners race each other to decode the encrypted data to do this the use of high-powered computers is employed. Miners get rewards for creating blocks and confirming transactions.
Types of Blockchain
There are 4 main types of blockchains namely;
- Public Blockchain
- Private Blockchain
- Consortium Blockchain
- Hybrid Blockchain
Each of the 4 types of blockchain is used for different purposes with benefits and limitations. The 4 types of blockchain are explained below.
Public blockchain
This is a type of blockchain that is open to every and anyone with no restriction or permission needed to join. A public blockchain is highly decentralized as everyone has the right to read, write and indulge in all activities in this network as transactions can not be altered by anyone. This type of blockchain is used in the creation of cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and Ethereum, and can also be used as a voting platform.
Benefits of Public Blockchain
- Open to every and anyone as no specific permission is needed to join.
- Highly decentralize as nobody has control over the network and activities on the network is open to everyone
- The public blockchain is very secured as no one can alter transactions done
- The anonymity of members is ensured. Identification is not required to join a public blockchain.
- Public blockchains gives complete transparency as all transactions performed are open to all
Limitations of Public Blockchain
- Consumes lots of energy to mine a block. Making it very expensive and also causes harm to the environment
- Slow when compared to other systems, bitcoin can only process 7 transactions per second compared to the visa that can process 24,000 transactions per seconds
- The scalability of the public blockchain has been an issue has more transaction needs to be saved in one block.
Private Blockchain
Private blockchain or permissions blockchain is a blockchain that requires permission before gaining access to the network. Used in the corporate and business world examples of the private blockchain are ripples and hyper-ledgers. Identification is required to access the network. There are rights and restrictions issued to specific members of this network.
Benefits of Private Blockchains
- It is fast and has fewer people on the network
- There is no place for dispute that can lead to a hard fork as there are people in charge of decisions unlike the public blockchain where everyone has a right and access to all activities on the network
Limitations of Private Blockchain
- It is not a truly decentralized network as there is a semblance of control on the network. Rights and access are given to selected nodes not everyone
- Security and trust are of great concern with the private blockchain. Trust that the nodes with access to perform activities are credible enough. Security since the nodes on the network is considerably less it is easier for hackers to get control over it like a 51% attack
- There is no anonymity on the network. Every member of a private blockchain identity is known as access has to be granted specifically to join the network
Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchain also known as Federated Blockchain is a permission-based network where nodes require access to be a part of it but is governed by different bodies or organizations. The consortium blockchain is similar to the private blockchain in that there needs to be access given to join the network but unlike the private network where the decisions made on the network are centralized the different organizations that govern the network can make decisions. This type of blockchain helps businesses interact with one another with no one having control.
Benefits of the Consortium Blockchain
- It takes up little energy to mine when compared to the public blockchain.
- In as much as it shares a lot of similarities with the private blockchain it is a centralized system as decisions made on the network are not controlled by one body.
- There is little to no fees for transaction on this network.
- it has a fast transaction time as access to activities is assigned. Meaning there are fewer persons performing transactions on the network.
Limitations of Consortium Blockchain
- No privacy as identification is part of this blockchain because to join you have to be given access
- Still centralized when compared to the public blockchain as access is still restricted and decisions made on the network is not open to all
Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchain can be defined as the mix of both public blockchain and private blockchain. It is the ideal blockchain as it gives the freedom of the public blockchain and the control of the private blockchain. The hybrid blockchain members decide who gains access to the blockchain but the activities on the blockchain are open to all as everyone has equal rights.
Benefits of Hybrid Blockchain
- Transactions are not open to the public only to those on the network.
- Security is guaranteed and there are no trust issues as every transaction is open to all members of the network
- Transaction cost is low on this network
- They are a perfect fit for a lot of industry as it tackles flaws from both the public and private blockchains.
Limitations of Hybrid Blockchain
- it is not truly decentralized. Not everyone has access to it and there's a bit of control over the network

Benefits of Blockchain
Blockchain has a lot of benefits, has it helps to tackle different issues in different areas of life. Examples of such benefits are:
Security
Transactions done on a blockchain network are secured from hacks as the data is stored on different nodes, not a particular server or database, and will require 51% of the node's computing power to verify any transaction
Immutability
Transactions done are permanent and can not be altered by anyone. Meaning duplicate transactions can not be verified and all transactions verified transactions cannot be reversed
Decentralized Structure
Activities on a blockchain are open to all and void from control from any entity ensuring trust and transparency have all activities are open to the public. Decision-making on the blockchain network is open to all active members.
Transaction Costs
Transaction cost on the blockchain network is way cheaper when compared to conventional methods. For instance, if I am to transfer money between 2 international banks the cost will be outrageous depending on the volume also but I can make a billion-dollar transaction on a blockchain network for little to no cost.

Explain Blockchain Distributed Ledger.
Blockchain distributed ledger is the distribution or sharing of databases across different nodes or computers. It allows for decentralization as every connected node owns a copy of every transaction carried out on the blockchain network and can verify and read all transactions.
Every update and modification done on the blockchain distributed ledger is received by all connected nodes almost at an instant.
Unlike the conventional centralized ledgers that store information in a database making it prone to a cyber attack the distributed ledger accurately stores this information across all connected nodes making it harder to hack as the information is encrypted increasing the security and are immutable meaning, it can't be changed or reversed.
Uses of Blockchain Distributed Ledger
Blockchain distributed ledger can be used in different sectors of life. Most notably in finance with inventions like bitcoin, ethereum and ripple built using this technology, the way money will be processed/transacted going forward has been revolutionalized. Blockchain distributed ledger can be used in government for situations like voting and issuance of passports.
Benefits of Blockchain Distributed Ledger
Security; in a blockchain distributed ledger data stored are highly secured as they are immutable and shared among members of the network and stored reducing the possibility of a hack.
Transparency; all data stored on the blockchain distributed ledger is open to all nodes to verify and read. Making the transactions done transparent
Privacy; the information present and stored on a blockchain distributed ledger is encrypted creating anonymity in the network. Plus identity is not always when joining a blockchain network
Immutability; all verified transaction data stored in the blockchain distributed ledger can not be reversed or changed as it is permanent

What is Blockchain Double Spending
Blockchain double spending is the theft of digital assets in the blockchain, when a transaction is verified twice, or in simpler words when a digital asset like bitcoin is spent more than once then double-spending has occurred.
Double spending occurs when the blockchain network has been manipulated into verifying transactions already made as new.
Double-spending is similar to counterfeit money for physical cash. It is the clone of the original, this hurts the network and devalues the digital currency.
Types of double-spending include; Race attack, Finney attack, and Vector76 attack.
How Bitcoin Handles Double Spending
Bitcoin uses a consensus mechanism when verifying transactions done on the network. That is to say for a transaction to be verified it must have at least a 51% verification from the connecting nodes to be confirmed. All transactions are timestamps increasing the difficulty to manipulate the blockchain.
This makes it extremely difficult for anyone to double-spend as they will need an insane amount of computing energy to confirm both transactions as legit. In blockchain also the longest string is considered the right string so for any transaction to be considered confirmed the hacker needs to create more blocks in that direction which is very difficult.
To explain better here is an analogy. Mr hacker has 1BTC and wants to double-spend, these two transactions are seen as unconfirmed transactions. The connecting nodes will verify one of the two transactions and will leave the second transaction as unconfirmed for Mr hacker to confirm the second transaction he has to have a computational energy equivalent to 51% of all connecting nodes to confirm the second transaction. In a scenario where he can confirm the second transactions he has to confirm more blocks in the direction of that transactions to make it valid, this is because blockchain considers the longest string the right string. This is why many bitcoin traders wait for at least 6 confirmations to accept a transaction.

Exploring Blockchain Demo
A blockchain hashing is the act of converting block data into a hash. A hash converts input or data of arbitrary length into a fixed length of alphanumeric characters. To fully have an understanding of how blockchain hashing occurs we will visit the blockchain demo site.
Hash

When we input data on the hash REMINISCENCE01 on the SHA256 a hash is generated.
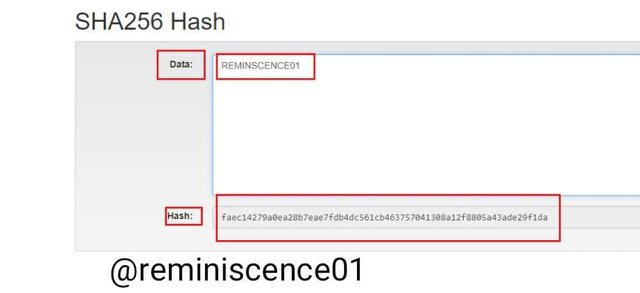
The hash generated for REMINISCENCE01 is efa05012b5b27f683d4fc6d2b58438d55846fbea61f92396b0fa20637cb87333
Any change on the data inserted creates a different hash, even if it is a change in the case of the same data
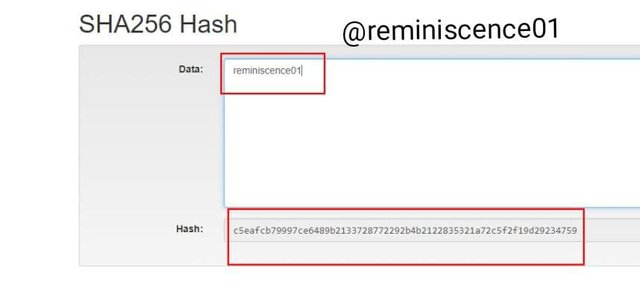
The hash generated for the data reminiscence01 is
c5eafcb79997ce6489b2133728772292b4b2122835321a72c5f2f19d29234759.
Block
Then we look at the block. The block contains the block number, Nonce, data, and the hash. A valid block hash starts with 0000, as shown below
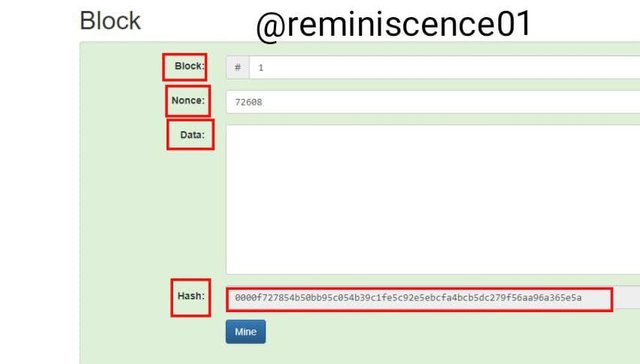
Any change made to the block changes the hash and invalidates it. To validate the block, there needs to be a change in the nonce. This could be a stressful and long process.
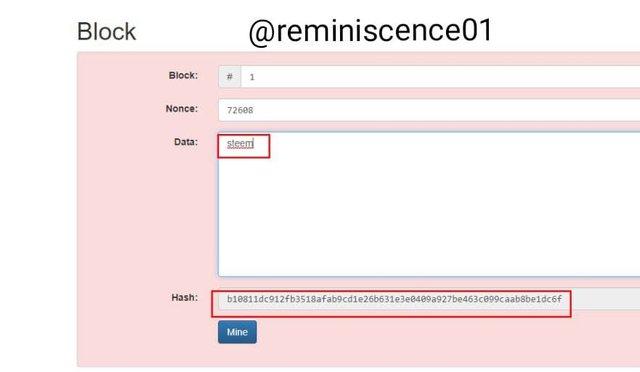
To find the right nonce for this block I click on the mine button that helps find the right nonce that suits the data to get a valid block. As shown below
Blockchain
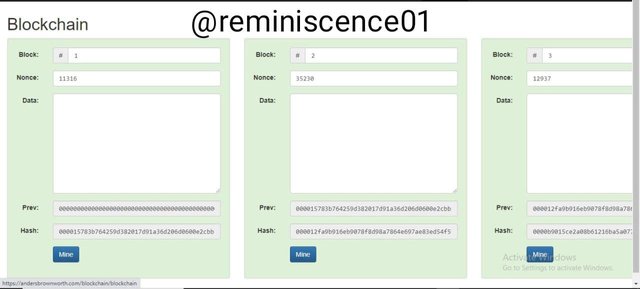
How Hash Works in Blockchain
Every block in a blockchain needs the hash of the previous block to validate the new block as shown below
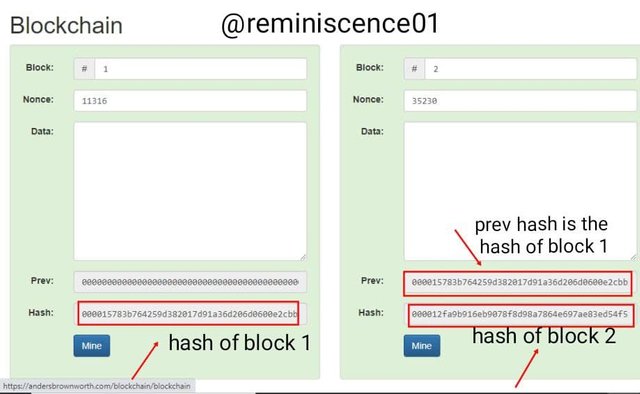
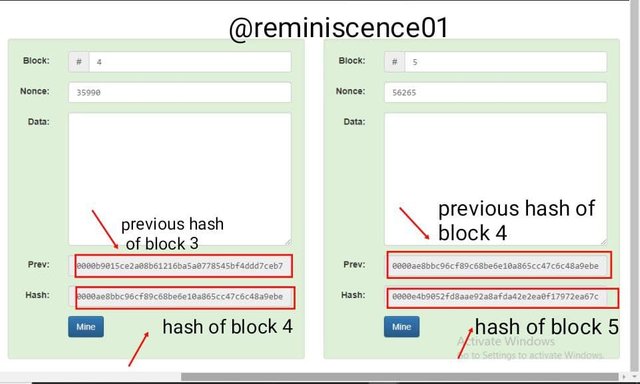
The hash of block 2 has the hash of block 1 has its previous hash
000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf
The hash of block 3 has the hash of block 2 has it previous hash
000012fa9b916eb9078f8d98a7864e697ae83ed54f5146bd84452cdafd043c19
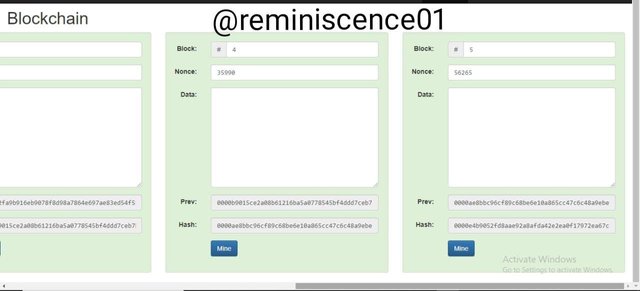
This trend goes on to the last block where the hash of block 5 has the hash of block 4 has its previous hash
0000ae8bbc96cf89c68be6e10a865cc47c6c48a9ebec3c6cad729646cefaef83
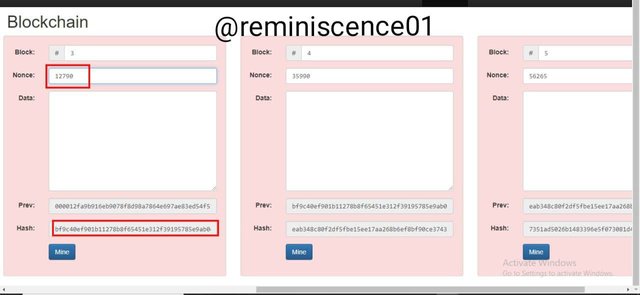
what will happen when any middle of the block gets changed
Every block in a blockchain is validated by the previous block, so any change made in the middle of the blockchain will affect all blocks succeeding it.
An example shown below is when a change was made to the nonce number of block 3 the succeeding blocks 4 and 5 became invalid.

What Is Race Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Finney Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Vector76 Attack in blockchain?
Race Attack in Blockchain
A race attack is an attack that occurs when a hacker performs 2 transactions with different nodes to 2 different users, with the hope that the first user accepts the transaction without confirming it. When this happens the unconfirmed transaction is returned to the attacker as a conflicting transaction is sent to the network which makes the first transaction invalid.
An instance is when a hacker tries to pay for goods worth 1BTC from two different vendors having just 1BTC but initiates the transactions using different nodes at the same time. If any of the vendors accept the transaction without waiting for confirmation from the blockchain he stands a chance of losing his goods has only one of the transactions will be confirmed and the second transaction termed invalid.

Limitations of Blockchain
- Scalability
The blockchain network can get congested with the transaction and this will lead to transactions taking hours to get confirmed, unlike the conventional network where a bunch of transactions can be confirmed at once.
- Consumes so much energy
Most blockchain runs on an algorithm called proof -of -work where lots of energy is consumed in the mining of blocks,
- Blockchain is immutable
As much as this good be an advantage it is also a disadvantage as all error transactions can no be reversed or changed. Meaning any loss incurred in transactions in the blockchain network is permanent
- Cost
The cost of setting up a blockchain is much. The amount of energy consumed by a supercomputer with high computational power in mining blocks in a blockchain is expensive.

Conclusions
Blockchain is a technology that allows for decentralization whereby all activities or transaction done on the network is transparent to all and the verification of the transactions is performed by everyone connected to the blockchain network called nodes. Blockchain gives high security, anonymity, and freedom from centralization to its users
Thank you Professor @stream4u for this amazing lesson.
Hi @reminiscence01
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 9/10
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hello professor @reminiscence01 this is my entry link for introductory course task 2
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hello professor @reminiscence01 this is my entry link for introductory course task 3
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hello professor @reminiscence01 this is my entry link for introductory course task 5
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hello professor @reminiscence01 this is my Entry link to task 6 of the introductory post
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Respected Professor, Here is My Task5 please give me marks,
https://steemit.com/hive-108451/@naveed15125/crypto-academy-season-3-beginners-course-task-5-dex-cex-popular-exchanges-and-trading-cryptos-or-naveed15125
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Exercise patience. Your task will be reviewed.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks dear respected professor
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit