 |
|---|
INTRODUCTION |
A blockchain like a cake is made up of layers. Just like the cakes, we add more layers to make it even more attractive and functional. These additional layers in blockchain add extra features to the technology. So let's learn about layer 2 then, shall we?
What is layer 2 in a blockchain and how does it differ from layer 1? |
|---|
As always, we will be looking into the literary meaning to draw our inspiration, hence in this case, what is a layer or layers?
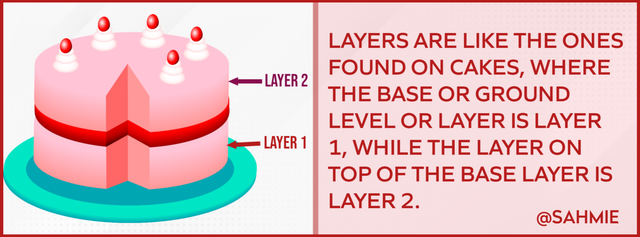
A layer, according to Dictionary is something lying over or under something else; I.e. a level or tier. E.g. our birthday cakes, which usually come in layers or levels.
This week, our discussion is centered on a different type of layer, the type found on blockchains and not cakes, however, we can still borrow the literary meaning to bring about emphasis.
The layers of blockchain technology like the birthday cake example where different layers are piled on top of each other, are blocks of information linked together to build a chain. The layers of a blockchain include;
- Layer 1 (protocol layer) and,
- Layer 2 (application layer)
- Layer 3
Where, we'll be looking into two types, layers 1 and 2.
 |
|---|
Layer 1 (the protocol layer);
Also known as the main or base layer, is the foundation of the blockchain, i.e. the ground level of the birthday cake that holds the other layers above. The base layer includes core functionalities like consensus mechanisms, cryptographic algorithms, and validation rules that ensure the security and integrity of the blockchain network.
Examples of Layer 1 blockchains include the likes of Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano, Binance smart Chain, Solana, etc. In Layer 1, every transaction is recorded on the main blockchain, and all participants in the network validate and store these transactions. This ensures security and decentralization but can lead to scalability issues because Layer 1 blockchains have limited transaction processing capacity and can become slow and costly when there's high demand.
Layer 2 (application layer);
Layer 2, like the cake example I gave earlier, is found on top of Layer 1 (the base layer). Layer 2 is where developers and users build and interact respectively with different decentralized applications (DApps) of the underlying layer of the blockchain.
Layer 2 solutions provide different solutions or protocols that help process transactions off-chain from the main chain or base layer, thereby reducing the workload on the base layer.
These layers work together to enable the functionality and usability of the blockchain. However, there are differences between these two layers, these differences include;
| Category | Layer 1 | Layer 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Is known to have limited scalability, as it can run only a certain number of transactions per second. | Helps increase the scalability by processing a large number of transactions off-chain, allowing for faster and more efficient transaction processing. |
| Speed and Cost | Can be slow and costly due to the need for consensus among all participants. | Makes the process faster and cheaper as it handles a larger volume of transactions without overloading the main blockchain. |
| Use Cases | Is used by applications that require the highest level of security and trust, such as financial transactions and smart contracts. | Are often used for applications that require high scalability, such as micropayments, gaming, and decentralized exchanges. |
| Security | It's considered to be more secure because it has a strong encryption protocol, hash functions, and consensus mechanisms that protect the integrity and stability of the network. | solely relies on the security of the underlying Layer 1 blockchain. |
| Decentralization | Are more decentralized, as they operate without any central authority or control. | Are often centralized or semi-centralized as they require a central authority to manage and validate transactions. |
| Fees | Requires users to pay transaction fees to validate a transaction on the network, which is often high due to the limited capacity of the network. | Provides a more cost-effective solution for users, as they can handle a larger number of transactions at a lower cost. |
Give real-world examples of Layer 2 solutions and explain how they work. |
|---|
There are several types of Layer 2 solutions, including:
- Lightning Network
- Raiden Network
- Plasma
- State Channels
- Sidechains
- Rollups
Lightning Network:
The Lightning Network is a Layer 2 solution for Bitcoin that enables faster and cheaper transactions by creating off-chain payment channels. It allows users to open payment channels between each other and conduct multiple transactions without having to record each one on the main Bitcoin blockchain. This helps reduce congestion and fees on the main chain.
A real-world example of a lighting network application would be creating a payment channel between two users, let's say friends who frequently go out for dinner and split the bill.
With the Lightning Network solution, they can open a payment channel between themselves so that every time they go out, they can instantly settle the bill by updating the payment channel without waiting for confirmations on the main blockchain, which in turn helps them save time and reduce transaction fees.
Raiden Network:
Raiden Network, on the other hand, is a Layer 2 solution specifically designed for Ethereum. The Raiden network operates in a similar way to the Lightning Network, as it allows users to create payment channels and conduct off-chain transactions, to improve the scalability and speed of the Ethereum network.
The Raiden network comes in handy when a user wants to trade ERC-20 tokens frequently with a friend. With the Raiden network, instead of executing each trade on the main Ethereum blockchain, which can be slow and expensive, the user can open a payment channel, and conduct multiple token transfers instantly and with minimal fees. Once the trading is done, the outcome is then settled on the main Ethereum blockchain.
Plasma:
Plasma is a framework that enables the creation of child chains or "plasma chains" connected to the main blockchain. It helps to scale the blockchain by processing transactions on these child chains and periodically submitting a summary to the main chain.
State Channels:
These are off-chain channels where participants can conduct multiple transactions without involving the main blockchain. The outcome is then settled on the blockchain, reducing congestion and increasing transaction speed.
Sidechains:
Sidechains are separate blockchains that can be operatable with the main blockchain. They allow for faster processing of transactions and can have their consensus mechanisms and rules. This way, assets can be moved between the main chain and side chains.
Rollups:
Rollups are Layer 2 solutions that bundle multiple transactions together and submit a single summary to the main blockchain. This reduces the computational load on the main chain while maintaining the security and decentralization of Layer 1.
How does layer 2 help reduce transaction fees on a blockchain and facilitate interoperability between different blockchains? |
|---|
From the first hint, where we were asked to give the differences between layers 1 and 2, I already gave a brief report on how layer 2 brings about less transaction fees, so how does layer 2 achieve this? Here is how.
Layer 2 solutions help reduce transaction fees by moving some of the transactions away from the main blockchain (layer 1), where fees can get pretty high. This is achieved by creating off-chain networks, such as payment channels or sidechains so that users can carry out multiple transactions without disturbing or interfering with the main chain with all the required details.
This in turn helps reduce the main blockchain congestion and, in turn, lowers transaction fees. This is likened to taking a shortcut to get your transactions done faster and at a cheaper rate.
 |
|---|
Interoperability is all about two different blockchains working together effectively, hence to bring about interoperability between different blockchains, Layer 2 solutions act as a bridge between these different blockchains, allowing the different blockchains to communicate and work together. With Layer 2 solutions serving as a universal translator or a mediator (middle man) between blockchains to help the different blockchains understand each other and work together effectively.
For example, with technologies like atomic swaps or cross-chain bridges which are layer 2 solutions, we get to transfer assets or tokens from one blockchain to another.
What is the underlying layer used by the Steem blockchain, and how does this layer facilitate transactions and interactions on the platform? |
|---|
From the Steem Whitepaper, I'm made to understand that the Steem blockchain is built on a technology called GRAPHENE as its underlying layer. Hence, the base layer (layer 1) of the STEEM Blockchain, the foundation or the building blocks of the STEEM Blockchain is GRAPHENE.
GRAPHENE is a powerful and efficient framework that ensures transactions and interactions on the platform are carried out smoothly and quickly.
 |
|---|
the STEEM blockchain uses GRAPHENE to help deal with the large number of transactions carried out per second, as graphene is estimated to scale up to 10,000 or more transactions per second. Helping the STEEM blockchain to process a high number of transactions and posts quickly.
GRAPHENE also employs a decentralized and democratic system of governance on the STEEM blockchain, as it uses a consensus algorithm known as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) where users of the Steem blockchain are allowed to vote for "WITNESSES", who help to validate and secure the blockchain, conveying transparency, security, and resistance to centralization of the platform.
 |
|---|
While also using a Bandwidth model over micropayments as with the Bandwidth model the blockchain automatically adjust the reserve ratio for the network during times of congestion, thereby improving scalability.
What would be the implications of integrating a layer 2 solution on the STEEM blockchain in terms of scalability, costs, and ease of use for users? |
|---|
Integrating Layer 2 solutions on the Steem blockchain will undoubtedly bring some excitement to the Steem blockchain in areas of scalability, costs, and ease of use for users. Here, let me explain how;
In terms of Scalability:
With Layer 2 solutions, the scalability of the Steem blockchain will improve by taking me of the transaction workloads off the main chain, which will help reduce transaction process time and allow for a larger number of transactions to be carried out at a time, meaning that more users can interact with the platform without experiencing delay.
In terms of Costs:
Layer 2 solutions when integrated can help reduce the transaction costs on the Steem blockchain by offloading some of the transaction processes to the Layer 2 network, helping to decrease the load on the main chain and lowering the fees associated with transactions.
In terms of Ease of Use:
Integrating a Layer 2 solution into the Steem blockchain can improve the overall user experience on the Steem platform. With faster and cheaper transactions, users can interact with the platform freely. This way, users get to post content, engage with others, and transfer tokens without worrying about high fees or long confirmation times.
CONCLUSION |
In conclusion, blockchain layers are like building blocks that make the technology even more powerful and versatile. Layer 1 forms the foundation, while Layer 2 and Layer 3 add scalability, speed, and interoperability. This multi-layered approach allows for exciting possibilities in terms of transaction execution, smart contracts, and cross-chain communication.
I wish to invite @starrchris, @yancar, @ngoenyi and @suboohi
Thank You for your Time
NOTE: Always have a smile on your face, as you are never fully dressed without one.

Hola amigo, como siempre has dado cátedra en el conocimiento de la materia, lo que me alegra mucho por ser una buena referencia comparativa y de conciliación de las ideas. Es muy didáctica tu analogía de las capas con el pastel, siendo una manera fácil de comunicar algo que resulta muy técnico.
Resalto la interoperabilidad de estas dos blockchains que siendo diferentes se integran para trabajar juntas como lo haría un equipo que aprovecha las capacidades individuales para el bienestar común. Creo que esta capacidad de interactuar abre las puertas para la evolución de la blockchain en general.
Saludos y muchos éxitos.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hey there, greetings friend, the reason I love the cryptoacademy challenges is that it gives me the opportunity to sometimes learn new things I've never even heard before. The real challenge becomes trying to pass down the message of what I've learned, what better way to learn if not the one of trying to explain and pass the message across in a way everyone can understand? This was the reason why I used the cake like every other week where I get to search for something common among us to explain the lessons learnt after my research. Thank you for your time and this encouraging comment, stay blessed.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Saludos y buena suerte, amigo.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Greetings brother.
I always love your content because you always try to elaborate every concept in well detailed manner. I really liked the images which you have created on Pixel Lab. These images act as examples to explain about these topics and these images helps in understanding about these topics.
You really have explained every topic in your own words and It will really help every user here in learning about Layer 2 Blockchain.
Best of Luck for the contest.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Greetings brother, thank you for your support and encouraging feedback, with such comment, I am encouraged to do my best as always.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you, friend!


I'm @steem.history, who is steem witness.
Thank you for witnessvoting for me.
please click it!
(Go to https://steemit.com/~witnesses and type fbslo at the bottom of the page)
The weight is reduced because of the lack of Voting Power. If you vote for me as a witness, you can get my little vote.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
You have written an in-depth article about blockchain layer. Example of cake layers explained in a very easy way. Thanks for sharing an informative article.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you for your kind words and support.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Fantastic breakdown of Layer 2 in blockchain! Your use of the cake analogy made it super easy to understand the complex concept. The real world examples like Lightning Network & Raiden brought it all to life. i appreciate how you explained how Layer 2 reduces transaction Fees and promotes interoperability making it all Sound like a breeze . your insights on the Steem blockchain and The potential integration of Layer 2 solutions were insightful. Wishing you the best of luck ! Your post deserves all the success it can get! 🚀✨
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you brother for this kind gesture of leaving such as a heartfelt comment, like you, I'm always intrigued with the features and protocols that springs up and I hope to keep learning everyday.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Saludos gran amigo sahmie.
Muchas gracias por la invitación a este reto, es siempre grato leer tus excelentes participaciones.
Las Blockchain de capa 2 vienen a resolver problemas que posees las Blockchain de capa 1, muchas veces dan escalabilidad y velocidad a estos ecosistemas, por lo tanto, son soluciones muy factibles.
Te deseo muchos éxitos, feliz y bendecido día.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you brother for you heart warming contributions, I feel honoured.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
That's very much informative post by your side on the Layer 2 and it's usage. I really liked the example of Cake for layer 1 and 2. I used the flyover example, and the house building example for this.
This is the big benefit for users in my thinking, they can get transactions done, fast with lower cost of fee.
With so many types of layer 2 you expanded the post for more and more. Specially the "Raiden Network" which is workings like state channels I think.
This is new to me that Graphene can deal estimated of 10,000 transactions per second. That's amazing"osouras.'
Overall I really appreciate your very much time in researchings, the post was indeed very much knowledgeable for me.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I'm hoping you did a good job too. It was a long read, therefore I say thank you for taking your time to go through the process. Thank you mate
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Great job! Everything is accessible and understandable!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hello Sahmie Friend,
This time, you have really impressed me a lot with a quite different and perfect explanation of the said topic. Layer 2 solutions are really great innovations in the Blockchain technology.
The main gain of the layer 2 is that the transaction speed of the main chain can be improved much as the transactions load is removed from the main chain and processed on the other layer.
A well explained and well presented article, thanks for sharing and great luck with this masterpiece 🤞
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
You've summarized a post of 2000+ words in a very concised and accurate way. That explains how well informed you are on these topics. Thank you for leaving such a wonder comment.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Graphene on which steem Blockchain is built is very robust. With it, layer 2 protocols can easily be added to the steem main chain. It s modularity makes it the toast of developers. And like is emphasized on the whitepaper, any additional infrastructure will move steems scalability to the next level.
Thanks for such educative writeup.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Greetings ma, the steemit platform seems to run on a reliable underlying layer in Graphene, allowing users to post, re-steemit, upvote and comment effortlessly. Therefore, it is indeed a great underlaying layer. Thank you for your time and the wonderful feedback.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit