This is Season 3 Week 4 of Steemit Crypto Academy and I'm writing Homework Task for Professor @pelon53

1)
Explain in detail the hash rate.
The hash:
A hash is a set of code consisting of a combination of alphabets and numbers. It has a fixed length. It is used to represent any message, information, data of any length. These hash codes are commonly used in the crypto ecosystem to code information. Crypto developers use different hashing algorithms to create hashes. The hashes can be thought of as random word combinations and the hashing algorithms as systems which set design these random words.
In the crypto world to add new data or to add a new block to the blockchain the miners have to first solve a set of mathematical expressions. The miners usually compete to guess these codes using computation power. These miners are in actuality trying to create a hash that is lower than or equal to the numeric value of the target hash by trying alternatives of a single value called nonce.
This can take millions of guesses as every hash is unique. The winner is the one who guesses it right and gets the right to add the new block in the blockchain. The miner is then rewarded with the block reward of newly minted coins along with the fees of the transactions stored on the block. Adding the block to the blockchain confirms all the transactions associated with the block.
Hash rate
Hash rate is the measure of total computational power that is being used to mine and process transactions on a network. It is an important way of assessing the strength of a blockchain network. The more the computers use their computation power to mine the next block the higher the hash rate and harder it will be to mine the next block due to more competition.
The hash rate of a machine can be calculated by assessing its ability to generate the number of hashes in a second.

2.1)
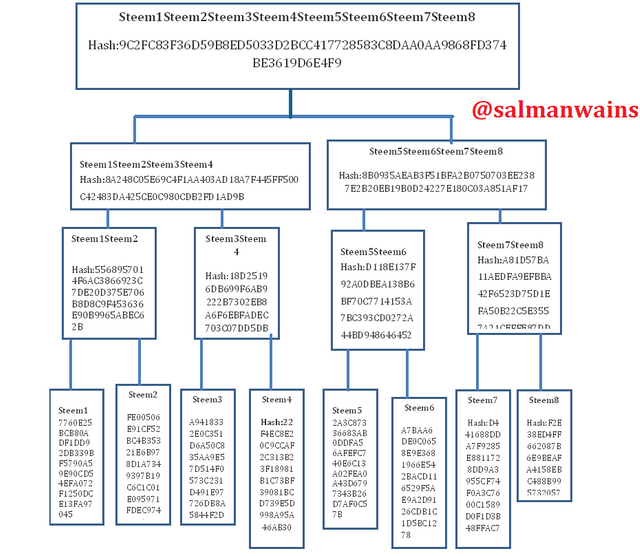
Make the following Merkle Tree:
Transaction (tree leaves): Steem1; Steem2; Steem3; Steem4; Steem5; Steem6; Steem7; Steem8.
A Merkle Tree can be formed in three simple steps
- Calculating the hashes for the leaves
- Calculating the hashes for the branches
- Calculating the root hash
Tree leaves hash
We always begin from the bottom and therefore we first calculate the hashes of the leaves
Steem1
Hash:7760E25BCB80ADF1DD92DB339BF5790A59E90CD54EFA072F1250DCE13FA97045
Steem2
Hash:FE00506E91CF52BC4B35321E6B978D1A7349397B19C6C1C01E095971FDEC9741
Steem3
Hash:A9418332E0C351D6A50C835AA9E57D514F0573C231D491E97726DB8A5844F2DC
Steem4
Hash:22F4EC8E20C9CCAF2C313B23F18981B1C73BF39081BCD739E5D998A95A46AB30
Steem5
Hash:2A3C87336683AB0DDFA56AFEFC740E6C13A02FEA0A43D6797343B26D7AF0C57B
Steem6
Hash:A7BAA6DE0C0658E9E3681966E542BACD116529F5AE9A2D9126CDB1C1D5BC1278
Steem7
Hash:D441688DDA7F9285E8811728DD9A3955CF74F0A3C7600C1589D0F1D3B48FFAC7
Steem8
Hash:F2E38ED4FF662087B6E9BEAFA4158EBC488B995732057BDA019A6A77FFB5F9F5
Tree branches hash
In branches we have First level hash branching and second level hash branching.
Steem1Steem2
Hash:5568957014F6AC3866923C7DE20D375E706B8D8C9F453636E90B9965ABEC62B
Steem3Steem4
Hash:18D25196DB699F6AB9222B7302EB8A6F6EBFADEC703C07DD5DB8D9455913A499
Steem5Steem6
Hash:D118E137F92A0DBEA138B6BF70C7714153A7BC393CD0272A44BD94864645224B
Steem7Steem8
Hash:A81D57BA11AEDFA9EFBBA42F6523D75D1EFA50B22C5E3557A21CEFFE87DDFC4A
Second level hash branching
Steem1Steem2Steem3Steem4
Hash:8A248C05E69C4F1AA403AD18A7F445FF500C42483DA425CE0C980CDB2FD1AD9B
Steem5Steem6Steem7Steem8
Hash:8B0935AEAB3F51BFA2B0750703EE2387E2B20EB19B0D24227E180C03A851AF17
Root hash
Steem1Steem2Steem3Steem4Steem5Steem6Steem7Steem8
Hash:9C2FC83F36D59B8ED5033D2BCC417728583C8DAA0AA9868FD374BE3619D6E4F9
The Merkle tree

2.2)
Verifying if hash of steem6 is added in the Merkle Tree
To verify we need to know the followings
Hashes of
- steem5
- Steem7Steem8
- Steem1Steem2Steem3Steem4
Procedure:
- The first Step is to calculate the hash of Steem6
- As we know the hash of Steem5 we can calculate the hash of Steem5 and Steem6.
- After we have found the hash Steem5Steem6 and the hash of Steem7Steem8 is known
- We can find the hash Steem5Steem6Steem7Steem8
- As we already know the Steem1Steem2Steem3Steem4
- We can calculate the hash of Steem1Steem2Steem3Steem4 and Steem5Steem6Steem7Steem8 to find the root hash
- Which is Steem1Steem2Steem3Steem4Steem5Steem6Steem7Steem8
If the root hash found now is the same as we found previously than it is verified that Steem6 is included in the Merkel tree

3.1)
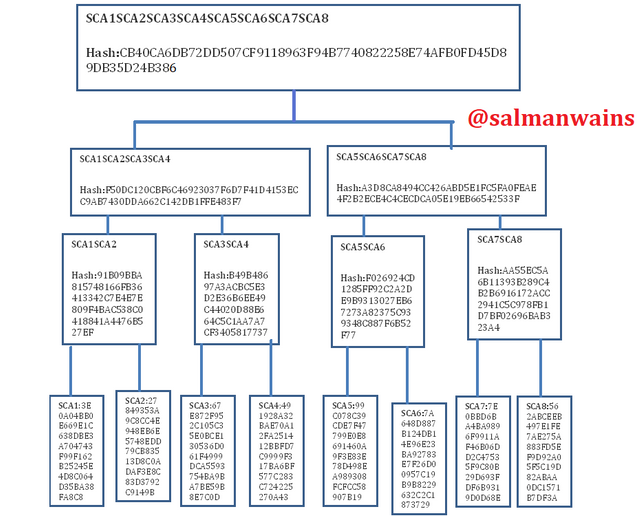
Using the SHA-256; you must place each complete hash in the Merkle Tree.
Transaction (tree leaves): SCA1; SCA2; SCA3; SCA4; SCA5; SCA6; SCA7; SCA8. Explain each step, show screenshots.
A Merkle Tree can be formed in three simple steps
- Calculating the hashes for the leaves
- Calculating the hashes for the branches
- Calculating the root hash
First of all we will calculate the hashes for the leaves
Hash Leaves
SCA1
Hash:13E0A04BB0E669E1C638DBE3A704743F99F162B25245E4D8C064D35BA38FA8C8
SCA2
Hash:27849353A9C8CC4E948EB6E5748EDD79CB83513D8C0ADAF3E8C83D3792C9149B
SCA3
Hash:67E872F952C105C35E0BCE130536D061F4999DCA5593754BA9BA7BE59B8E7C0D
SCA4
Hash:491928A32BAE70A12FA251412BBFD7C9999F317BA6BF577C283C724225270A43
SCA5
Hash:99C078C39CDE7F47799E0E8691460A9F3E83E78D498EA989308FCFCC58907B19
SCA6
Hash:7A648D887B124DB14E96E23BA92783E7F26D00957C19B9B8229632C2C1873729
SCA7
Hash:7E0BBD6BA4BA9896F9911AF46B06DD2C47535F9C80B29D693FDF6B9319D0D68E
SCA8
Hash:562ABCEEB497E1FE7AE275A883FD5EF9D92A05F5C19D82ABAA0DC1571B7DF3AD
Then we will calculate the branches
Branches hash
SCA1SCA2
Hash:91B09BBA815748166FB36413342C7E4E7E809F4BAC538C0418841A4476B527EF
SCA3SCA4
Hash:B49B48697A3ACBC5E3D2E36B6EE49C44020D88E664C5C1AA7A7CF34058177379
SCA5SCA6
Hash:F026924CD1285FF92C2A2DE9B9313027EB67273A82375C939348C887F6B52F77
SCA7SCA8
Hash:AA55EC5A6B11393B289C4B2B6916172ACC2941C5C978FB1D7BF02696BAB323A4
The second branch hashes
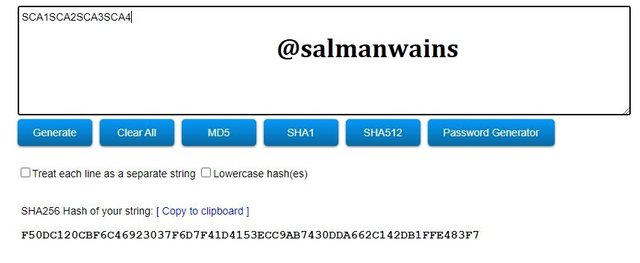
SCA1SCA2SCA3SCA4
Hash:F50DC120CBF6C46923037F6D7F41D4153ECC9AB7430DDA662C142DB1FFE483F7
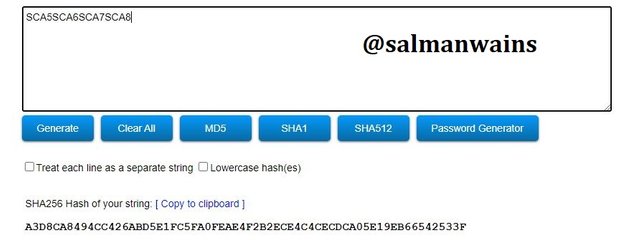
SCA5SCA6SCA7SCA8
Hash:A3D8CA8494CC426ABD5E1FC5FA0FEAE4F2B2ECE4C4CECDCA05E19EB66542533F
The final step is to calculate the Root hash
Root Hash
SCA1SCA2SCA3SCA4SCA5SCA6SCA7SCA8
Hash:CB40CA6DB72DD507CF9118963F94B7740822258E74AFB0FD45D89DB35D24B386
The Merkle Tree

3.2)
If the number of leaves on the tree is odd, what should you do? Explain.
In order to reach a valid root hash it is important that you have an even number of leaves. This is the general rule on the basis of which the Merkle Tree is designed. In any event where we have an odd number of leaves they should first be converted by any means into an even number.
The most practical way of doing so is to repeat the least leave. In doing so the tree will be balanced.
For example if we take 7 leaves from the last question SCA1; SCA2; SCA3; SCA4; SCA5; SCA6; SCA7 then the tree has to be made by duplicating the SCA7 hash.

Conclusion
Hashing is what secures blockchains and blockchain products. It ensures a competitive way of validating transactions and adding new blocks. A block is only added when the complex and unique hashes of transactions are computationally minted.
Understanding how hashing works is an important phenomenon for all those interested in mining. For mining we need high-speed and powerful computers and continuous sources of energy. The Merkle Tree helps u understand the hierarchy of a transaction and the processes involved.

Gracias por participar en Steemit Crypto Academy Season 3:
Espero seguir leyendo tus publicaciones.
Pregunta 1, hay que investigar más.
Pregunta 2, todos los hash coinciden. Para verificar Steem6 se puede hacer con un gráfico y se entiede mejor.
Pregunta 3, todos los hash coinciden.
Recomendaciones:
Mayor investigación en las tareas.
Explicar que todas las personas puedan entender.
Calificación: 5.8
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit