Designed by Canva

💫Introduction💫
Hi Everyone!...
I will be addressing Question 1 of the schoolwork task.
Entire Question
(1) What is the difference between PoW & PoS? Advantages & Disadvantages? Which one is better in scaling Capacity? Examples?

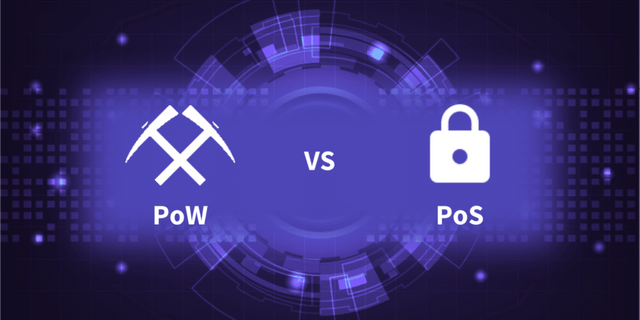
⚜ What is the difference between PoW & PoS?
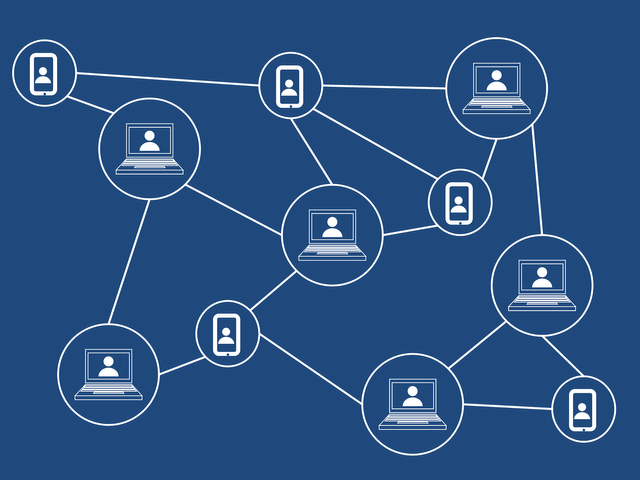
Blockchain advancements have become extremely unmistakable in the beyond a couple of years, and are apparently starting to rule the fate of money, and surprisingly the web overall. A blockchain is, basically, a shared decentralized appropriated record that is made and safely connected using progressed cryptographic strategies. It disposes of the requirement for an agent through a shared framework that permits members of the organization to approve records through agreement.
- How is an agreement reached? Through Consensus mechanisms.
Consensus Mechanisms are frameworks set up to keep up with trust between members/hubs in the organization. These are the components by which hubs on the decentralized organization can check and get records made on the blockchain. There are various kinds of agreement systems that have been made and are utilized in blockchain networks. We will be taking a gander at the Proof-of-Work (PoW) framework and the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) framework.

⚜ Proof-of-Work (PoW)
The Proof-of-Work agreement component is a strategy by which blocks on a blockchain are confirmed, and new coins, created.
The PoW framework was presented with the very first digital money: Bitcoin. Basically, it requires block validators, called excavators, to address complex numerical riddles, to track down the right hash (which is an alphanumeric code interesting to each hinder) for the current square.
Tackling these mind-boggling riddles and tracking down the right hash, for the most part, devours a specific measure of time and needs for a great deal of figuring ability to be spent. In return for their time and registering power, diggers are compensated with a specified measure of the digital currency, just as exchange expenses.
Since it utilizes a huge load of registering power and energy, excavators can be trusted to approve hinders accurately and not control any of the data inside the squares.

⚜ Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
The Proof-of-Stake agreement component is one more means of arriving at an agreement that was promoted by Ethereum.
With this framework, the square validator isn't needed to tackle any conditions, rather, block validators are considered dependable because of the stake they have in the framework.
In this framework members vow a portion of their claimed digital currency, to be permitted to approve blocks on the blockchain. The more noteworthy the sum marked, and the more it is marked for, the higher the likelihood of approving squares.

⚜ Differences between PoW and PoS
| PoW | PoS |
|---|---|
| Bock approval likelihood depends on the speed and nature of equipment of the validators | Block approval likelihood depends on the measure of cryptographic money marked and the measure of time it has been marked for |
| Utilizations an extremely tremendous measure of computational power and electrical energy | Uses substantially less computational power and electrical energy (around 10% or less) |
| Block validators/diggers are compensated in cryptographic money for the addressing of the numerical riddles | Block validators get network expense as an award dependent on the amount they have marked. |
| Observing the confirmation of work sets aside time, subsequently, this strategy is slow | A lot quicker than the evidence of work strategy |
| To direct a 51% assault one would have to claim basically 51% of the all-out computational power utilized in mining | To lead a 51% assault one would have to possess essentially 51% of the marked digital money |

⚜ Advantages & Disadvantages of PoW & PoS?
⚜ Proof-of-Work (PoW)
♻ Advantages
The confirmation of work model of agreement is extremely challenging and expensive to assault thus avoiding programmers and conceivably pernicious specialists.
Diggers are compensated with a specific measure of digital money and this is the means by which new units of digital currency are added into the framework.
It is exceptionally decentralized and makes a trustless framework for recording exchanges.
Diggers are likewise compensated with exchange expenses from handled squares.
♻ Disadvantages
The confirmation of work strategy utilizes a high measure of computational power and electrical energy.
It costs a great deal to keep up with and oversee.
It isn't climate cordial.
This framework has helpless versatility and thus low exchange speed.
The confirmation of work strategy is an exceptionally lethargic technique because of the need to settle the complex numerical riddles
It requires the acquisition of weighty costly equipment for the mining of squares
⚜ Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
♻ Advantages
It is more versatile than the confirmation of work technique bringing about higher exchange speeds.
One doesn't have to buy weighty costly gear to start approving squares.
The confirmation of stake strategy devours considerably less energy and power than the verification of work technique
♻ Disadvantages
Coins are marked briefly and can't be utilized inside that timeframe
It has a higher inclination to words centralization than the evidence of work strategy because of the way that it just requires validators to stake coins thus whales can undoubtedly capture the framework.
This framework might be somewhat less secure than the verification of the working framework.

⚜ Which one is better in scaling Capacity? Examples?
Adaptability is a vital idea in any organization. An organization's versatility is the capacity of that organization to deal with a developing measure of work. For a cryptographic money blockchain network, it is the organization's capacity to deal with a higher measure of exchanges within a given timeframe.
Between the proof-of-work agreement instrument and the proof-of-stake, the proof-of-stake is more versatile than the proof-of-work. The proof of-work instrument requires weighty, costly, huge scope equipment, and makes some set memories for mining of blocks. In any case, the proof-of-stake system doesn't need mining equipment or programming. This permits it to be a more adaptable framework than the verification of work and empowers it to do more exchanges within a more limited timeframe.
A few instances of profoundly versatile digital currency blockchain networks that utilization the proof-of-stake framework include:
Cardano: This blockchain organization can process up to 250 exchanges each second
Solana: The Solana blockchain organization can go a beating 50,000 exchanges each second.
Algorand: 1,000 exchanges each second.

~CONCLUSION~
The blockchain consensus mechanism is a vital component to think about while dissecting a blockchain, and is a vital piece of the blockchain network. Decentralization, adaptability, and trust are the central point that is viewed when assembling a consensus mechanism. These consensus mechanisms empower blockchains to work in a decentralized way.
This is all about my homework task 06 and I like to thank Professor @sapwood because preparing a meaningful lecture.
Thank You!
@sathsara



Follow me
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit