Thank you so much professor @awesononso for this lesson. It was great to learn about blockchain fork. Below is my homework task for this week. Please join me!
1. A Blockchain Fork
A fork may be referred to as a CHANGE IN PROTOCOL of an existing blockchain network or an addition of new features to a blockchain which results in an update by the nodes. This implies that the history of the blockchain is not formatted by the changes introduced in anyway. Rather the protocols used in the validation of the transaction in the said blockchain are being updated. Here the existing blockchain rules may become invalid or may still remain valid.
Forks occur as a result of a dissatisfaction derived from the existing functions offered by the blockchain. Here developers may seek to augment or improve the features/offerings of such blockchain thereby leading to the creation of a new token. Essentially blockchain fork result in a split in the network as well as an introduction of new features into the existing network for the purpose of improved performance.
2. A HARD FORK
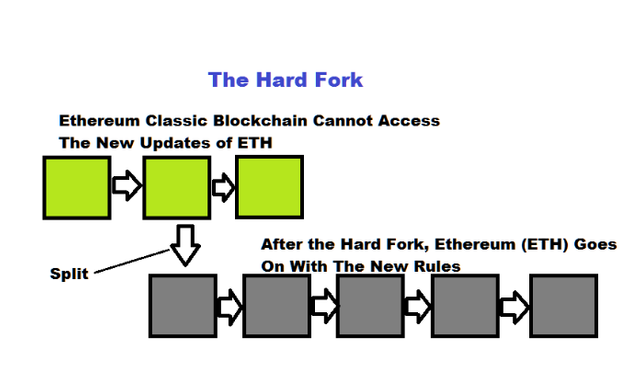
A hard fork is a change in a blockchain network that leads to a split in the chain of a blockchain network. Hard forks occur as a result of changes in the rule of the game. Once a new chain branch is created, the previous protocol will become invalid in the new chain while the old chain continues with the existing protocols.
The transactions and blocks which were considered invalid will become valid in the new chain while those considered invalid in the old chain will become valid in the new chain. Hard forks are a result of a dissatisfaction in the provisions of an existing blockchain which causes miners to introduce new rules that alters their old beliefs.
An example of a hard fork
The ethereum blockchain witnessed a hard fork in July 2016. After a hack that was caused by a third party project. A new version of Ethereum was created with new features that wiped the theft DAO. With the creation of the new version, the original chain was renamed as Ethereum Classic while the new version won the Ethereum foundation trademark and was named Ethereum. The token of Ethereum classic has its ticker symbol as ETC while Ethereum token is Ether (ETH).
3. SOFT FORK
A soft fork is a blockchain change that causes valid transactions to become invalid and only the transactions that follow the new rules are regarded as being valid. Soft forks are backward-compatible. This compatibility is due to the fact that existing nodes will only accept the new blocks as "valid blocks".
When a majority of nodes are in agreement with the changes in features that are to be introduced, a soft-fork is created. The old nodes or existing nodes do not have to upgrade for the new rules to be enforced. It is noteworthy that softworks cannot be reversed unless a hard fork is created.
An example of a soft fork is the Bitcoin pay to Script Hash (P2SH) which was incorporated into the Bitcoin blockchain in 2012. This fork allows users to create an address that can be unlocked only after a set of conditions are fulfilled or followed.
4. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HARD FORK AND SOFT FORK
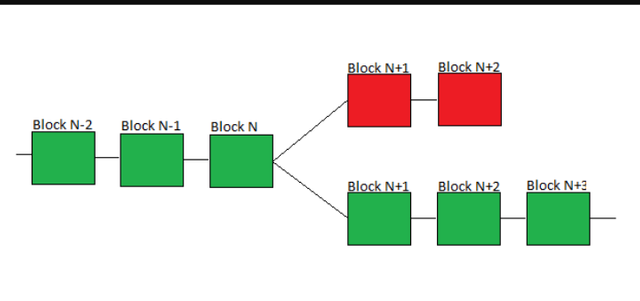
The key difference between a hard fork and a soft fork is that the hard fork leads to a split in the chain and a generation of a new token. In the split, one chain will continue from previous chain while the other takes on new features and move in its own direction. However, there are other differences which include;
- For a hard fork, A new blockchain is created. But the previous and new chain exist side-by-side and the notes have to decide which team to follow they either upgrade to the new train or maintain the protocol of the old chain.
Whereas, in a soft fork, No new chain is created. The existing chain remains valid and all the nodes execute the updates introduced. This means that the changes do not result in the creation of a separate block chain. Rather, it lands in an upgrading of one chain. - A hard fork often result in the creation of a new token. Example is BTC to BCH. While a soft fork doesn't create any new currency or token.
- A hard fork upgrade often leads to a backward incompatibility of its functions. While the upgrades for a soft fork often lead to a backward compatibility of its functions.
5. Bitcoin Cash (Hard Fork) and Segregated Witness (Soft fork)
Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin cash emerged as a hard fork of Bitcoin that was created by some bitcoin miners and other developers which also led to the creation of a new currency, BCH. Bitcoin Cash is a peer-to-peer decentralized network that processes transactions faster and cheaper than Bitcoin (BTC).
Bitcoin cash was developed when these miners who were much concerned about the future of digital currency settled to address the problem of scalability. Bitcoin segregated witness (Segwit) program was perceived to be non-transparent as well as ineffective in following the roadmap of cryptocurrency blockchain.
In 2017, BCH was created with an increased block size of 8 MB as opposed by the initial 1mb block size of Bitcoin core. Bitcoin cash has its separate blockchain. The block size later increased by 300% from 8 MB to 32 MB. Its transactions are processed faster than that of Bitcoin. In November 2018 bitcoin cash also witnessed a hard fork that led to the creation of Bitcoin SV.
Segregated Witness (Soft Fork)
This is a soft fork protocol of the bitcoin blockchain that was implemented for the purpose of changing Bitcoin transactions' format. Segwit was implemented also with an intention to alter the Bitcoin block size that caused a slowdown in transaction speed. Also another initial intention of Segwit was to guard against unintentional transactions malleability and allow data to be transferred optionally.
Segwit protocol was initiated in 2015. Another feature of Segwit is its ability to separate input and output data from a witness data known as signature. When signature data are altered by any one without making such signature invalid, it creates what is known as a malleability bug.
This bug can cause the transaction in the network to be altered by incoming transactions. Segregated witness however helps in fixing this problem by separating the witness data from transaction.
6. Steem Block chain and Hive
Hive is a Steem blockchain hard fork that was launched out of Steem code. Hive operates independently from the existing Steem blockchain and the developers are of the claim of providing true ownership experience as well as a fast and scalable blockchain.
Hive offers a free transaction service with a little transaction time of as low as 3 seconds; as well as savings services. It was also developed to operate as a web 3.0. The developers of Hive were passionate about true decentralization as they felt that Steem blockchain has been under the control of a central authority, Steem Inc.
The Similarities Between Steem And Hive Genesis Block
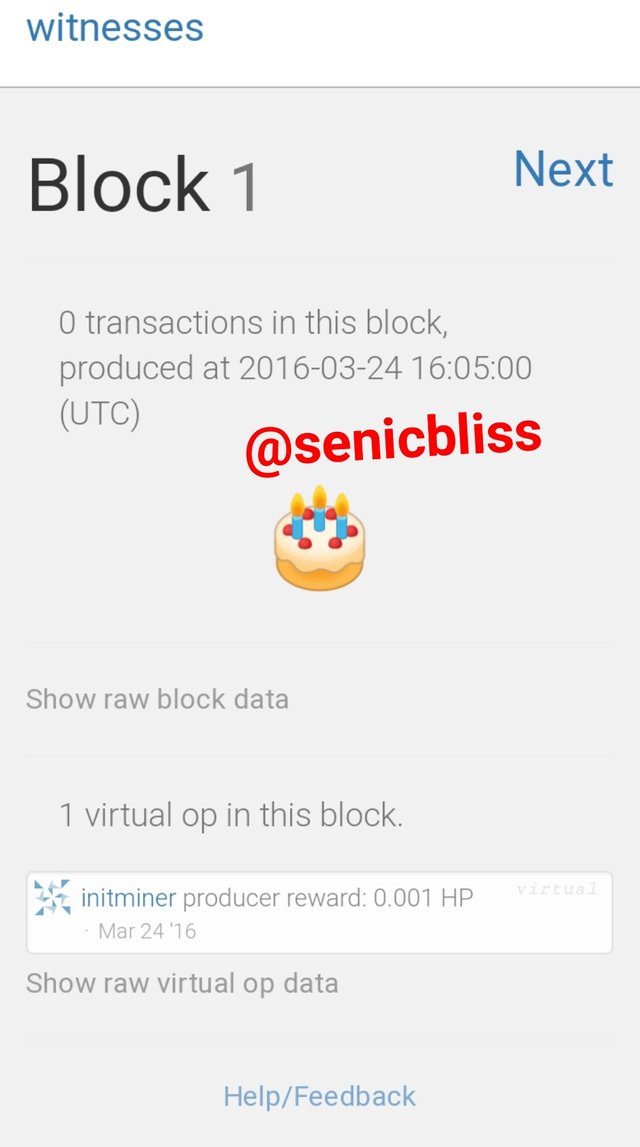
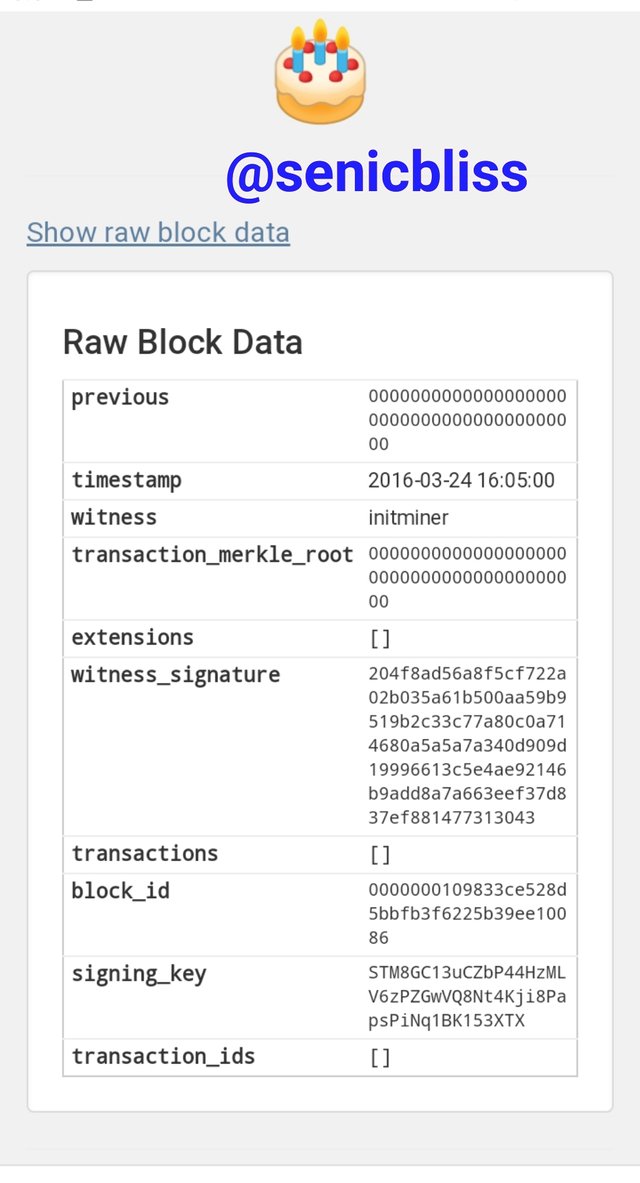
Looking at this Steem Genesis block and hive Genesis block, there are many similarities in the block details.
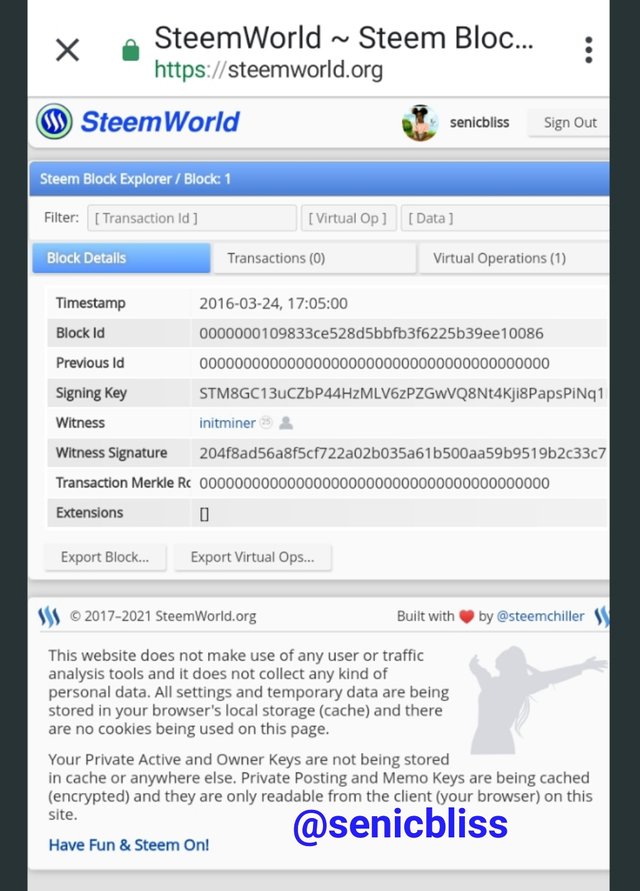
First, The witness on Steem @intiminer is also the witness for Hive.
The block ID for steem is the same as Hive and the timestamp as well is similar to both blockchains.
Thank you so much for stopping by! I really do appreciate! Steem on!


Hello @senicbliss,
Thank you for taking interest in this class.
Unfortunately, you have been blacklisted and are not eligible to perform tasks in the academy.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Reasons?
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit