Greetings beautiful people of steem!
It is a pleasure to participate in this week's crypto academy class which was lectured by @stream4u. I had fun learning and I also had fun attempting the questions asked. It is always interesting to learn about something new and Cryptography, which happens to be the topic of this class is actually new to me and it has helped me in understanding about Cryptography.

So let's head to providing answers to the homework given.
Q1. Explain the Blockchain CryptoGraphy and mention few names which are the Blockchain Platforms
Blockchain simply is a method of storing data and data in blockchain are stored in blocks or groups which are held together in a chronological way. Each group contains different data and when each of these groups are filled up, a new group takes up the task of storing datas and so on it goes.
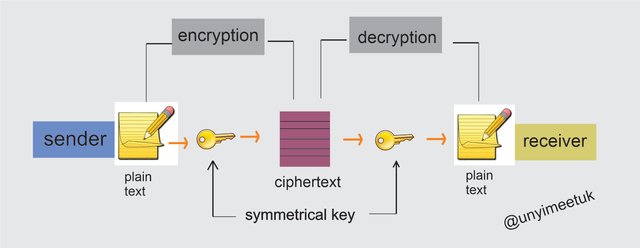
Cryptography in simple terms is a method employed in hiding an information intended to be shared between the source and the receiver from being accessed by a party third party or a wrong hand. This means that any information that is sent and which shouldn't fall into the hands of person(s) not intended for, will be encrypted making it unreadable and to convert such information into a readable format, it has to go through a process called decryption.
Cryptography is employed in keeping the events and happenings in the blockchain secure. And as we learn earlier that the blockchain stores data in blocks, each block could contains different blockchain networks and each of these networks have users and each of these users have their own unique private keys which is their own personal and private property that serves as access and also as a digital signature of their transactions.
Each of the Blockchain blocks are linked together by hash functions which is a type of cryptograph and any slight change in the data produces a significant different output which is called the avalanche effect. So hash functions are used to maintain the integrity of datas contained in a particular block
Terms ralated to cryptography are encryption, decryption, ciphers and keys
Encryption is converting a plain or readable data to a ciphertext(random sequence of bits)
Decryption is the reverse of Encryption which is converting the sequence of bits back to a readable format(plaintext)
Cipher is an algorithm which is employed in converting a plaintext to a ciphertext
Keys is a small amount of information that is required to create the output of the cryptographic mechanics(algorithm)
Blockchain platforms are platforms which uses the blockchain technology for it operations
The following are some blockchain platforms:
- Ethereum
- Open chain
- Steem
- EOS
- Quorum
- IOTA
- Hyperledger sawtooth
- Openledger
- Ripple
- IBM
*Corda

Q2. Explain the Public Key CryptoGraphy
Public key CryptoGraphy which can be likened to the operations of Asymmetric Cryptography. It makes use of a pair of key, where one key is public and the other is private this is generated by Asymmetric encryption.
And as the name implies, the public key can be seen by anyone and they are made up of codes which are alphanumeric(i.e numbers and letters). The public key is hashed and this hash creates different crypto wallet addresses for transactions. One of the main algorithm that public key Uses is the Digital signature algorithm.
The public key is used to convert a plain or readable message to a non readable form known as the cipher and such messages are called ciphertext.
Messages encoded or encrypted by public keys are decrypted by its private key and public key helps in the verification of digital signatures
Public key can be applied in the security of web servers, for digital signatures and authentication of identity

Q3. What is Private Key CryptoGraphy?
Private key Cryptography can still be likened to the operations of the Asymmetric-key Cryptography. The private key is same with the public key and as with the public key, the private key is also alphanumeric and as the name implies, it must be kept secret and known by only the user. Private keys are used to sign transactions digitally and it is used when transferring or making asset transactions.

Q4.Explain the Digital Signatures Cryptography and what is Singing Of Transaction/Message?
A digital signature is an electronic verification of a sender and it serves three purposes which are to show that the message sent is authentic, and that the sender can't deny sending the message later on and also to make sure that the information wasn't altered on the way.
Digital signatures are used to provide more security to data or information. The act like our personal signatures we use in bank transactions where everyone have a unique signature.
The digital signature works by adding a signature to a transaction before it is being added to the network and it takes the public key of the same user to check if a transaction is authentic. Some application of the Digital signatures are to detect forgery, to distribute software, and also in financial transactions
The process involved in digital signature is as follows:
A memo is Created by user A, and a digest is created by hashing the memo using hash algorithm; the digest is then encrypted using private key and this encrypted digest is the Digital signature of the message. The receiver then uses the public key of user A to decrypt the digital signature to get the digest and if the digital signature cannot be decrypted, The receiver will then know that the message or memo wasn't from User A.
Advantages of Digital signatures
Like I mentioned earlier, the core advantages of digital signatures are to:
Verify the authenticity of a message
Make a message free from manipulation or alterations
Make sure the message sent isn't denied by the sender

5. Explain what is Symmetric and Asymmetric CryptoGraphy
Cryptography is very crucial in today's world. The cyber activities especially in the area of finance can be so unguarded and hence a more appropriate way of enhancing security is needed and this is where Cryptography comes in handy
Cryptography has two main types which are:
Symmetric Cryptography
Asymmetric Cryptography
Symmetric Cryptography
Symmetric Cryptography makes use of a single key for encrypting and decrypting of data and this private key is only known to the sender and the receiver. For a example, user A and user B have the same private key and user A sends user B an encrypted message. User B since he has the private key, uses it to decrypt the message and digests the content of the message.
Symmetric Cryptography makes use of two method which are Stream Ciphers and Block ciphers.
Stream cipher works on a single bit at a time and it is not commonly used while
Block cipher as the name implies is an algorithm which operates on a fixed length of bits, called blocks and it encrypts data in chunks.
Symmetric Cryptography is a simple encryption method but it has its disadvantages. Getting the key to a receiver whom a data is shared with is a major setback of private key Cryptography and this setback makes the public key Cryptography a better alternative to the private key.
Symmetric Cryptography can be applied in payment, it can be used to confirm that the sender of a message is the right person and to generate random numbers also called hashing.
The Symmetric Cryptography has its advantages and also disadvantages.
Some of the advantages of the Symmetric Cryptography are:
It is relatively fast
It is easy to use
It is efficient for large chunks of data
Some of the Disadvantages of The Symmetric cryptography are:
Getting the key to the receiving party
It causes more damage if it is compromised or tampered with.
Asymmetric Cryptography
The Asymmetric Cryptography which is also called public key encryption makes use of two pair of keys(Public and Private key)
These keys are used to encrypt and decrypt a data and these two keys are mathematical linked together.
A public key is public to the public and private key is private to who created the two keys.
This method of transaction starts with the receiver. The receiver creates a pair of keys, one private and one public. He sends out the public key to the other person he wants to be in communication with. The sender now sends a message using the public key to encrypt it and the receiver uses the private key to decrypt it and this encryption/decryption processes are automatic.
Application of Asymmetric Cryptography
The Asymmetric Cryptography has the same advantages as the digital signature since it uses digital signature in it's operations.
These advantages are:
It is convenient to use (No key distribution)
Improved security
Confidentiality
Authenticity using Digital Signatures
Integrity of information
Non-repudiation
While there are advantages, there are also disadvantages which are:
It lacks speed as compared to the symmetric Cryptography
If a private key is lost, it cannot be replaced

Q6. How Blockchain Wallets Cryptography works and explain the available types of Crypto Wallets
To fully understand the working principle of the Block wallets Cryptography, we first of all get acquainted with the The keywords involed
First is;
Crypto wallet
Crypto wallet is a digital wallet that aids users to store and manage their crypto assets. Different crypto assets have different wallets and each of these wallets have both the public key and the private keys and these keys are used to acess the wallet and carry out transactions
Crypto Wallet Public Key
Public keys are used to vertify the authenticity of a transaction by miners before a new block of transaction is added.
Example of a public key is;
040e40a3a38af786fcd639104e3487ea78e614e3709d4968624907f6f8145729c176a434b4108e2057e2b115122dc0f34a06045801ffe817ba578f85129bb7b311
Example generated from blockchain demo
Crypto Wallet Private key
Like we learned earlier, Private key is used in digitally signing a transaction and it's a very important tool, as crypto assets depends on it for security.
Example of a private key
38006915876083507591349627823438056415588083752014952008695350090996732078960
Example generated from blockchain demo
With the use of a hash algorithm alongside with the crypto wallet keys, a crypto wallet address is created and these address are used to store, and carry out transactions of crypto assets. It is quite safe to share our wallet address to the public because the hash algorithm ensures that our private key is free from compromise.
Types of Crypto wallet
The crypto wallet is classified into two type; the Hot and the Cold wallet
Cold Wallets
Cold wallets or hardware wallets are physical offline wallets which are not connected to the Internet. They are a more secured wallet because they are free from online vandalism(i.e it cannot be hacked)
Though they seem to be a better option, it still have it's downside too.
Advantages/Disadvantages of Cold wallets
They are immune to attacks because it is void of Internet connection
They are more secure because it uses a microcontroller to to limits its interfaces with the outside world
If lost, Wallet recovery is possible with a new acquired wallet
Disadvantages of Cold Wallets
Offline wallets are not very flexible as you will have to be sure that wherever or whenever you are using it, you are alone and free from prying eyes and also you will have to manage it using some web interfaces in a computer
They are costly to acquire
Most wallet, if not all, accepts very limited crypto assets
Hot Wallet
Hot wallets also called online wallets are accessible online and they are connected to the internet. And because they are connected to the Internet, They are not immune to online attacks or vandalism.
** Advantages and disadvantages of Hot wallet **
Advantages of a Hot Wallet
They are easily accessible
They are user friendly
They cost no money to procure and they support multiple platforms
They can help in facilitating basic transactions
Hot wallets are friendly to beginners
Hot wallets provided by exchanges gives provides insurance for funds that are being deposited by users
Disadvantages of Hot Wallets
They are not immune to online attacks
Some Hot wallets don't give users full control of their funds.

7. What is the Merkle tree and what is it importance in blockchain
The merkle tree also called Hash tree was first discovered in 1979 by by Ralph Merkle. He uses the merkle tree to describe a more suitable way of verifying an entire set of information through the creation of digital signatures.
It is a data structure that allows for verification of a transaction and to know if a transaction has been added in a block.
The lowest node is the merkle tree is leaf node and the leaf nodes are labelled as Data block hash and the none leaf nodes are labelled cryptographic hash.
The merkle trees are binary and even number of leaf nodes is required but if the total number of leaf node sums to an odd number, the last hash will duplicate thereby forming an even number of leaf nodes.
The markle trees ends with the merkle root(a single string of data) and A combination of data produces a single 256-bit string which is called the Merkle root.
Transactions in blockchain, after verification are stored in blocks and the Merkle tree generates a single and unique data from the different transaction hash which forms the summary of all data.
How the Merkle tree works
A Merkle tree works by summarising all the transactions in a block thereby producing a single digital signature of the entire set of transactions. This enables a user to check if a transaction has been added to a block
The repeated hashing of node pairs to produce a single hash called the merkle root or the root hash is what creates the Merkle tree
The merkle tree is a bottom to top construction. The operation starts from the leaf and each leaf has a data hash of transactions. It has the nature of a binary tree with even number of leaf nodes. In a case where the leaf nodes are not even, the last hash will form a duplicate to create even number of leaf nodes
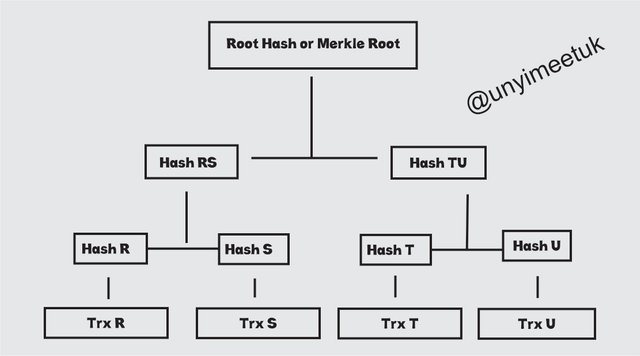
As seen in the above picture,
This Merkle tree consists of 4 transaction blocks which we know as the leaf nodes. Let's Label the transaction blocks R,S,T,U.
When each of this transaction block is hashed, it creates Hash R,S,T,U. When Hash R and Hash S are Hashed, It summarises it and creates a parent node Hash RS and also separately Hashing Hash T and Hash U will result in Hash TU. The two Hashes Hash RS and Hash TU are again hashed and this produces The Merkle Root or the Root Hash.
The Merkle Root creates a summary of all the related data transactions and this summary is stored in the block header. The merkle process can be done on large set of data and it will still Hash the datas consecutively, till a single node is created at the top.
The block header consists of the merkle root, nonce and hash of the last block and the presence of the merkle root in the block header makes all the transactions in Block header secure and free from alterations.
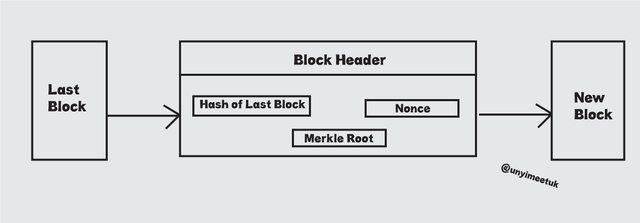
The Merkle tree retains the integrity of data and when there is a change in the transaction or order of transactions, the merkle root changes thereby making the block invalid.
Benefits of the Markle tree
The Merkle tree helps in proving the integrity and to check if a data is valid
The computation is easy and fast and requires little memory space
Little amount of information is needed for transmission.

Q8. Practical + Theory, do some practical research, study on Blockchain Demo: Public / Private Keys & Signing and then explain the functionality of Key, Signature, Transaction, Blockchain with proper screenshots of yours practical. (Do study well for this topic)
Keys
As we learnt in the first part of this lesson, that Asymmetric Cryptography makes use of two keys pair which are the public and the private key and that the private key creates it's unique public key
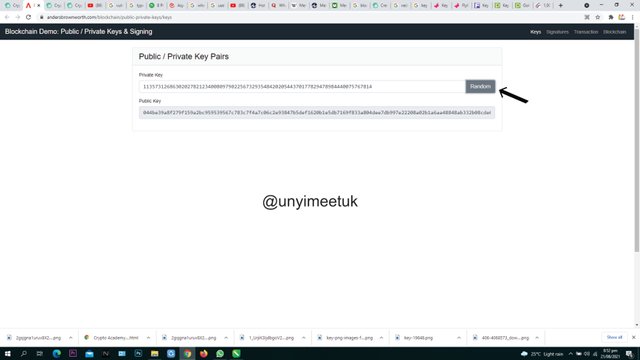
As seen in the picture above, the private key and the public key are in synchronisation with each other.
Private key:
113573126863020278212340080979022567329354842020544370177829478984440075767814
Public key:
044be39a8f279f159a2bc959539567c783c7f4a7c06c2e93847b5def1620b1e5db7169f833a804dee7db997e22208a02b1a6aa48848ab332b08cde658f69ea9154
The private key above is related to the unique public key beneath it.
Now let's run some test. Let us try altering the private key to see what happens.
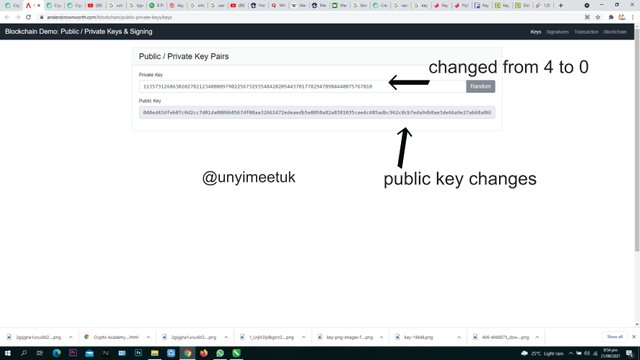
As a digit in the private key gets altered, The public key changes as well
Private key:
113573126863020278212340080979022567329354842020544370177829478984440075767814
Public key:
044be39a8f279f159a2bc959539567c783c7f4a7c06c2e93847b5def1620b1e5db7169f833a804dee7db997e22208a02b1a6aa48848ab332b08cde658f69ea9154
Here we notice when I changed the last digit from 4 to 0 the public key also changed completely. What this indicates is that a private key always have it's own unique public key.
Public key:
048ed43dfeb07c0d2cc7d01da0806b8567df08aa32661472edeaedb5e8058a82a8381035cee4c485adbc962c0cb7eda9db8ae3de66a9e27ab68a868695d890c6c7
Now let us try something different.
Let me create a private key say 2021, notice here that it creates a public key that is in synchronisation with the private key. This still goes to show us that a private key possesses it's own unique public key.
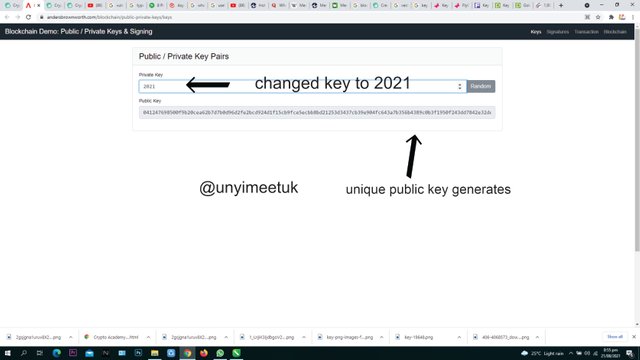
Public key
041247698500f9b20cea62b7d7b0d96d2fe2bcd924d1f15cb9fce5ecbb8bd21253d3437cb39e904fc643a7b356b4389c0b3f1950f243dd7842e32de16d2b522004
Signature
Signature are used to verify the authenticity of an information or message received.
Procedure:
First, we go to blockchain demo
We click on the signature tab
We create a message in the message box, let us use "Preach Love Always" as the message. This message can be anything though
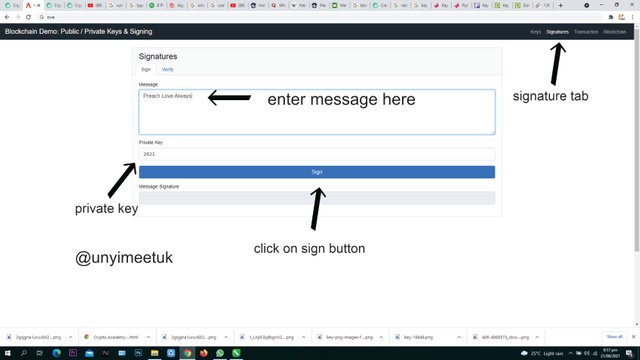
After the message is entered, we provide a private key lf our choice. Here we use 2021 as our private key. After we click the sign button to sign our message digitally.
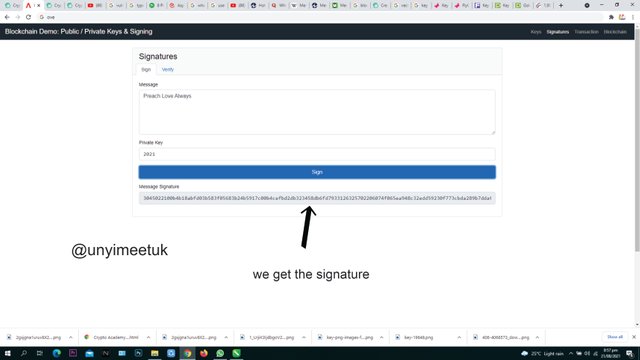
Here we see our signature which contains the message: "Preach Love Always" and a private key: 2021
Sign:
3045022100b4b18abfd03b583f05683b24b5917c00b4cefbd2db323458db6fd7933126325702206074f065ea948c32edd59230f773cbda289b7ddaf19b53ff521fc7ea395d0957
This is how to digitally sign a transaction.
Verification:
To verify our digital signature, we locate the verify button which is found on the signature tab still on the Blockchain Demo website
We find the public key and the signature in the verification tab.
When we click on verify, the private key digit signature becomes authenticated.
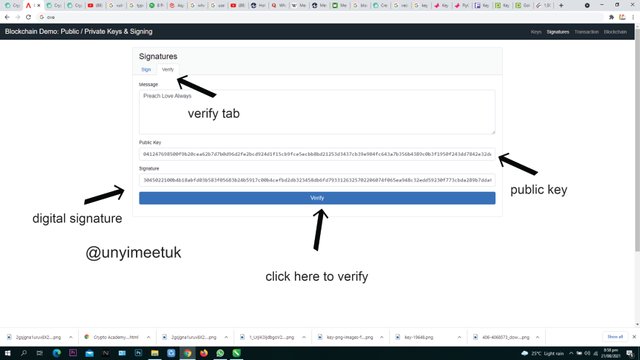
My public key together which is in synchronisation with my private key: 2021 gets shared to miners and this is what they use in verifying transactions. And to complete the verification, we click on the verify button.
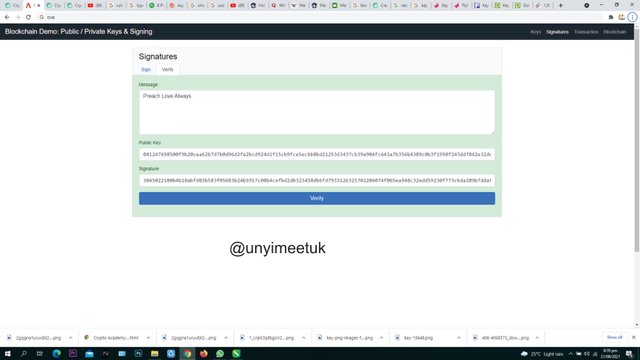
After a click has been made on the verify button, the colour highlighting the signature and the public key, changes to green and this signifies that the signature added by my private key has been verified.
Transaction
After verification has taken place, transaction is added to block.
Let us get it done
We go to blockchain demo
We navigate to the transaction tab, here we find the sign tab, I make an input of the amount I would love to send. I still have my private key as 2021 and also my public key which is in synchronisation with my private key and the public key has been shared to the recipient.
The amount I would love to send is $5000
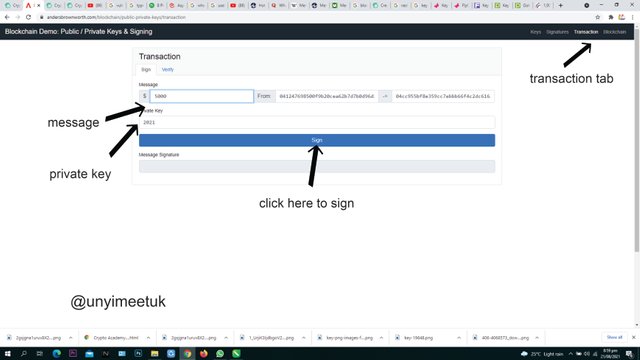
We then click on the sign option as shown in the picture.
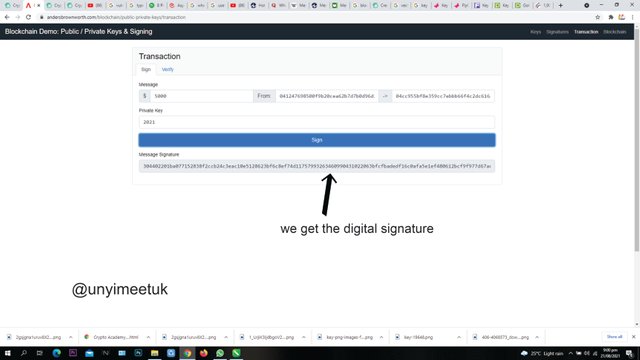
And we get a message signature as:
304402201ba077152838f2ccb24c3eac10e5128623bf6c8ef74d11757993263460990431022063bfcfbadedf16c0afa5e1ef480612bcf9f977d67ace2e1c82cf86f9e1865c3e
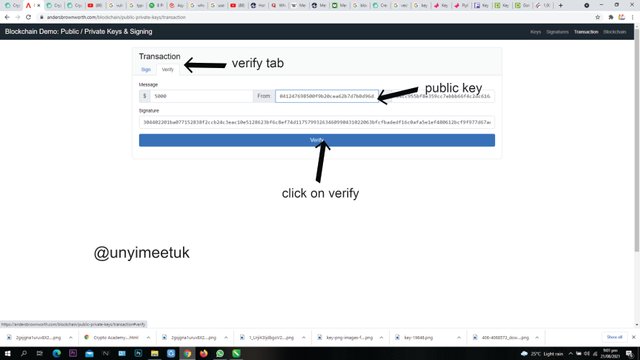
Verify
Let's verify the signature received. We click on the verify tab as shown below. Remember that for a transaction to be added to a block it must first of all be verified.
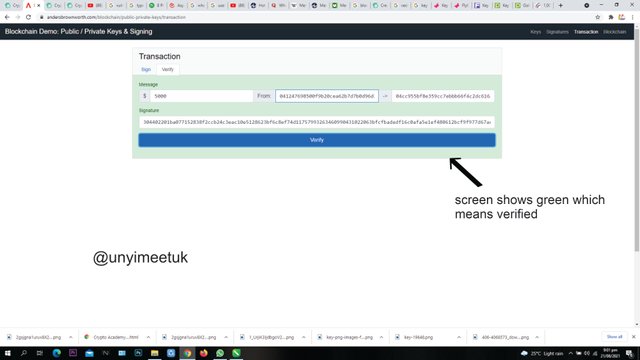
On clicking the verification button, the highlighting area turns to green which signifies that the transaction is successfully verified.
Blockchain
This is how we know how transactions are stored in blocks
Let's go blockchain demo
First we click on the blockchain tab
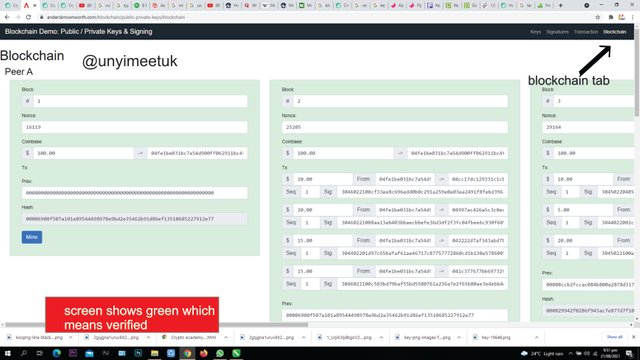
In the picture above, all the verified blocks are seen and each of the blocks contains all the transaction details such as hash, nonce, block etc. And if we effect a slight change to any of the blocks here, then the block will indicate a non verification.
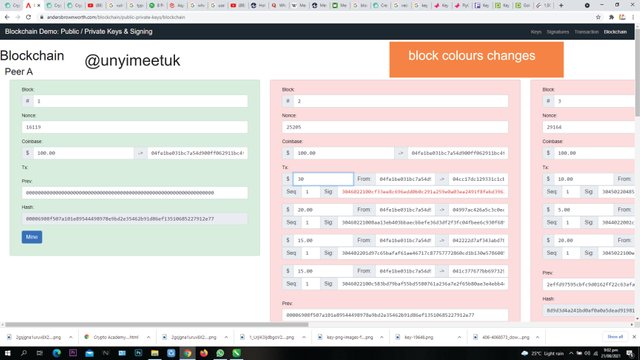
As seen in the picture above, When I made a change in block 2, the block colour changed.
Here I made a change from 10 to 30 and the colour changed invalidating the block. Block 3 which is after block 2 changes colour as well. The red colour that it changes to signifies invalidation.
As we had discussed earlier, that a change in a block will affect the block following it. And here we made a change in block 2 and it affected block three which is after block 2. This alteration makes the two block invalid because its formation depends on the block header and the block header contains the hash of the previous block. And for us to validate this block, we have to mine again as shown below
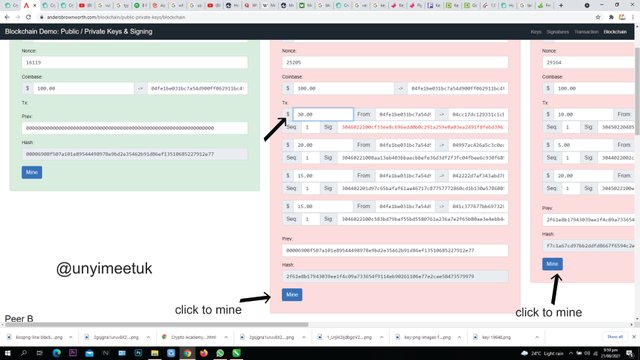
As soon as we click the mine button, the nonce of block 2 changes from 25205 to 143479 and that of 3 changes from 29164 to 19411
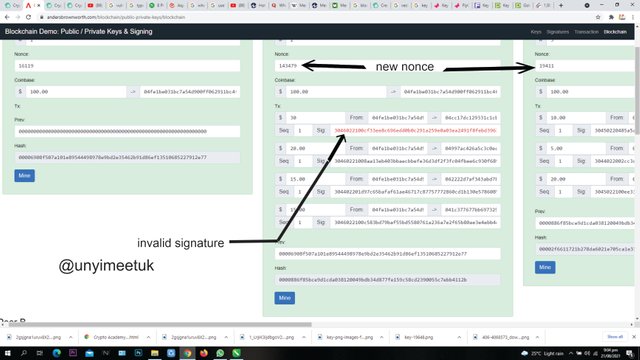
But after mining, we observe that the signature of block 2 shows red which indicates that it is not verified. This happens because the keys used now and the key used to previously sign the message is different. And when this happens we detect invalid transactions and what we notice again here is how the details of a particular block changes that of another block.
Conclusion
Blockchain employs the operations of Cryptography to help in securing the blockchain. Cryptography is so efficient in that a small change or alteration in the blockchain can be detected.
There are two main types of Cryptography and they are the symmetric and asymmetric Cryptography. The Symmetric cryptography makes use of one key which is always a private key and the Asymmetric Cryptography makes use of two keys which are a pair, one private and one public. The Private key is used in the generation of the public key. The private key is useful in signing transactions and the public key is unique to the private key that formed it
The Cryptography plays a major role in making signing and verification of transactions easy. We learnt about merkle tree, which makes blockchain transaction easy and efficient in data storage. Hash algorithm was talked about and we learnt that hash algorithm assists in turning a big data block into a single block and the Merkle tree uses this algorithm in its operations.
We also learnt about some practical approach which assisted us in understanding the theories and applications of what we learnt. Some practical approach that we learnt are how to generate keys, how to run verifications of digital signatures and transactions, how to digitally sign a message, how the blockchain work and how to detect when the blockchain has been tampered with.
I really learnt a lot in this lecture and I say a big thank you to professor @stream4u for taking time to lecture us on this Topic.