Hello Dear Friends on Steem, how are you, hope you are all fine and safe?
I am glad to be part of this class by our able professor @pelon53 on the topic; Hashgraph technology. I can assure you that after the class and the research I conducted thereafrer on the topic, I have assimilated and digested this topic, and will therefore attempt the assessment test.
Before I digress to the assignment on subject matter, let's first of all, discuss the meaning of Hashgraph technology.
INTRODUCTION:-
Hashgraph technology is a technology, developed to improve the performance of the blockchain technology. Hashgraph technology became important because of the limitations of blockchain. One one can conformably say that; Hashgraph technonlogy is the future of blockchain.
Question 1
Explain in detail the Gossip protocol, used in Hashgraph.
Introduction of Gossip Protocol:-
Just like Bitcoin uses SHA-256 hashing alogorithms, Gossip Protocol is the alogorithms used by Hashgraph to make validation process faster. This protocol allows the nodes to transfer information randomly with other groups of nodes connected to the system, these groups will also replicate same information received and also pass it on to other nodes and so on to help achieve a consensus.This means that if a note sends information to 100 notes, each of the 100 receiving notes should replicate the information and also spread it to another group of 100 notes as so on as so forth till all the notes have received the information. This helps achieve a consensus quicker than any other Blockchain.
Consensus is the the agreement on same value
Therefore, Gossip Protocol in Hashgraph involves the spreading of information from notes to notes. Because the essence of Gossip Protocol is to spread information from one note to another to the same extent it received it.
The History of Gossip Protocol have been traced to 1987, to the epidemic replication alogorithms described by Demers Alan, Greene Dan, Hauser Carl, Irish Wes Larson John, Shenker Scott, Sturgis Howard, Swinehert Danm and Terry Doug in their study of 'Epidemic Alogorithms for Replicated Database Maintenance"
This work is essential for the development of the development of the alogorithms for Hashgraph and other branches of computing.
The name Gossip Protocol was coined from the word GOSSIP which means the spreading if rumours.
The synchronization of information between members in gossip protocols is known as Gossip Sync. On completing of a each process of Gossip Sync, each member involved in the process commemorates the Gossip Sync with with an event.
An event is stored in the memory as data structure composed of a time stamp.
Types of Gossip Protocol:-
The following are different types of Gossip protocols in Hashgraph, they are also refered to as rumour mongring protocols. They include
- Group communication; here the various groups of nodes are in frequent communication.
- Aggression Protocol:- here, the first nodes receive data, process them and pass on information to other nodes.
- Protocol for Broadcasting:- these protocols functions under a multicast system.
Question 2
Explain Tolerance to Byzantine Faults in Hashgraph.
Byzantine Faults are faults that occur when "some" nodes fail to pass on information to other nodes, who continue to work without noticing the failure of those nodes.
Byzantine Faults Tolerance (BFT) is the feature of a distributed network to reach consensus while other nodes fail to respond.
The a of Byzantine Faults Tolerance is to safeguard against system failure, this is possible by employing collective decision making bodies which may include correct and faulty nodes. Byzantine Faults Tolerance is derived from Byzantine general problem Byzantine Faults can be acheived when working nodes in the network reach an agreement on their value without the faulty ones affecting the agreement.
Types of Byzantine Failures:-
Byzantine Failures are of two basic categories; viz;
a. Fail Stop; here, notes fail and stops operating.
b. Others are arbitrary nodes failure. Which may include:
- Failures to return results.
- Response with an incorrect results
*Response with a deliberately misleading results. - Respond with a different result to a different part if the system.
Security in Byzantine Faults Tolerance:-
Here, there are Byzantine Failures Asychronous tolerance (aBFT) a kind of BFT to guarantee the security of data stored within the network in order to to prevent manipulating information from their convince.
This security ensures that no one member of the group can prevent the community from acheiving a consensus.
The security also helps to ensure that the consensus is not changed. The process is processed ascrononously.
Question 3.
Make a comparison between Hashgraph Vs Blockchain, for a voting process in your country. Which technology would you choose? Why?
Part a
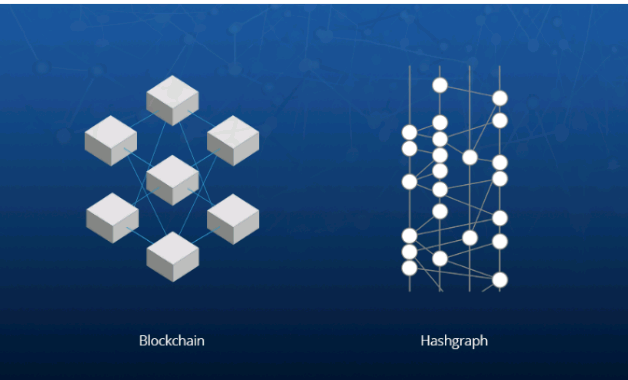
Hashgraph and Blockchain can be compare on four different sub-headings, which may include;
- Speed:- because Hashgraph uses Gossip, which provides faster transaction speed even as it requires lesser information to propagate more events. It can process up to 500,000 transactions per second.
While Blockchain depends on the implementation on protocals such as hyperledger or other solutions which generates lesser speed than Gossip. Blockchain processes 100 - 10,000 transactions per second.
Open Sourses Vs Patented:- blockchain is an open source DLT platform and therefore has many people contributing cryptocurrencies and utility tokens. However, Hashgraph is based on patent alogorithms owned by Swirlds. New entrants must pass through Swirlds.
Efficiency:- miners finds it difficult working on blocks in Blockchain, when two blocks are mined same day, they have to decide on a single day and discard the other block this is a waste of resources and capacity.
While Blockchain doesn't work with blocks and as a result it operates on 100% efficient capacity and all resources are maximized.Consensus mechanism:- Blockchain uses various alogorithms which normally depends on the the cryptocurrency and the currencies. Some of this these alogorithms may include; Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-Work, Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
While Hashgraph uses visual voting to gain network consensus. It doesn't require other alogorithms and it can perform effectively at a lower cost and doesn't need high computation power nor does not need so much power supply.
Part b
Am a Nigerian, and Nigeria at present has about 200 million eligible bitters at present.
Truely, both Blockchain and Hashgraph can be comfortably used in an election in my country, but. But I will choose Hashgraph because;
- It has a better speed and can transmit information from one pooling unit to another faster and help in the final collation.
- Since Blockchain operates with blocks and if a politician or a party owns majority blocks (though it difficult) He/they are capable of dominating the decision making and the eventually influence the outcome of the election.
Question 4
Explore Hedera Hashgraph link show screenshots.
This link source will help you navigate. When it opens, your home page will be same as what you have bellow

Click on the lines at the top left hand side of the page above.
It will take you to the screen bellow.

From the screen above, click on NETWORK.
It will take you to a page where you will see; Tocken services, Consensus services, view all services the platform offers. Haven seen that, go back and seller DAVS

Under DAVS, you will find;
Resources, Ingredients, Fees, Open resources, and Learning center.
After exploring DAVS, go back and sellect USE CASES.

Under USE CASES:- payments, tocken, Assets, fraud mitigation, identity, data compliance, permissioned, Blockchain.
After eploring, go back to sellect HABAAR

HBAAR here you will see; Overview, be account creation, wallets and exchange.
After exploring, Go back to sellect Governing Council.

Governing Council
Below will be the the display of the screen. scroll up, to be able to also see the organizations that makes up the governing council.
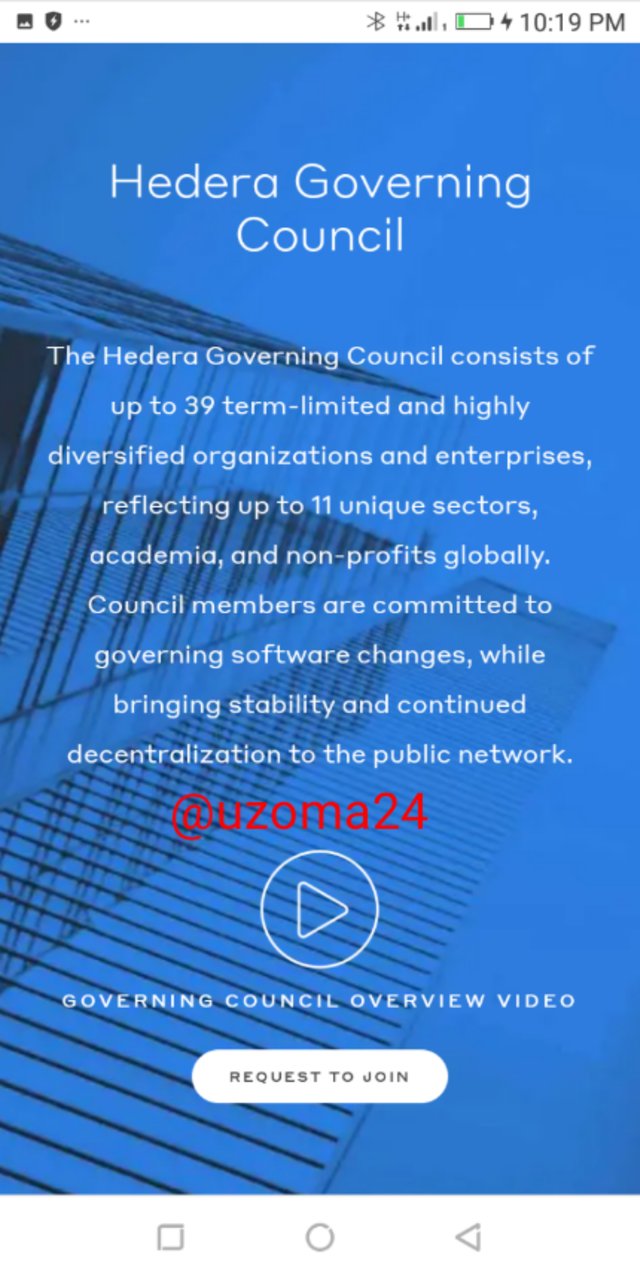

This represents all the companies that make up the governing council of Hedera Hashgraph
When you are done exploring, Go back and sellect About.
Attention @pelon53.
Please this is to bring to your notice that this my post have not been voted till now. @steemcurator02 kindly assist.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Ten calma. Paciencia.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
@pelon53 please assist. This post will expire in less than 24 hours
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Ten paciencia.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
thanks @pelon53 and @steemcurator02
Am grateful
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Gracias por participar en Steemit Crypto Academy:
Se llega a un consenso siempre y cuando existan 2/3 de nodos válidos.
Espero seguir leyendo tus publicaciones.
Calificación: 7.9
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank You Prof.
Will improve subsequently
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit