
Hey guys,
I welcome you'll to the 2nd week of the SteemitCryptoAcademy course by Professor @imagen. In this course, I will run a comprehensive review of Yield Farming - Yearn Finance
All images used in this post unless otherwise stated are not mine and were extracted from MT5, Yearnfinanceand Tradingview for the purpose of this assignment.

Question One
Describe the differences between Staking and Yield Farming.

In the course of my previous assignment on Audius platform, I had to discuss the whole process of staking on the Audius blockchain and it was the first time I really pondered on attempting to put words together to define the idea of “Staking”. I defined it as “a crypto technique involving putting up an amount of asset or security for the purpose of believing a blockchain will work and when it works, you make profits. It is like buying shares in a company. It is available for blockchain platforms that use the POS (Proof of Stake Mechanism)”. This definition encapsulates the processes involved with staking. Like the word “staking” connotes, it is taking a set-aside amount and putting it into a process that is expected to yield returns. It is very easy to link both terms together because like in the second definition of “Staking” that I provide, the common term is “yielding”.
Yield Farming works the same way as Staking, in fact, to utilize pun, I may say it is the process of staking tokens for the purpose of returns. At surface definition, they are the same but it is that which is yielded that makes the difference and that which I would describe in subsequent paragraphs. But first, let’s discuss more on both concepts.
Yield Farming is a much newer concept in market compared to Staking and is recorded to have started in 2020 associated with the launch of Compound Finance (a lending Protocol-COMP token) and today in 2021, several platforms exist that encourage yield farming.

It basically works this way, a lender deposits the assets he is willing to stake on a Defi Platform (collateralization), and from the platform, he takes a loan to carry out activities with the hope of yielding interest. Yield farming has both processes synced together so that in a case of loss, that which was staked is gone. This is explained marvelously in the picture below:
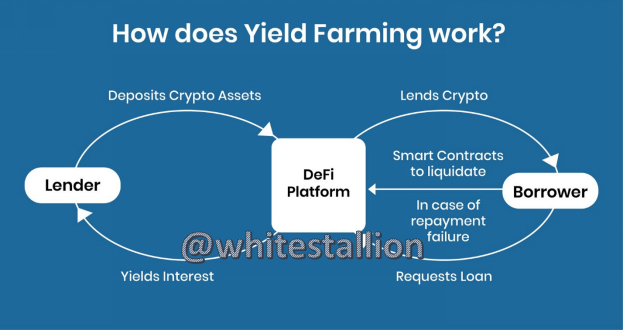
In Yield Farming, the Lenders are called farmers or liquidity providers, and their task is to offer liquidity to the pool, and they are rewarded for their deposit.
Staking on the other hand works in a way that investors partake by means of staking their securities in verifying and approving transactions performed on the blockchain. It is basically like earning interest for the money left in a bank or an investment business. The money is used to perform actions that benefit the wallet/bank/investment/Defi and in return, profit is made.
The first difference between both terms is that for Yield Farming, there is oftentimes a stipulated time in which investors are meant to submit or rather stake their tokens for and sometimes a minimum amount or based on privilege. For example, in Auduis platform, it is given as an incentive to those who were early partakers of the technology, but typically it is often given to those who are big owners of shares or tokens in this case (and this may be the way for Audius with time). Yield Farming on the other hand does not require locking up of funds for a given amount of time but allows investors select time.
Another difference is that the energy put into Yield Farming is deliberate and passive while Staking most often is based on passiveness. Let me explain this because Yield Farming is a new technology, it is possible to lose easily especially through liquidation. While Yield farming can bring more gains than Staking can, it is important to note that in the lending situation, one may have to be very careful that they do not lose their assets, especially because of liquidation and the Bugs on smart contracts which makes it susceptible to hackers. All these can be insured against by doing it the right way, but it still connotes the fact that there must be a deliberate act involved in the whole process of Yield farming. However, where it becomes passive is in the fact that when done rightly; it brings in profits steadily while the investor does little or nothing. However, Staking of Coins is more passive, it involves you merely holding a particular amount of security and by virtue of what you hold, you can make decisions and make profits, in general, the passiveness associated with Staking is what makes it have fewer disadvantages but makes it less profitable compared to Yield Farming.
Yet another difference between Yield Farming and Staking is in what is yielded from what is staked (expected profit from investment). In Staking, the typical expectation hardly surpasses 5% of that stake, while in Yield Farming, it may yield over 100%. The profits in Staking are usually based on incentives and there are usually not many losses or risks (known as impermanent loss; a word in Yield Farming discourse that helps describe the risk of volatility on liquidity pools).

Question Two
Enter Yearn Finance. Fully explore the platform and indicate its functions. Describe the process for trading on the platform (wallet connection, funds transfer, available options). Display screenshots.

To attempt this question, I will visit the website: https://yearn.finance/#/home of which the home page looks like the below image:
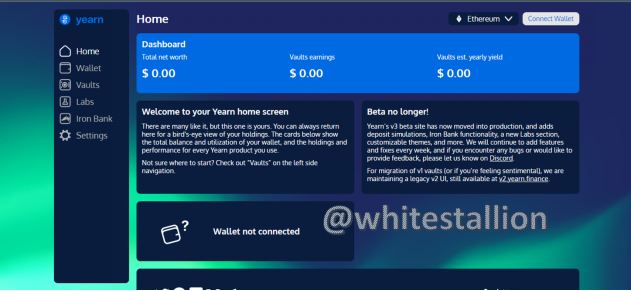
To explore this platform, I will describe its functions as can be seen on the entire webpage. First on the Home page, I see a Dashboard showing the Total net Worth, Vaults Earning, Vault net Yearly Yield, the option to connect wallet, wallet, vaults, labs, Iron Bank, Settings, a Welcome page, and a notification page.
The idea of this webpage is the facilitation of Yield Farming by offering processes and strategies. It also is intended to be an autonomous and decentralized system handling protocol transfers between investors and dApps. As can be seen above on the right-hand corner, it is running on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (a clearer picture is shown below):

When you click on the Arrow beside “Ethereum”, you see “Fantom”, a less popular option. However, there is a promise that Yearn Finance would run on more exchange but for now, according to class activities, users can only deposit stable coins that are on the ERC-20 platforms like USDT, USDC, etc.
- The next feature is the connect wallet feature seating right next to the Ethereum logo above.

- When you click on this feature, the next option as shown below is an option for the selection of several wallets:
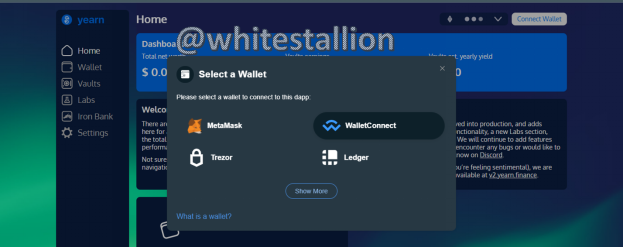
- If I decide to click MetaMask wallet, seeing I have one, the MetaMask wallet plugin on my browser pops up and the process links up and connects as can be seen below:
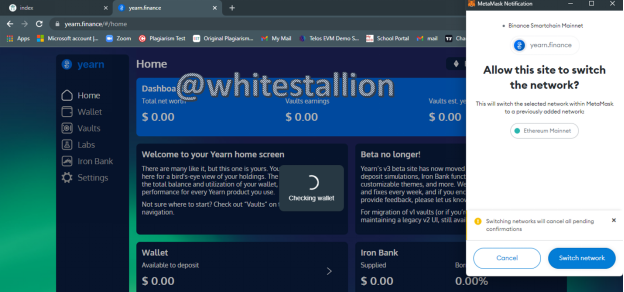
- Preceding the final connection, the “Connect Wallet” icon shown above is replaced with my wallet address as can be seen below:

This is basically the process involved in connecting the wallet to Yearn Finance.
Next is Fund Transfer: this process is found under the vault feature and the Iron Bank feature of the wallet. When we click Vaults, we are taken to this page:
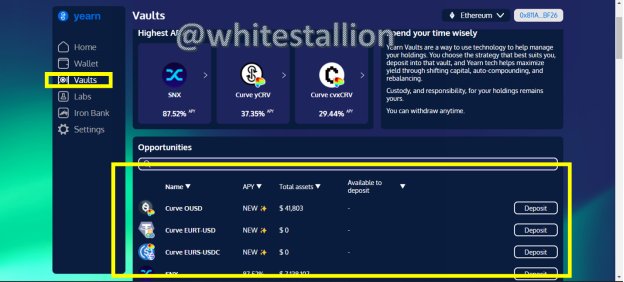
- Here we see available options from which funding of my wallet can help us partake in. To experiment, I click on Curve OUSD, and below is the pop up:
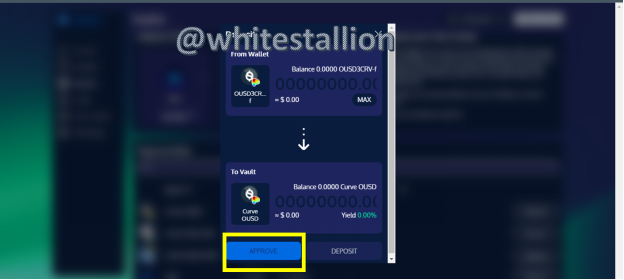
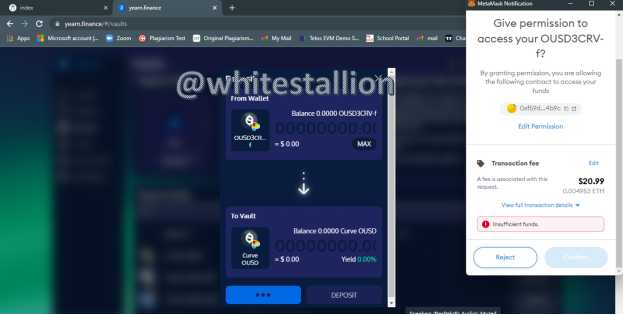
- When I click on Approve, I get a pop up that intends to connect to my metamask wallet, and this is the process needed for transfer; unfortunately, I do not have sufficient ETH to burn for this process and I am replied with “insufficient balance” as seen below:
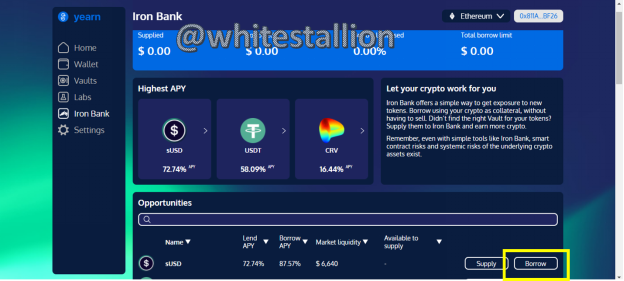
- Beneath the Labs icon is Iron Bank. The difference between the vault and the Iron bank is that vault is basically an option to choose from where to store tokens while the Iron is for investors who are unable to find the correct fit in the vault. Everything else on the Iron Bank section is similar and functions similarly to the vault:
- Returning back to the Home Page is the function of Wallets as can be seen below:
Here the function is to act as an aggregate of all tokens available and let users know when there are available options to lend by displaying supply or deposit buttons below.
Then there is the Labs feature. Here, we see a Dashboard that is supposed to be a reflection of holdings and then we see the highest APY’s and available opportunities, as the name suggests, the lab is a place to find specimens to experiment on.
When we click on the Deposit icon, it takes us through the similar process like it does in Vaults, insinuating that this is also another key area to partake in Yield Farming activities.
Finally, is the Settings Page which is just an interphase to customize the webpage to ones taste as can be seen below:

Question 3
What is collateralization in Yield Farming? What is the function?

In my opinion, I like to view collateralization in the light of what banks would usually request when a loan is sorted. For instance, Mr. X wants a loan from ABC Bank, the typical way is that the bank asks him to submit his assets that can be seized if he fails to pay them back. This is how I see collateralization in Yield Farming, but from a technical perspective, I will define it in simple words as the process of staking assets in order to borrow crypto tokens. How it works is basically an explanation of how yield farming works; an investor deposits his coins into a lending pool through a dApp and that deposit acts as leverage for the loan he is about to take. It is sometimes referred to as the lending process or most frequently the staking process of yield farming.
The function of it is to act as collateral chiefly, when you look at the bank scenario of a loan, if the investor is not able to pay back his loan, the collateral is confiscated. Similarly, if by virtue of loss or whatever reason, an investor is not able to repay, then the collateral is affected.
It also functions as liquidity provider, by the lending of assets, it provides liquidity to the market. Because for a token to be given out, another is brought into the system, keeping the market active and in economic terms “injecting liquidity”.
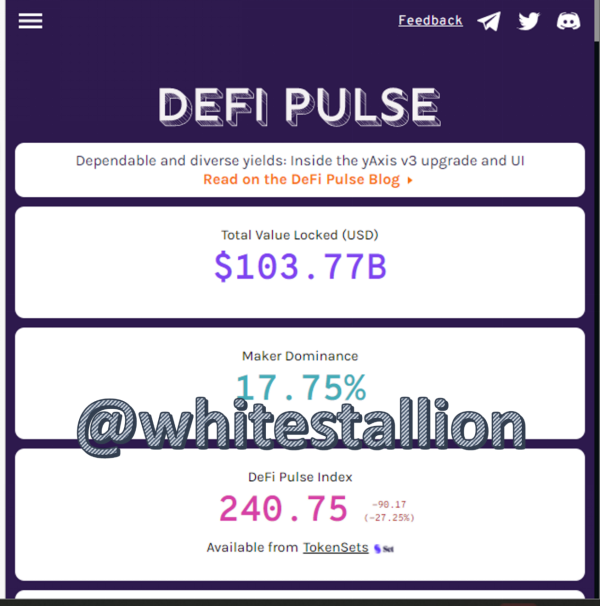
At the time of writing your assignment, what is the TVL of the DeFi ecosystem?
According to Defi Pulse, the current TVL of the DeFi ecosystem is about $103.77 billion and it places the largest contributor to be Maker with about $18.30B locked..
**What is the TVL of the Yearn Finance protocol? **

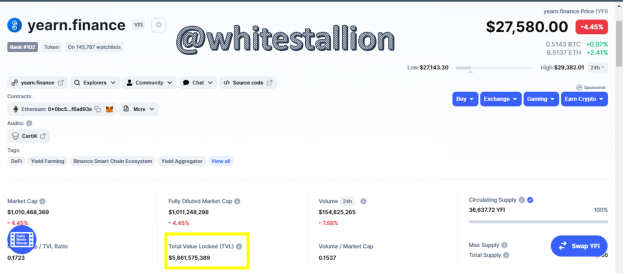
As of the time of writing, the TVL of Yearn Finance Protocol is $5,861,575,389.
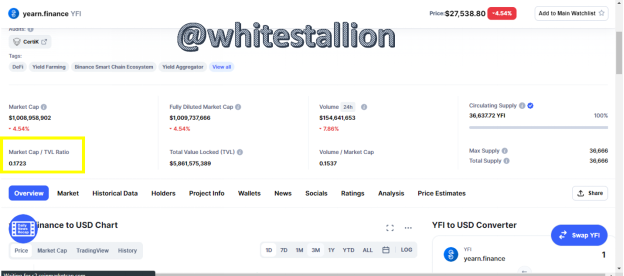
What is the ratio (ratio) Market Capitalization / TVL of the YFI token? Display screenshots.
The ratio of Market Capitalization/TVL is 0.1723 with Market Capitalization being $5,861,575,389.
Question 4.1
Is the YFI token overvalued or undervalued? State the reasons.

In my opinion, the YFI token is currently at the time of writing this essay undervalued, this is because it has a current price of $27,585.83/YFI but it has a Market capital of $1,011,626,311. One other reason I believe it in being undervalued is that it has prospects in drawing massive users because of the Yield Farming feature and with more users learning more about the relatively new Yield Farming procedure, many more would likely influx on the platform thereby pushing the market.

Question 5
If on August 1, 2021, you had made an investment of 1000 USD in the purchase of assets: 500 USD in Bitcoin and the remaining 500 USD in the YFI token, what would be the return on your investment today? Explain the reasons.
To understand this answer, we have to know the price of BTC as at that time, so I pull my chart via Trading View and pull out the price of BTC as at August 1st, 2021

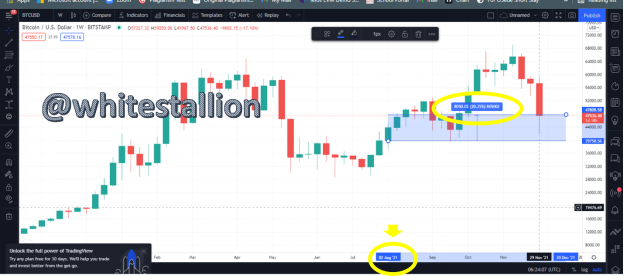
From the above, the price of BTC on August 1st when I made an investment of 500$ in BTC was $39,758, and then currently as of today, the price is $47808 this is about a 20.25% increase. By that logic, my 500$ investment in BTC will be 500X20.25%+ 500= 101.25+500= 601.25.
For the YFI token, the price at August 1st according to my Trading View is $31943 but as at now, the price is $22620. This is a loss of about -25%.
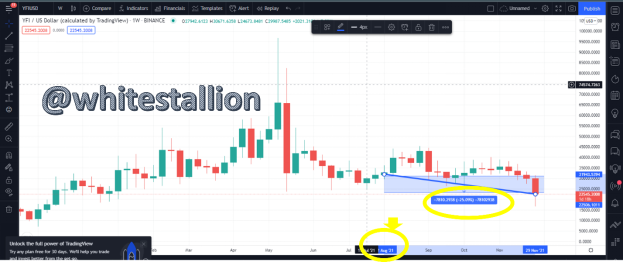
By that logic: 500$ investment in YFI token will be -25% of 500 =-125. Therefore, 500+(-125) = 375$.
The return of our total investment will be $601.25+$375=$976.25. A gain for BTC but a minute loss for YFI token, illustrates the need for crypto investors to diversify their holdings as being in one market makes you susceptible to lose without recovery.

Question 6
In your personal opinion, what are the risks of Yield Farming? Reason your answer.

During my research on Yield Farming, one idea that interested me was the fact that I can make 100% returns through it. With this, I had already quickened my desire to want to partake in it, however, with further study, I soon discovered that the saying “with big risk comes big reward” is applicable to Yield Farming. Here are what in my opinion are the risks of Yield Farming:
Volatility: this is basically the biggest risk faced while trading. With the uncertainty of market movement, especially with the capability of being able to move several hundred percentage quickly in an up or downtrend, the investor faces the risk of price moving in a downtrend and making all held assets to be lost. When the currency lent decreases in value, it is called impermanent loss.
Liquidation; the enemy just like volatility makes market moves beneficiary and dangerous to us, market may move in a manner in which our position becomes liquidated and so we may lose our staked securities.
Liquidity Pool Problems: it is important to be very selective about the choice of liquidity pool used, in most cases liquidity pools that are not popular have a higher interest rate, just so that they can attract investors, but eventually these liquidity pools themselves may be scams and can be another risky way to lose one’s security, some even get hacked.

Conclusions

In my opinion, it would take a well-schooled person on the knowledge of Yield Farming to invest in it and pull profits. It is a high-risk but also a promise of high reward. I look forward personally to exploring more on it and perhaps staking or farming for profits. Despite this, I look forward to many ways that Yield Farming will get more advanced and popular than it already is with more user taking advantage of it.

Special thanks to Professor @imagen
