- Define in your own words what is the Stochastic Oscillator?
A stochastic Oscillator may be defined as an indicator of momentum that compares a specific security closing price to a range of its prices over a known period. The oscillator's capability of making responses to movements of the market can be reduced by making adjustments on the period or through taking the result of a moving average. It is used to produce trading signals of overbought and oversold, making use of a 0–100 bounded range of values.
The stochastic oscillator is range-bound, that is to say, that it is always between 0 and 100. This makes it a serviceable indicator of conditions of overbought and oversold. Readings, when it is over 80 points, are seriously thought about in the overbought range, and readings below 20 are on the other considered oversold. Nevertheless, these are not often serving as a sign of imminent reversal; overbought or oversold conditions can be maintained by trends that are very strong for an elongated period.
Some key facts about Stochastic Oscillator
- Stochastic oscillator is a famous technical indicator for giving rise to overbought and oversold signals.
- It is a momentum indicator that is common among the general public, first developed in the 1950s.
- Since Stochastic oscillators rely on an asset's price history, they have the tendency or predisposition to differ around some mean price level.
2.. Explain and define all stochastic oscillator components (line %k, line %D + overbought and oversold limits).
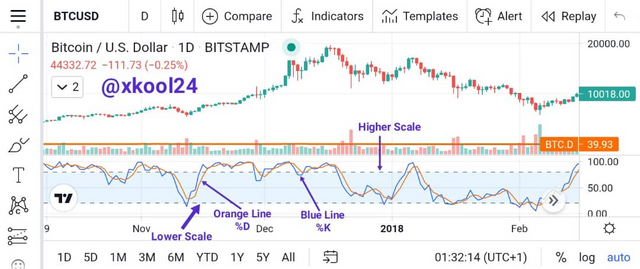
The Stochastic Oscillator is composed of two distinct lines. When the two lines are included on a price chart, it is alluded to as the full stochastic. %K and %D are the two lines are.
- %K
%K also known as “stochastic fast”, monitors the present market rate for the currency pair.
%K is calculated this:
%K = 100 x (Closing Price - N Periods Lowest Price) / (N Periods Highest Price - N Periods Lowest Price)
- %D
%D which is also known or referred to as the signal line makes use of the last three valuations of %K in a typical manner to produce a moving average of the %K stochastic. For the reason that %D is a moving average of %K, it is alluded to as "stochastic slow" because it reacts to changes in market price more at a slow pace than %K.
%D is calculated thus:
%D = 3 – Period Moving Average of %K
- OVERBOUGHT AND OVERSOLD
Overbought and Oversold limits are other components of the stochastic oscillator. Hence;
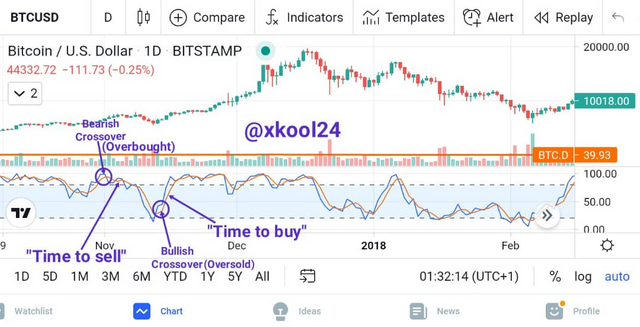
Any time the %K of the stochastic scale line rises above 80, it is interpreted by analysts as an overbought condition and can produce a sell-off forcing the price to a downward movement.
The market can be translated as oversold any time that the %K line declines below 20 on the stochastic scale, at such traders may begin buying.
- CROSSOVERS
This is another component of the stochastic oscillator, it happens any time %K (the fast stochastic) cuts across the %D (slow stochastic). Since the %K line reacts more speedily to changes in the market, it oscillates at a more rapid rate than the %D line. Under definitely known conditions, it can overtake, and cross over the %D line.
Any time the %K Stochastic transverses over and moves higher than the %D Stochastic, by translation, it means that the market rate is making gain at a faster rate than the average that %D Stochastic represents. This increase in the potency of price is considered a buy signal.
A sell signal is an outcome of the %K Stochastic crossing beneath the %D Stochastic for the reason that the faster-moving %K line is moving downward more speedily than the overall downward trend.
3.. Briefly describe at least 2 ways to use the Stochastic Oscillator in a trading operation.
- Stochastic Oscillator and Price Chart Divergence
A divergence happens in case the Stochastic Oscillator varies from the price chart. Divergence can be either Bull or Bear
Bull divergence - a signal to buy - comes into view any time the price chart features a new lowest limit, during the same time the Stochastic Oscillator makes evident a more shallow minimum than the previous one. This means that the bears are losing strength, just moving by inertness. After creating a second minimum and the starting of the Stochastics lines progressing up, buying is recommended. The signal is regarded as stronger supposing the first minimum of the Stochastic Oscillator was lower than the level of 20% and the second one higher than it.
Bear divergence - a signal to sell - comes into sight any time the price chart displays a new highest limit, during the same time the Stochastic Oscillator makes evident a max lower than the previous one. This means that the bulls are losing strength, just moving by inertness. After creating another highest limit and the commencing of the Stochastic Oscillator going down, selling is recommended. Signals are usually stronger if the first Stochastic Oscillator highest limit was higher than the level of 80% and the second one lower than it.
- Crossing of the %K and %D
Supposing the main speedy %K line crosses the sluggish %D line upwards, this signals to buy, supposing vice versa, top-down — to sell.
Supposing the crossing happens in the areas of overbought or oversold, this is regarded as a strong trading signal; supposing it occurs outside these areas, this is regarded as a weak signal.
4.. Define in your own words what is the Parabolic Sar?
The Parabolic SAR, also known as parabolic stop and reverse, is an indicator common among the general public which is mainly used by traders to ascertain a given asset's future short-term momentum. The famous technician J. Welles Wilder, Jr. developed the indicator and it can easily be put into practical use to a trading strategy, empowering a trader to ascertain the place in which stop orders should be placed.
Graphically, the parabolic SAR indicator is displayed on an asset chart as a dots series positioned either above or below the price; with regards to the momentum of the asset. Any time an asset trend is upward, a small dot is placed below the price, while a dot is positioned over the price any time the trend is downward.
5.. Explain in detail what the price must-do for the Parabolic Sar to change from a bearish direction and vice versa.
The parabolic SAR indicator being shown on an asset chart as a dots series positioned either above or below the price bars is dependent on whether the price is bullish or bearish. When the price is bullish, the dots of the parabolic SAR is positioned below the price. On the other hand, the dots move above the price when the price is bearish. The dots will rise as the price of a stock rise.
This implies that the change of the parabolic SAR either too bullish or bearish is determined or dependent on the change of price.
6.. Briefly describe at least 2 ways to use parabolic SAR in a trading operation?
The primary use of the Parabolic SAR is to buy any time the dots move below the price bars — which signifies an uptrend — and sell or short-sell any time the dots move above the price bars — which signifies a downtrend. This will lead to constant trade signals, as the trader will at all times have a position. That can be good supposing the price is making big swings back and forth — generating a profit on each trade — nevertheless any time the price is only making little moves in each direction, these consistently recurring trade signals can yield many losing trades in a row.
It is better to carry out an analysis on the price action of the day to ascertain (supposing there is a trend) whether the trend is down or up. Another indicator, like trendlines or moving averages, can also be used to confirm the overall trend direction. Supposing there is a trend, it is needful to take trade signals in the direction of the overall trend. For instance, if the trend is down (based on one's analysis), the short trade signals — when the dots flip on top of the price bars — should be taken and then exit as soon as the dots flip below the price bars. In this way, the indicator is used for its potency which is catching trending moves.
Practice (Only Use of own images)
- It shows a step-by-step of how to add the Stochastic Oscillator (Pointing to Line %k and Line %D, the overbought and oversold zone) to the graph.
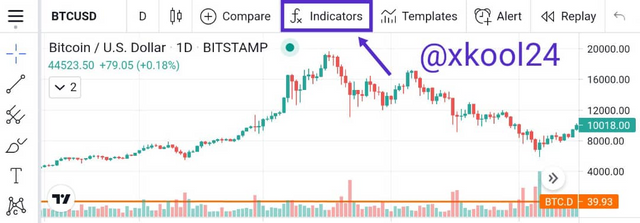
- Login to Tradingview
- Choose coin pair of your choice (I will be using BTC/USD for this lesson)
- Select Indicators
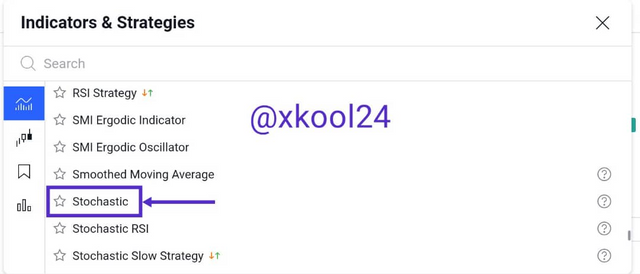
- Under Indicators & Strategies, select Stochastic
2.. Show step by step how to add the Parabolic Sar to the chart and how it looks in an uptrend and a downtrend.
- Login to Tradingview
- Choose coin pair of your choice (I will be using ETH/USDT for this lesson)
- Select Indicators
- Under Indicators & Strategies, select Parabolic SAR

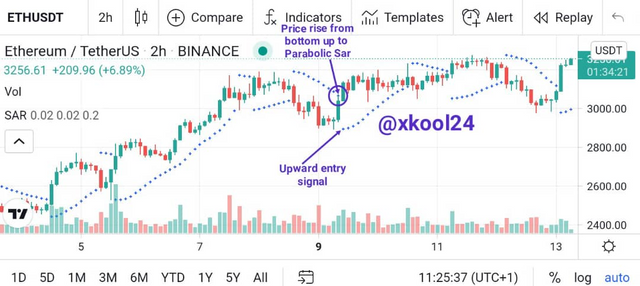
Parabolic SAR (Uptrend)
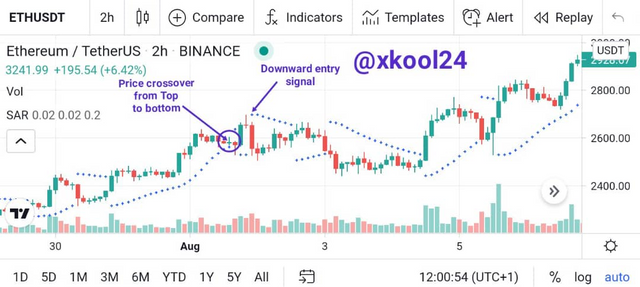
Parabolic SAR (Downtrend)
3.. Add the two indicators (Stochastic Oscillator + Parabolic Sar) and simulate a trade in the same trading view, on how a trade would be taken.
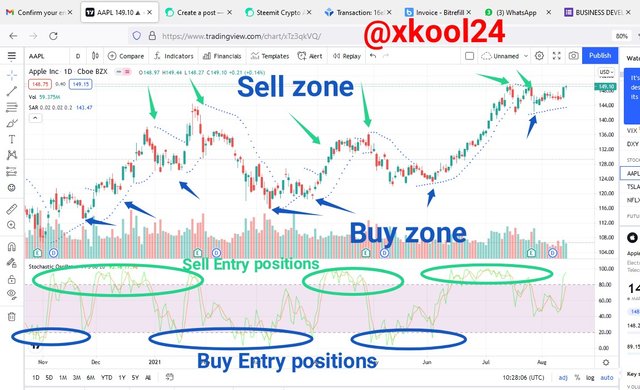
We can see the two different indicators on the chart. The SAR with the indications of buying and sell Entry positions are all marked and visible and the Stochastic Oscillator with trend like lines of the Moving average showing price movements. The Price high and Low are well-identified as well as the average Market price.