The type of energy conversion system used to produce electrical power from a geothermal resource. Geothermal energy is heat carried to the surface by hot water and steam (fluid) under pressure that is warmer than the regional atmospheric average temperature and may contain more dissolved minerals, salts, and gases than normal underground and surface waters around the temperatures formed by accumulated heat in various depths of the earth's crust. can be characterized as
Geothermal energy is often extracted from surface waters or specifically drilled boreholes by exploiting weak zones generated by ground-to-ground cracks and fractures.
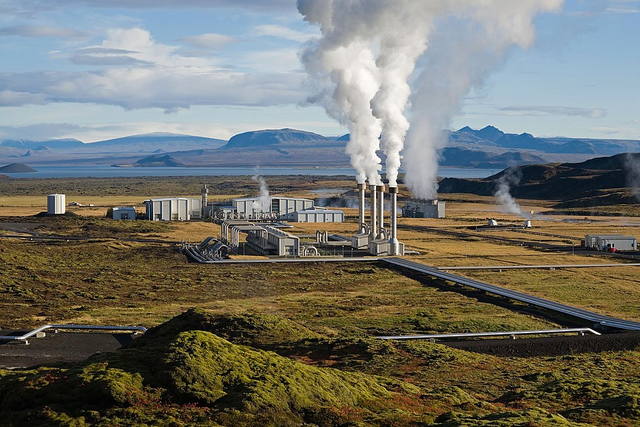
Water, steam, hot rocks, and magma are examples of geothermal energy sources found in close proximity to the earth. The fluid contains more molten minerals, different salts, and gases than regular subsurface and surface waters because to the heat source's overheating. Geothermal energy is one of the most important fossil-fuel-free energy sources.
"Geothermal fluid" is one of the most significant components of geothermal energy systems. The fluids (liquids and gases) trapped in the rocks or circulating in various ways are heated by the heat in the ground (convective, conductive, etc.). Geothermal fluids refer to all of these heated liquids or gases.
Geothermal energy is a domestic energy source that is renewable, sustainable, inexhaustible, affordable, reliable, and ecologically beneficial.
There are three major components to geothermal resources:
Geothermal energy source; this is the area where geothermal energy is generated.
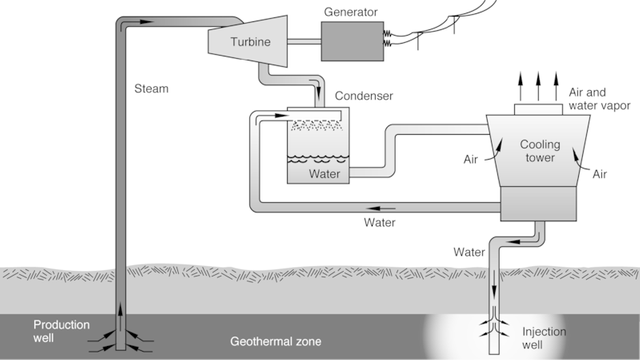
Fluid that transports heat from beneath to the surface; in a geothermal energy system, it is the fluid that transfers energy from the geothermal heat source to the turbine and provides work.
Rock permeability adequate to flow water; the region should be suitable for drilling in order to reach the heat source.
Hot rock and high groundwater temperatures are found in shallower areas in geothermal areas than in typical settings. The following are some of the key causes for this:
- Because magma rises towards the crust, it carries heat.
- Heat flow, which happens as a result of a large temperature difference in areas where the crust is thinner.
- After a few kilometers underground, the water warms up and rises to the surface.
Applications of Geothermal Energy
There are seven different uses for geothermal energy. These are:
At temperatures of 130°C and above, electricity may be generated economically.
Buildings, cities, greenhouses, and other structures that require air conditioning (heating and cooling).
Heating, drying, frying, and other industrial applications
Dry ice (CO2), Li, various salts, H2, Heavy water, Boric Acid, Ammonium Bicarbonate, Fertilizer, and other chemical substances are produced.
Thermal tourism (use for spa purposes): In balneology, a temperature of 36-45°C is ideal.
Aquaculture
Use as a mineral water substitute
Integrated Use: Integrated applications refer to the usage of the above benefits in combination based on their physical and chemical qualities (electricity generation, heating-cooling, industrial use, chemical production CO2, greenhouse, spa, etc.).
Reference:


Electronic-terrorism, voice to skull and neuro monitoring on Hive and Steem. You can ignore this, but your going to wish you didnt soon. This is happening whether you believe it or not. https://steemit.com/fyrstikken/@sqube/3dhq8e-i-am-the-only-motherfucker-on-the-internet-pointing-to-a-direct-source-for-voice-to-skull-electronic-terrorism
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit