Introduction.
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is an advanced database mechanism that allows transparent information sharing within a business network.
A blockchain database stores data in blocks that are linked together in a chain. A blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology.
The technology was developed to allow a secure way for two parties to deal directly with each other without the need for a third party in between to intermediate.
History of Blockchain Technology
The concept of blockchain technology first appeared in David Lee Chaum’s Berkeley PhD dissertation in 1982 entitled ”Computer Systems Established, Maintained and Trusted by Mutually Suspicious Groups.
However, blockchains came to the forefront in 2008 in the Bitcoin whitepaper published pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto titled “Bitcoin:
uses
you can use blockchain technology to create an unalterable or immutable ledger for tracking orders, payments, accounts, and other transactions.
Source
The system has built-in mechanisms that prevent unauthorized transaction entries and create consistency in the shared view of these transactions.
Blockchains can also be used for any variety of decentralized record-keeping purposes.
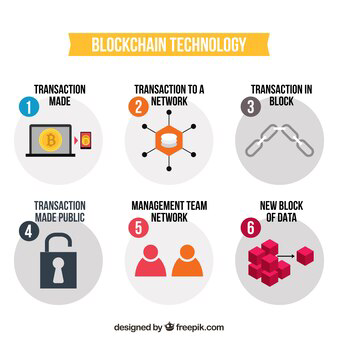
Blockchain Work.
Blockchains can be understood as something simple, like an analogy of an on-line purchase, say from Amazon.
The chain works in one direction only via a time-stamp, just like your Amazon order tracker, which means that no one can go back and tamper with earlier steps so the delivery person can’t go back and status the order to steal your purchase.
What are some real-world applications of blockchain technology?
Blockchain has a wide range of applications in healthcare, including improving payment processing, electronic medical records, provider directories, and data security and exchange.
There are some common applications to use through the blockchain database.
Money transfer
Internet of Things
Healthcare
Government
Media
Blockchain in Money Transfer.
Eliminating bureaucratic red tape, making ledger systems real-time and reducing third-party fees, blockchain can save the largest banks lots of money. Most of the companies use blockchain to efficiently transfer money.
Blockchain and internet of things.
Blockchain-infused internet of things adds a higher level of security to prevent data breaches by utilizing transparency and virtual incorruptibility of the technology to keep things “smart.” a few companies using blockchain to make the Internet of Things safer and smarter.
Blockchain in Healthcare.
Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain in healthcare solutions have shown the potential to reduce healthcare costs, improve access to information.
to wait on insurance information. The blockchain can automatically verify whether a patient has insurance and is covered.

Source
Additionally, drug and clinical trials can easily identify top candidates through a blockchain-based portal that safely shows patient medical records and identifies.
Blockchain in Government.
One of the most surprising applications for blockchain can be in the form of improving government.
As mentioned previously, some state governments like Illinois are already using the technology to secure government documents, but blockchain can also improve bureaucratic efficiency, accountability and reduce massive financial burdens.
Blockchain in Media.
Many of the current problems in media deal with data privacy, royalty payments and piracy of intellectual property.

Source
Additionally, blockchain can maintain data integrity, allowing advertising agencies to target the right customers, and musicians to receive proper royalties for original works.
What are the key differences between public and private blockchains?
Difference between Public and private blockchains.
Public blockchain.
Public blockchain are open to anyone and operate on the principle of transparency, allowing anyone to join the network, validate transactions, and contribute to the consensus proces. Public blockchains prioritize decentralization and are commonly used for cryptocurrencies.

Source
Public blockchains are maintained by a distributed network of nodes, which work together to verify and validate transactions.
One of the key advantages of public blockchains is their security, as the decentralized nature of the network makes it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the data.

Source
Public blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, have transformed the world of cryptocurrencies. They offer transparency, security, and accountability, making them ideal for industries that require trust.
private blockchain.
A private blockchain is one in which only specific users have access and abilities and is generally used only by the entity it belongs to.
Source
Private Blockchains are restrictive and operate within closed networks, suitable for internal use within organizations. Examples include Hyperledger Fabric and R3 Corda.Private blockchains are often used by businesses, organizations, and government agencies to implement secure and transparent record-keeping systems.
Private blockchains can also provide added security to sensitive information and allow for greater control over who has access to the data on the network.
According to my point of view, blockchain very useful Tarnsferring database with private and public place so, the blockchain difficult for anyone to hack or change. I hope it will be very beneficial post.
@mona01
Improve your performance by becoming a part of any club and member so that you can get more support
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Good morning Mona, first of all it's not steem for Pakistan community.
It's #steem4blogger community in which you post your blog.
It surprised me that being a new user you have shared a detailed post on blockchain .
Your post is réaly very informative.
Keep it up
And best of luck in future
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit