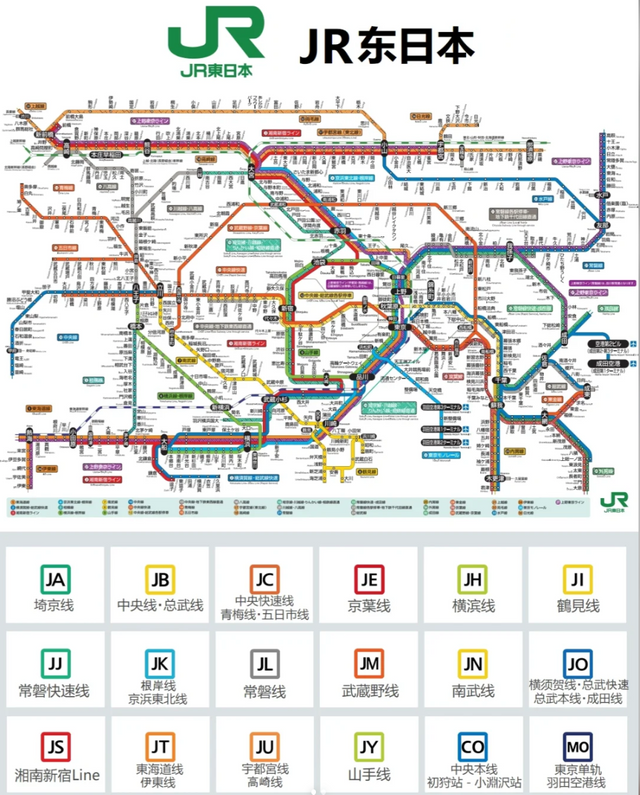
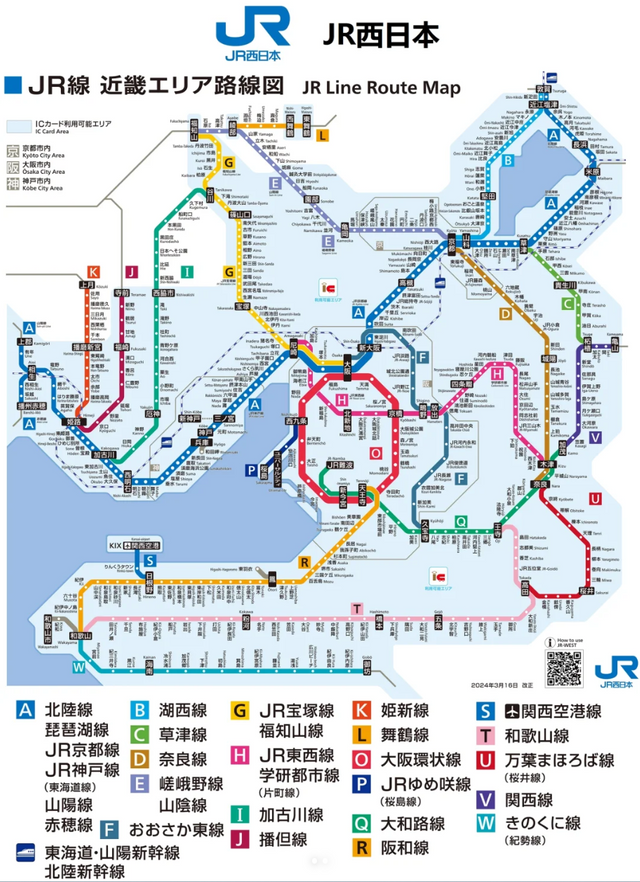
Japan is renowned for having one of the most intricate railway networks in the world. Even seasoned travelers may find themselves caught in the "wrong train" curse when navigating this vast system for the first time 😇😇😇. You might realize that relying solely on Google Maps and a sharp mind isn’t quite enough. Standing on the platform, you could find yourself asking, "Is this the right train? Should I get on this one?❓"
The root of this confusion lies in the significant differences between Japan’s railway system and the transportation habits in many other countries. To truly master Japan’s railways, it’s essential to understand the underlying logic and recognize how it differs from what you might be accustomed to. By doing so, you’ll find yourself navigating Japan’s complex rail network with confidence.
Here are the 7️⃣ key elements you should consider: Destination, Operator, Platform, Train Type, Train Number, Time, and Seat.
Railways in other countries: In many places, the primary reference for travel is the train number. For instance, the number might represent a specific high-speed train from one city to another. Once you know the train number, you can easily figure out the departure time and platform. Hence, the travel logic is: Train Number > Other Elements.
Japan’s Railways: In Japan, such integrated train number information is often lacking. Therefore, you must rely on other elements to ensure you board the correct train. The priority and sequence of information to consider when traveling by train in Japan should be:
1️⃣ Destination > 2️⃣ Operator > 3️⃣ Platform > 4️⃣ Train Type > 5️⃣ Time > 6️⃣ Seat
1️⃣Destination 🌍: Knowing your starting point and destination is the foundation of all your travel decisions. For example, traveling from Kansai Airport to Osaka is a simple but essential piece of information.
2️⃣Operator/Line 🚇: This is one of the primary sources of complexity in Japan’s railway system. Unlike in some countries where the railways are typically managed by a single national entity, Japan's railways are operated by multiple companies, such as JR, Kintetsu, municipal subways, and private railways. Each line may have its own entrance gate, so you’ll need to find the correct gate, much like transferring from a high-speed train to a subway where you must exit and re-enter through different gates.
3️⃣Platform 🛤️: Japanese platforms are usually organized by the direction of travel. Trains heading in the same direction generally depart from the same platform. After entering the station, your first step is to check the large screens for the destination and platform number. Of course, Google Maps can also help you confirm this information.
4️⃣ Train Type 🚆: Once on the platform, look at the signs to identify the "Train Type" and "Time." The train type indicates whether it's an express, rapid, local, etc. Since trains in the same direction can arrive frequently, if there’s a slight time discrepancy on Google Maps, you can use the train type to decide whether to board.
5️⃣Time ⏰: Japan's railways are known for their punctuality, so checking the departure time on Google Maps is a reliable way to ensure you’re getting on the right train.
6️⃣Seat 💺: Seats in Japan are divided into reserved and unreserved categories. Reserved seats require prior booking, while unreserved seats are first-come, first-served. Trains often have designated cars for each type of seat.
In Summary:
Japan’s railway system might remind you of pre-digital era travel habits in some countries. Once you’ve mastered these 7 key elements, you’ll be able to navigate Japan’s complex railway network with ease, even without GPS!