Components of Road Structure | Methods of Construction of Road Structure. Sub Grade:
Subgrade is the foundation of the road, thus its the lowest and most important component of road structure.
Construction:
If natural surface is above the formation level then the surface is cut down to proposed sub grade surface
If natural surface is below the formation level then the sub grade will be above the ground level
It should be constructed at least 60 cm (2ft) high from highest flood level of the area
Function of Sub grade:
Bears all the load thus acts as a foundation of road
Material:
Material of sub grade should be strong enough to bear the loads, easily accessible and available in the vicinity and cheap.
Construction:
Constructed above the sub grade
Not needed if the sub grade is of very high strength
In case of flexible pavement upper and lower base courses are separated having different materials
In case of rigid pavement only upper base course is provided
Thickness varies from 7.5 (3in) to 15cm (6in)
Functions of sub base:
Prevent rise of water or capillary action
Material:
Should be better than the material of Sub Grade
The Upper Base Course is made up of sand, gravel, and stone
The Lower Base Course is made up of cheaply available material i-e rock and stone fragments
- Road Base:
Due to quality of material used in the road base it is divided into
Upper Road Base
Lower Road Base
Construction:
Constructed above the Sub Base
Functions of Road Base:
To avoid the distortion of wearing course due to its sufficient density
Supports the wearing course
Material:
In case of Upper Road Base the material is of high quality as the load intensity is high
In case of Lower Road Base the material is of high quality as the load intensity decreases
- Surfacing:
It is the upper most layer of road cross section. It can be provided in one or two layers:Construction:
Constructed usually in two layers
Binder Course
Wearing Course (It is the layer which is in direct contact with the tyres of the vehicle)
Functions of Surfacing of Road:
Prevent penetration of water in to the pavement
Binder Course binds the Wearing Course with the Road Base
Wearing Course provide a smooth riding
Saves the lower layers from abrasion and weathering effects of the moving vehicles
Material:
Made up of bituminous material
For Flexible Pavement asphalt concrete is used
For Rigid Pavements Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC) is used
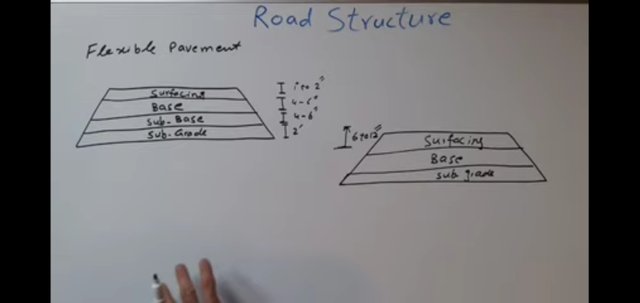
- Sub Base:
Transfer load through grain to grain contact