Navigating Your Data Career: A Comprehensive Guide to Planning and Progression
The world of data careers is vast and varied, offering numerous paths and opportunities for growth. Whether you're just starting out or looking to pivot within the industry, understanding the data career landscape and typical migration paths can help you make informed decisions about your professional future. In this guide, we'll explore the data career landscape in detail, examine common migration paths, and provide practical tips for selecting and progressing in the right track.
The Data Career Landscape: A Closer Look
The data career landscape is a map of roles and opportunities, each defined by specific job activities, deliverables, and skill sets. Here's an in-depth look at the various roles and how they fit into the broader landscape.
Role Classes and Their Focus
Individual Contributor Roles: These roles are typically focused on executing specific tasks and responsibilities. They include:
- Data Analyst: Analyzes data to provide actionable insights and support business decisions. Skills often include data visualization, statistical analysis, and proficiency in tools like Excel or Tableau.
- Business Analyst: Bridges the gap between business needs and technical solutions. Responsibilities include gathering requirements, creating reports, and suggesting improvements based on data analysis.
- Data Engineer: Designs, builds, and maintains the infrastructure required for data generation and processing. Key skills include programming (e.g., Python, SQL), data warehousing, and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes.
Management Roles: As you advance in your career, you may take on roles that involve leading teams and managing projects:
- Data Team Lead: Oversees a team of data professionals, ensuring projects are completed on time and meet quality standards. Requires leadership skills, project management experience, and a deep understanding of data processes.
- Data Engineering Manager: Manages the data engineering team, focusing on optimizing data pipelines and ensuring data quality. This role combines technical expertise with team management skills.
Executive Roles: At the top of the career ladder, executive roles involve strategic decision-making and high-level leadership:
- Chief Data Officer (CDO): Responsible for the overall data strategy and governance within an organization. This role involves setting data policies, ensuring compliance, and driving data-driven decision-making at the executive level.
- VP of Data Strategy: Focuses on aligning data initiatives with business goals, overseeing data projects, and ensuring the effective use of data across the organization.
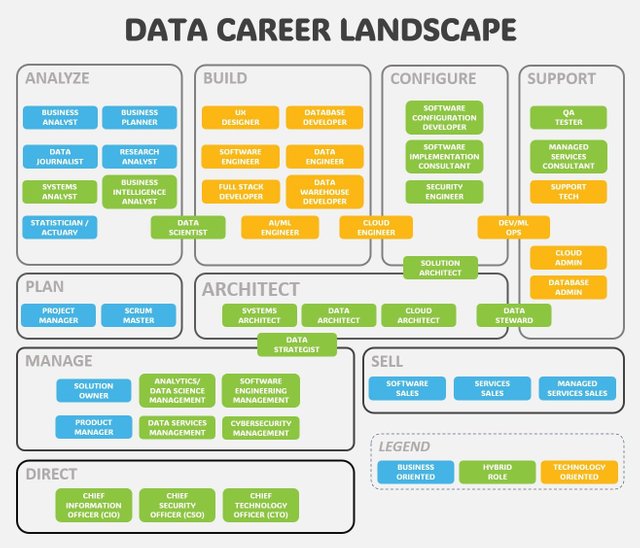
Color-Coded Tracks
In the career landscape, roles are often color-coded based on their focus:
- Technical Focus: Roles with a strong emphasis on technical skills and data manipulation, such as Data Scientist or Dev/ML Ops.
- Business Focus: Roles centered around using data to drive business decisions, such as Business Analyst or BI Analyst.
- Hybrid Focus: Roles that require a blend of technical and business skills, like Data Scientist or Product Analytics.
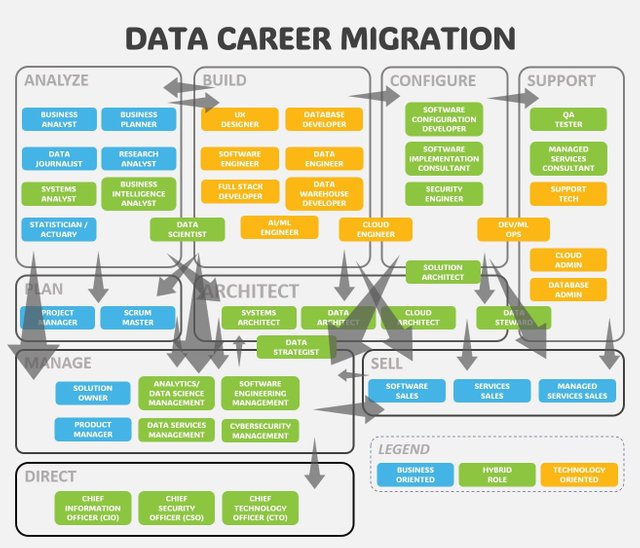
Exploring Career Migration Paths
Understanding how to transition from one role to another can help you plan your career development and identify potential opportunities for growth. Here’s a closer look at typical migration paths:
From Individual Contributor to Management
- Progression Example: A Data Analyst might evolve into a Data Engineering Manager. This transition involves gaining experience in project management, leadership, and a deeper understanding of data architecture.
From Technical Roles to Hybrid Roles
- Progression Example: A Data Engineer might move into a Data Scientist role. This transition involves acquiring additional skills in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data modeling.
From Management to Executive Roles
- Progression Example: A Data Team Lead might advance to a Chief Data Officer position. This path requires demonstrating strategic vision, leadership capabilities, and a proven track record of successful data initiatives.
Challenges in Career Migration
- Cross-Class Transitions: Moving between roles in different classes, such as transitioning from Project Management to Salesforce Development, can be challenging due to differing skill requirements.
- Reverting to Technical Roles: Shifting from an executive role back to a technical position can be difficult due to skill attrition and a potential decrease in salary.
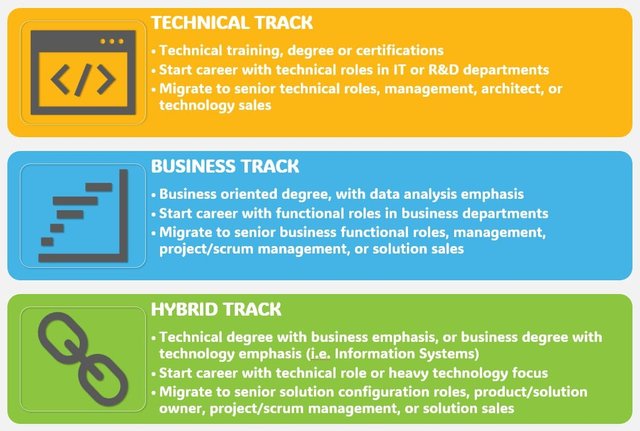
Choosing the Right Track: Tips and Considerations
Selecting the right career track is crucial for long-term satisfaction and success. Here’s how to evaluate and choose the best path for you:
Evaluating Your Interests and Skills
- Technical Track: If you enjoy coding, data manipulation, and working with complex systems, a technical track might be suitable. Roles in this track often lead to hybrid positions and involve hands-on technical work.
- Business Track: If you’re interested in using data to drive business decisions and enjoy interpreting trends and patterns, a business track may be more appropriate. Transitioning to technical roles from this track can be challenging, so consider additional training if needed.
Gaining Relevant Experience and Skills
- Further Education: If you’re aiming for a role that requires skills you currently lack, consider pursuing relevant coursework or certifications. For example, if you want to become a Data Scientist, courses in machine learning and statistics can be valuable.
- Networking and Mentorship: Connect with professionals in your desired roles to gain insights and advice. Mentors can provide guidance, help you navigate career transitions, and introduce you to new opportunities.
Staying Informed About Industry Trends
- Industry Growth: The data industry is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging regularly. Stay updated on trends and advancements to ensure your skills remain relevant and to identify new career opportunities.
Conclusion: Embrace Your Career Journey
Navigating your data career is a dynamic and ongoing process. While it’s natural to feel uncertain about your long-term future, focusing on understanding the data career landscape and exploring various roles can help you make informed decisions and plan for success.
The data field offers a wealth of opportunities, and with continuous learning and adaptability, you can carve out a fulfilling and rewarding career. Remember, career progression is a journey, not a destination. Embrace the possibilities, stay curious, and take proactive steps to shape your career path.
Thank you, friend!


I'm @steem.history, who is steem witness.
Thank you for witnessvoting for me.
please click it!
(Go to https://steemit.com/~witnesses and type fbslo at the bottom of the page)
The weight is reduced because of the lack of Voting Power. If you vote for me as a witness, you can get my little vote.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit