Major depression can seriously impact your quality of life and ability to enjoy living life. It can also cause a dramatic reduction in your relationships, job and work life and more frequent depressive moods can occur. Depressive mood swings can last for weeks to months, and cycles can occur over time as well. In women, depression is often linked to menopause or the hormonal changes that accompany it. Depression can be a silent killer, but if left untreated, it can destroy your quality of life, relationships and sense of self.
There are certain risk factors that increase the likelihood that someone will develop depression. These include stress, substance abuse, poor diet, not getting enough exercise, having a faulty understanding of one's body and/or brain chemistry, and not getting enough sleep. As we have mentioned before, depression is a common symptom of many illnesses including Alzheimer's disease, which is a degenerative mental disorder that takes several years to develop. Stress, poor diet, not getting enough sleep, not exercising, and a faulty understanding of one's body and/or brain chemistry can lead to serious mood problems throughout life.
There is an important distinction between stress and depression. While they both can be very real problems that can cause physical pain, they are not the same thing. Depression is a depressive state, and a stressful response in the brain is what pushes your mind into that state. On the other hand, stress response is how your body deals with actual threats or dangers, such as physical injury or a dangerous situation.
Antidepressant medications can play a role in managing mood swings and depression. They work to change the chemical compounds in the brain which are responsible for causing mood changes. There are three types of antidepressants, including tricyclics (TCA), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or SSRIs. These medications are divided into two main categories: monoamine oxidase inhibitors or MAOIs, which inhibit the conversion of serotonin into its constituent molecules, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or SSRIs, which help regulate serotonin levels in the brain. Because some people respond to treatments differently than others, it is important to discuss your treatment options with your doctor to determine the best course of treatment for you.
As mentioned above, people with mild depression may feel better after taking an anti-depressant. However, if your depression lasts for more than a few weeks, it may be time to talk to your doctor about possible side effects. Some of the side effects of depression may include excessive weight gain, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, decreased sex drive, sleep disturbance, increased appetite, nausea, and general feelings of anxiety, agitation, or fatigue. While the symptoms may vary from case to case, most people who experience these symptoms will be prescribed a form of medication to help them through their depression. Common depression medications include anti-depressants and tranquilizers.
Another type of depression medications include mood stabilizers, also referred to as MAOIs, that are usually used to treat patients who have already experienced significant changes in their moods but do not yet qualify as bipolar disorder. Doctors often prescribe MAOIs such as Man1 Manco, Prozac, and Zoloft for those who are depressed but do not yet have Bipolar or Clinical Depression Disorder. MAOIs work by changing the chemical balance in the brain, causing the cells to assume a more stable state and allowing the patient's moods to return to normal more quickly. This is often vital in people who have had heart attacks or who have been sick and are not responding to other forms of treatment. Some people with depression who take MAOIs find that they enjoy a sense of well being after the medication has been prescribed.
There are also alternative forms of treatment available for those who suffer from depression or bipolar disorder. Yoga, hypnosis, acupuncture, relaxation techniques, biofeedback, and psychotherapy can all be effective in treating depression and controlling mood disorders. Many of these methods are often used in conjunction with traditional forms of medicine. Many patients find that a combination of prescription medications and alternative forms of treatment are most effective. A person with depression or Bipolar Disorder should discuss all of their options with their physician to determine which treatment will offer the best results.
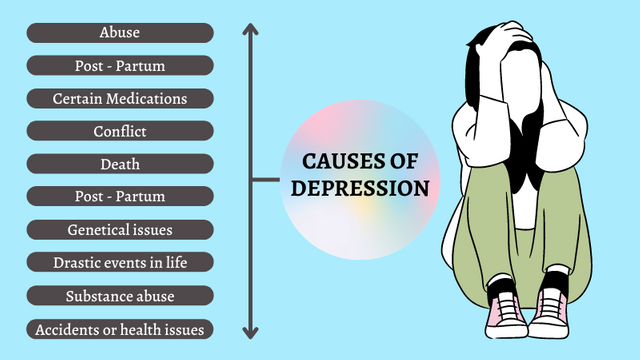
There is no one single cause of depression. Although there is a strong connection between major events in a person's life and the onset of depression, there is no known cause, as well. What research suggests is that major life changes, especially the loss of a loved one or a traumatic experience can change brain chemistry and cause changes in the chemical balances of the brain that lead to depression. Alternative treatments, such as those mentioned above, may help to alleviate the symptoms associated with depression and allow a person to get back to living their life normally. When suffering from depression, it's important to consult your doctor to ensure that the treatment you're considering is one that can work for you.
References
https://www.webmd.com/depression/guide/causes-depression
https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/conditions/clinical-depression/causes/
https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/what-causes-depression