20% Beneficiary to @steemit-pak for community grown up and support to Newcomers like me
Preface
Remote Sensing data is one of the primitive data sources in GIS analysis. The purpose of this material is to provide basics of Remote Sensing technology and its applications in GIS to students and the one who wants to study about Remote Sensing technology by prominently (Read less learn more).However, Remote Sensing technology had been well inaugurated for many decades and still rising. Controlling and interpretation of remote sensing data will never be handy or easy. It requires many practical works and digital image processing information. It is not possible to cover all topics in here. So, here I provide further learning information.
I hope you’ll enjoy it
Definition
What is Remote Sensing? If you are reading this question, now you are doing Remote Sensing. In fact, any information acquired from the object without touching by yourself is Remote Sensing. Following is a scientific explanation of Remote Sensing.
The science of getting information about the earth using different instruments which are remote to the earth's surface, generally from aircraft or satellites. Instruments may use visible light, infrared or radar to collect data. Remote sensing provide the ability to observe and collect data for large areas relatively very fast, and is an main source of data for GIS.
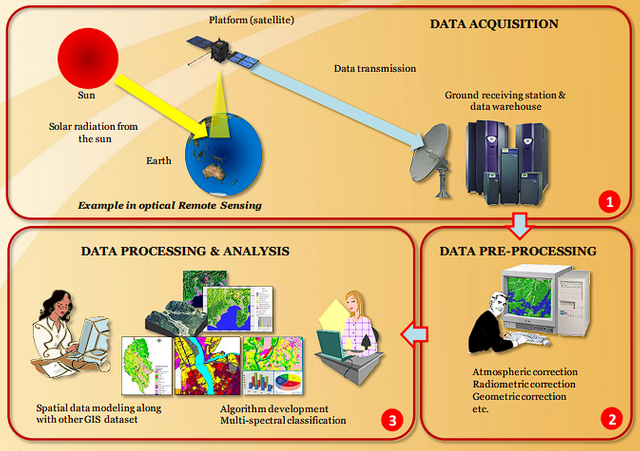
Remote Sensing and GIS Work Flow
Components In Remote Sensing
Platform
The vehicle which holds a sensor. i.e. satellite, aircraft, balloon, etc...Sensors
Device that accept electromagnetic radiation and transform it into a wave that can be documented and displayed as either numerical data or an image.Type Of Remote Sensing
| Passive Remote Sensing | Active Remote Sensing |
|---|
Passive Remote Sensing
Remote sensing of energy naturally reflected or radiated from the terrain.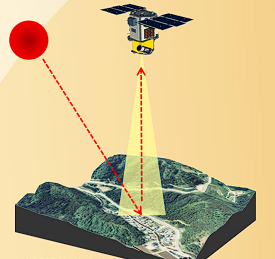
Active Remote Sensing
Remote sensing methods that sustain their own source of electromagnetic radiation to clarify the terrain. Radar is one example.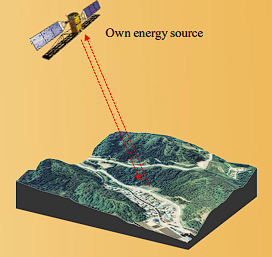
Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis
Remote Sensing Data Pre-processing
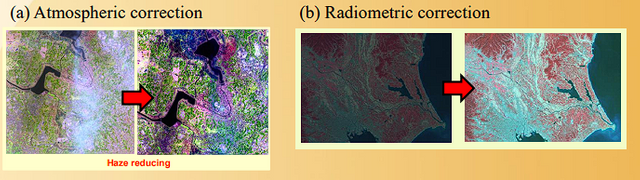
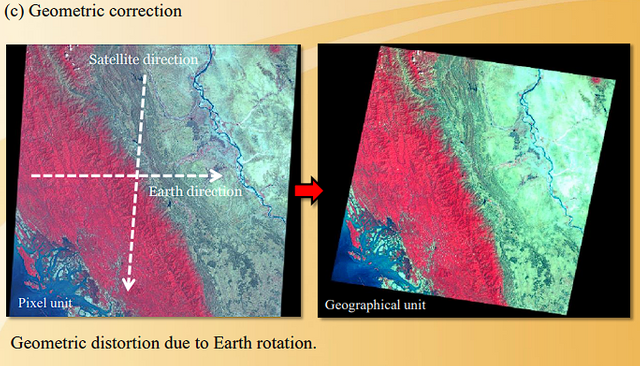
(a) Atmospheric correction(b) Radiometric correction
(c) Geometric correction
However, most remote sensing data can be obtained or purchased atmospheric, radio metric and geometric corrected data. Here, we will introduce briefly.
Methods of Geometric correction
1.Using satellite header file (satellite onboard GPS)
2.Image to image registration
3.Image to map registration
4.Manually entered GCPs (Ground Control Points)
Remote Sensing Data Applications in GIS
Urban Greenness (Eco-friendly Walk Score Calculator)
Eco-friendly Walk Score measures the degree of greenness (green density) by user defined geographic patterns based on Normalized Different Vegetation Index (NDVI).
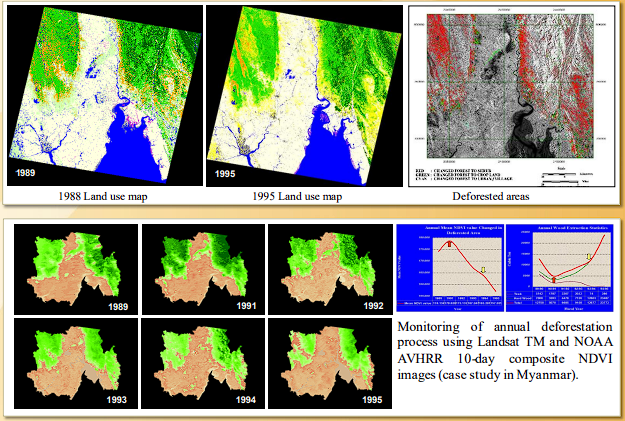
Monitoring of Deforestation Process
Surface Steepness Measurement from LIDAR

DTM and DSM propagation form LIDAR data to measure terrain height and surface height (from sea level).
DTM = Digital Terrain Model
DSM = Digital Surface Model
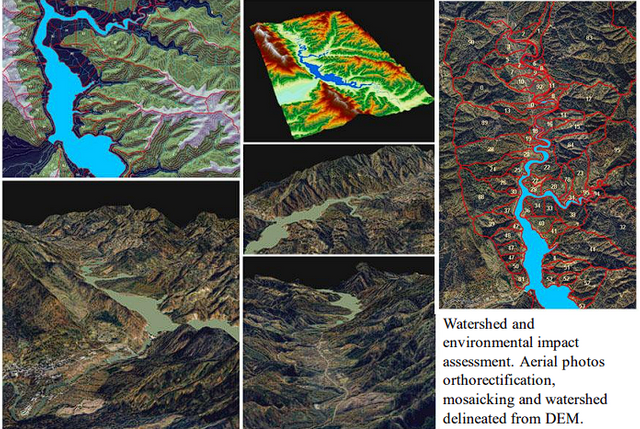
Watershed and Environmental Impact Assessment
Conclusion
In “stating our case” as to the importance of both RS and GIS in making a contribution to the future success of both aquaculture and inland fisheries. There will be an enlarged demand for GIS effectiveness at all levels of government, reflecting local, regional, national, multinational; and global concerns…” The daily life application of RS and GIS to aquaculture and inland fisheries can be our helping hand to meeting these needs.CC,
@steemcurator02
@steemcurator01
@hassanabid
@haidermehdi
@salmanwains
@rashid001
@event-horizon

| 50 SP | 100 SP | 200 SP | 300 SP | 400 SP | 500 SP |
|---|
| 1000 SP | 1500 SP | 2000 SP | 3000 SP | 4000 SP | 5000 SP |
|---|