Credit : Shutterstock
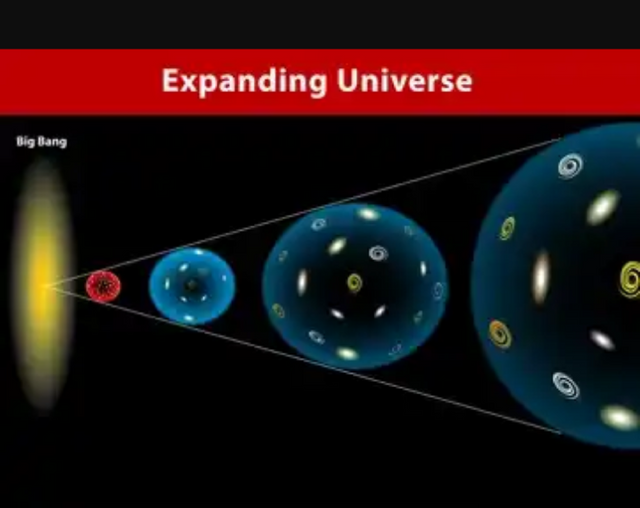
The universe is expanding due to the presence of an assumed entity called ''dark matter '', however the concept of the universe's expansion began originally in 1917 when Einstein introduced the cosmological constant in his field equations - A mathematical representation of the theory of general relativity, to account for a static universe. Later in 1922 the Russian physicist Alexander Friedmann showed mathematically that Einstein's field equations including the cosmological constant were valid in a dynamic universe and later in 1998 it was discovered experimentally that the universe was indeed dynamic (expanding).
What is generally concluded about the universe's expansion is that it's expansion speed/rate is greater than the vacuum speed of light, but the exact expansion rate is still a matter of debate, which has now been dubbed the '' Hubble tension ''.


The reason being that different rate values has been reported from different collaborating observers and also due to the different techniques used. Some group reports the Hubble consant (used in calculating expansion rate) as 73.24 ± 1.74 Km/s/Mpc while some reports it as 67.4 ± 0.5 Km/s/Mpc, this has prompted some physicists hinting at the possibility of a new physics.
However a new technique published recently in Physical review A has been proposed to tackle these challenges. According to this technique Read more.