A hydrocarbon is a natural compound in which hydrogen and carbon particles are the sole components. In other words, hydrogen and carbon must be present to form hydrocarbons.
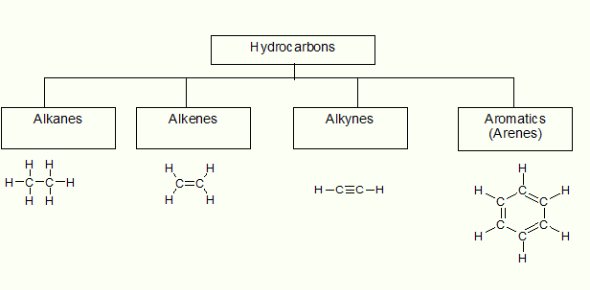
Depending on chain structures, open chain organic compounds and closed chain organic compounds are the deciding factors for the classification of hydrocarbons. Furthermore, open chain organic compounds refer to alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes, whereas Benzene (aromatic hydrocarbon) is one of the most discussed closed chain organic compounds in organic chemistry. In organic compounds with open chain structures, single chemical bonds (σ) between carbon and carbon create saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes). On the other hand, double chemical bonds (σ : 1, π : 1) and triple chemical bonds (σ : 1, π : 2) between carbon and carbon, initiating alkenes and alkynes, respectively, refer to non-saturated hydrocarbons.
The general form of alkanes (CnH2n+2), alkenes (CnH2n), and alkynes (CnH2n-2) denotes the number of carbon and hydrogen in which “n” is a whole number. In contrast, the transferrable and delocalized (4n+2: where n = 1 for Benzene) number of π electrons (which is 6 for Benzene) among carbon and carbon bonds are entirely responsible for Benzene’s (C6H6) structure.
Hydrocarbons’ derivatives can be obtained by welcoming different chemical elements and compounds replacing hydrogen(s), bearing in mind the existence of carbon and hydrocarbon in the respective chain. Hydrocarbons and derivatives can be converted from one into another by active chemical reactions with different catalysts and temperatures.
Hydrocarbons are profoundly burnable and the principal energy wellspring of the world. Hydrocarbons are achievable and getable from natural sources such as crude oil, natural gas, coal, and relevant energy sources. Saturated, non-saturated, and aromatic hydrocarbons are easy to prepare in chemical Labs although natural sources are available.
Nice post
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit