THE anatomy of blocks in a blockchain
The structure and components that make up a block in a blockchain.
Anatomy of a block
✅ A chain of blocks is digital information stored in a distributed database.
✅ A block contains information about transactions, digital signatures and a unique code called a hash.
✅ Each block has a height that indicates its number and a date of creation.
✅ The hash of the previous block is used to connect the blocks as a chain from the genesis block.

✅ Modifying information in a block is difficult due to cryptographic algorithms and the collective capacity of the network.
✅ The body of the block contains the transactions or financial information, users, products, suppliers, etc.
✅ Blocks can contain thousands of transactions and are limited by block size to avoid network congestion.
✅ Each block has a nonce (arbitrary number used by miners to find the hash of the block).
✅ Miners are rewarded for finding valid hashes, but this job is very difficult and time consuming.
✅ Anyone can download a copy of the blockchain and become a node on the network.
Building and Continuity of the Blockchain
Explores how the blockchain is built and maintained.
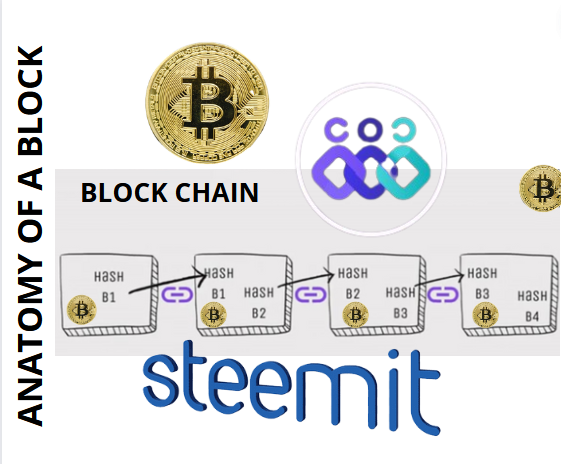
✅ Nodes in the network are notified when a new block is created and verify its hash before adding it to the chain.
✅ Each new block contains the hash of the previous block, which ensures the continuity of the chain.
✅ This process guarantees that the blocks are sequentially linked and cannot be modified without breaking the chain.
✅ Building a block marks the beginning of a new job to build the next block.
Conclusions
In short, the blocks in a blockchain contain information about transactions, digital signatures, and a unique code called a hash. Each block is connected to the previous one through its hash, forming an immutable and irreversible chain. Building and maintaining the chain requires significant computational effort on the part of the miners. The nodes in the network verify each new block before adding it to the chain to ensure its integrity.

✅ SteemPro Official
........Download SteemPro Mobile.
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.steempro.mobile
........Visit here.
https://www.steempro.com/
........SteemPro Discord
https://discord.com/invite/Bsf98vMg6U
If you like my publication, I will be gladly accepting your valuable consideration, a thousand blessings for your generosity @oscardavid79
✅ Vote @bangla.witness as lead witness please. Thank you for reading me grateful.....
Let's remember to comment on my publication, I will gladly answer you. This article is written by @OscarDavid79 free of copyright 🇻🇪 |
|---|
.gif)
Twitter
https://twitter.com/oscardavidd79/status/1690151274753208320
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you for supporting
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
good explanation guys.
in the hash, sometimes we don't only see our transactions, but there are other transactions wrapped in the same way as our transactions in that one block. 😉
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
thank you for your comment and that you liked it
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit