
The Floppy Diskette 💾
The first floppy disks, a 1971 invention by International Business Machines (IBM) was an 8-inch storage device. It was improved into a 51/4 mini disk, and later in 1982 Sony introduced a 31/2 microfloppy disk which was later called the diskettes. Able to hold a then whooping 1.44 Mb of data.
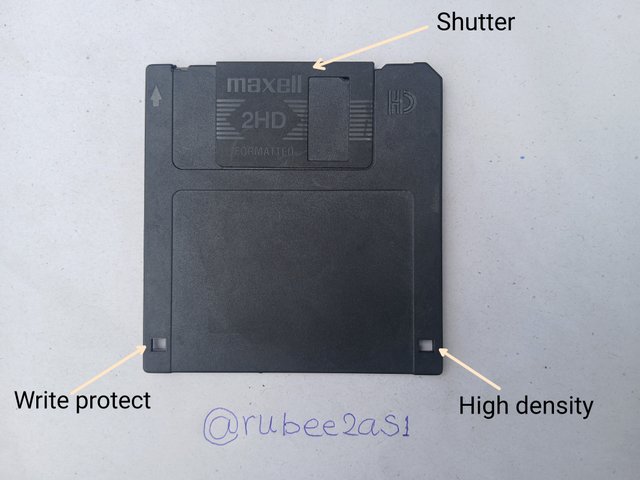
Compared to the full or mini floppy, the floppy diskette was protected by a thick outer cover and a shutter that automatically covers the read/write area of the diskette.
It was improved into the 2.8 megabyte Extended Extended Density and the 120 Mb super diskettes, which did not really make the market due to high cost.
Insights into the technology
The floppy diskette technology used magnetism to save data, the same technology used in storing music on cassette tapes. Inside the diskette was a flexible magnetic disk with a thin magnetic coating on its surface. A read/write head hovering above the diskette's surface, using magnetisation for reading and writing data on small areas of the disk called domains. For proper organisation, during formating, the flexible magnetic diskette was arranged into tracks and sectors which stored the data.
When you saved data to a floppy diskette, the read/write head would magnetise the domains on the diskette, encoding your data onto the diskette's surface.
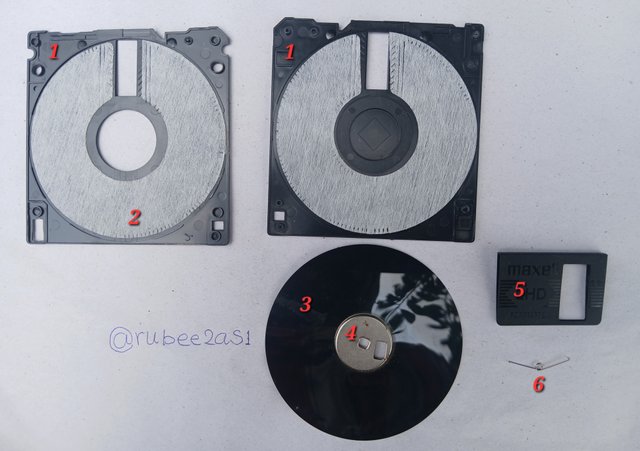

1- The external jacket
This is the outer cover that protects the flexible magnetic diskette from mechanical damage.
2 - The liner
The liner is a soft paper material that lines the inner walls of the jacket to prevent the magnetic disk from scratching on the jacket during operation.
3 - The Mylar
This is a flexible plastic material coated with a magnetic coating. It is on this material that the data is being stored.
4 - The Hub
This is a circular metal at the centre of the diskette's mylar. The diskette drive hooks and spins the mylar through the hub.
5 - The shutter
Thus is a protective door that covers the read/write opening on the diskette's jacket. It prevents sand and dust from entering the diskette.
6 - The shutter spring
Most shutters on a diskette would close automatically, and this is the work of this loaded spring.

Picture showing front and back of this old technology.
The Zip disk with its higher capacity, marked the beginning of the fall of floppy diskettes, but it was wiped out of existence by the compact disc and DVDs which offer more storage capacity and durability.
Uses of floppy diskettes
Boot diskette
Floppy diskette were formatted with bootable files to help jump-start a faulty computer. It could hold a disk operating system, making it possible to operate a computer from it.
For troubleshooting
Many computers had the option to boot from drive A: which is a floppy diskette.
Software Installation
Software distribution used floppy diskettes, it was also used to carry device drivers and configurations.
I remember having some utilities and games in my floppy diskette
Drawbacks of the technology
The standard floppy diskette had a very small storage capacity of only 1.44 mb.
The diskettes were very vulnerable, and data was often lost as the technology had magnetism as its weakness.
Data transmission speed was also very low, and the diskette were also affected by light, temperature, and humidity.
I am planning to travel deep into the past to exhume another relic from an almost forgotten time.
Appeal to community members:
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit