
Design is a broad field streamlining numerous subjects; It isn't limited to just Graphic Design but also encompasses several other disciplines in the Design industry today. When a person says: "I'm a designer", it isn't clear enough what they do every day. There are numerous piers of responsibility that hold design upright.
Design-related roles exist in a set of areas; Visualisation, graphic design, textile design, ceramic design, fashion design, print design, interior design, and many more. With the recent influx of tech organizations focused on creating interfaces for screens, many more design roles emerged.
Today we would be discussing one of the disciplines the design industry has birthed and some key roles/responsibilities involved in such a field.
--
UI/UX DESIGN
We’ve all overheard conversations, chats, talk shows, and even seen videos discussing the great ‘UX’ of a product or the poor ‘UI’ of an app. Probably you got confused while watching or listening to those conversations. Well, you need not freight because we are here to sync you into the basics of this field.
What is UI/UX Design
UI design is simply referred to as User Interface Design while UX design is referred to as User Experience Design. Both areas are crucial to an IT product and also work closely together. Although they are integral to each other, the roles involve are quite different with distinct processes.
UX is User Experience
The user experience is still a relatively new area of discipline, with numerous companies awakening to the fact that they need someone on their payroll if they want to succeed in charming and retaining customers.
Part of the perplexity might lie in the name: " UX Design". For many people, the word “design” is related to graphics, color, styles, etc when its true meaning lies in the functionality and also methods behind producing products that provide a seamless experience for the users.
UX designer's job probably seems puzzling and confusing at first ("wait, you don't make drawings or graphics?") ("Why is the designer interviewing a lot of people?")
Well, knowing who your target customer or audience is, and how to create a delightful experience with your product is one of the responsibilities of a UX Designer. Doing such, usability, functionality, and user-adaptability ranks high in their priorities for the product.
UX Design generally focuses on the development of digital products using theories and processes.
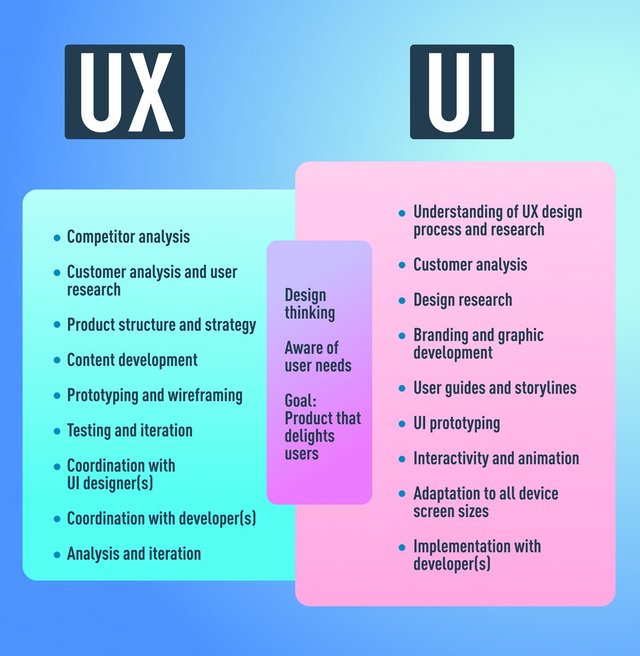
Strategy and Context:
- Product strategy and structure
- Competitor and Customer Analysis
- Content Development
Wireframing and Prototyping:
- Wireframing
- Prototyping
- Testing
- Development Planning
Analytics and Execution:
- Coordination with UI UX designers
- Coordination with developers
- Tracking goals and integration
- Iteration
UI is a User Interface
A user interface is like a joke. If you have to explain it, it's a bad one.
We all know that a car can be driven on the road. The UX to drive it is there, but the controls are arranged in such a way that it’s not intuitive , and then it is said to have a complicated UI. Creating a good UI is a challenge because it has to be intuitive.
During the research, people were asked to choose which phones they liked among Samsung phones. The majority of them said that they liked Apple. Although both brands have the same experience of a phone as a product, the majority preferred one over the other, why?
Their response was immediate and consistent: “I find Apple phones more intuitive.” some said because it was simpler, self-explanatory, the apps have a more consistent look and feel, and a lot more.
Apple’s User interface is embedded in the User experience so well that it doesn’t feel like it’s there.
UI Designer’s job includes the following:
- Look and Feel:
- Customer Analysis
- Design Research
- Branding
- Graphic Development
- User Guides/flows.
Responsiveness and Interactivity:
- UI Prototyping
- Interactivity
- Animation
- Responsiveness to all screen size
- Collaboration with developer
A UI designer makes technology easy and intuitive for users. They work on areas where users directly interact with the product in the process.
In conclusion, Something that looks good but is difficult to use is an example of a good UI and poor UX. While Something very usable but looks terrible is an example of a great UX and poor UI.
Thank you for contributing to #LearnWithSteem theme. This post has been upvoted by @reminiscence01 using @steemcurator09 account. We encourage you to keep publishing quality and original content in the Steemit ecosystem to earn support for your content.
Regards,
Team #Sevengers
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit