
INTRODUCTION
Hello and welcome to my blog. My name is Otis patience and today I will be writing on two disease that are most commonly found in an cattle abattior.
After every industrial training you will have to defend your technical report. My topic was to talk about animal diseases. As group leader I was in charge of the presentation which I did. Let's go into it.
ANIMAL DISEASE; TUBERCULOSIS
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection. It is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium. As a genus, mycobacteria are Gram-positive, acid fast bacilli. They are highly resistant to most environmental factors, many disinfectants and a large and increasing number of antibiotics.
CAUSES OF TUBERCULOSIS
CATTLE: it is caused by the bacterium
Mycobacterium bovis (M.bovis). It is mainly a respiratory disease. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but can attack any part of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain in more severe conditions.
GOAT: Tuberculosis in goat is usually caused by Mycobacterium bovis and Mycobacterium caprae
FISH: Tuberculosis in fish is usually caused by Mycobacterium marinum.
BIRDS/POULTRY: Tuberculosis is usually caused by Mycobacterium avium.
PIGS: The three Mycobacterium species that cause tuberculosis in swine are Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium bovis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
SYMPTOMS OF TUBERCULOSIS (TB)
Weight loss, fever
Night sweats
Persistent cough
Emancipation
Discharges through the nose
Difficulty in breathing
Loss of appetite
Chest pain
Fatigue
Coughing blood and sputum
STAGES OF TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION
Exposure
Latent
Active disease
ANIMAL DISEASE; CONTAGIOUS BOVINE

PLEUROPNEUMONIA (CBPP)
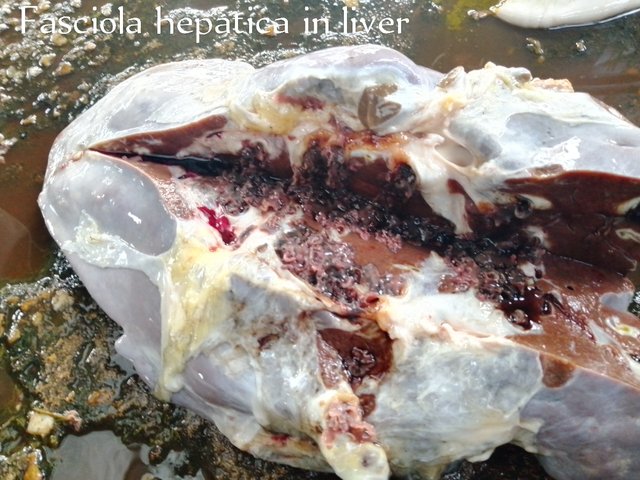
The causative agent of CBPP is Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. Mycoides (M.mycoides). It attacks the lungs and the membranes that line the thoracic cavity (the pleura) causing fever and respiratory signs.
TRANSMISSION AND SPREAD: transmission of the disease occurs through direct contact between an infected and a susceptible animal which becomes infected inhaling droplets disseminated by coughing. There is no evidence of transmission through fomites (inanimate objects such as clothing, implements or vehicles) as the organism does not persist in the environment.
PUBLIC HEALTH RISK: Humans are not known to be susceptible to CBPP, so there is no public health risk.
SIGNS:
Loss of appetite
Fever
Respiratory signs such as rapid respiratory rate, cough and nasal discharges and difficulty in breathing
Animals become recumbent (lie down)
In severe cases, animals die after 1-3 weeks.
Presence of fibrin makes the lung rigid during chronic stage of infection
STAGES OF CBPP INFECTION
Congestion – reduction of gases in the lungs
Red Hepatization – red blood cells enters the lung
Grey Hepatization – this is the worst stage of infection. The red blood cells begin to change to grey
Repair/Resolution – the lung begin repair itself
Treatment: CBPP can be treated with antibiotics such as azithromycine (zithomax), tetracycline (doxycycline) or danofloxacin which help prevents the spread of the causative mycoplasma to in-contact cattle after recovery from treatment, animal should be isolated from other animals. At chronic stage, infected animals won’t respond to treatment.
Thanks
Cc;
@focusnow
@peterabagi
@ngoenyi
@samuel20
@patience-otis, thank you for sharing your knowledge on animal diseases with us.
Please what causes tuberculosis in human body? Is it same cause as the animals? Because I noticed that some animals have similar causes while some don't........
Keep sharing quality content in steemalive community.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
We have supported this post. Keep on making great content in our community. Always check @steemalive for community updates. Thank you being an active member.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit