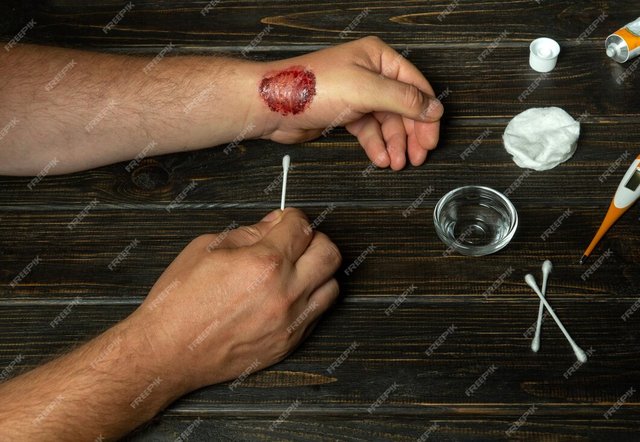
If possible, elevate the wound above the heart. This position reduces blood pressure at the injury site, slowing the bleeding further. Do not remove the cloth, even if it becomes saturated; instead, add layers of material on top to maintain constant pressure.
It is also important to be calm and assess the level of severity. If bleeding stops within 10 minutes under pressure or if it's spurting, it would be best to call the doctor immediately.
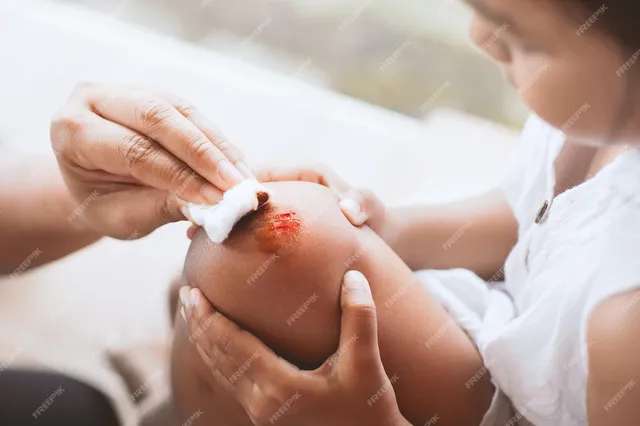
To clean a wound, rinse it gently with clean water or a saline solution to flush out dirt and debris. Mild soap can be used around the edges, but avoid applying it directly to the wound. Avoid harsh chemicals like hydrogen peroxide or alcohol, as they can damage tissue and slow healing.
Timely cleaning also minimizes inflammation and promotes faster recovery. If debris remains or bleeding persists, seek medical attention promptly to avoid further complications.
Apply pressure to the wound immediately if it is bleeding significantly. Use a clean cloth or gauze and press firmly on the wound to help slow or stop the bleeding. This is particularly important for deep wounds, as they may involve blood vessels that need time to clot. Do not lift the cloth frequently to check how things are going, as this will break the clot.
Professional medical attention is required if bleeding does not slow after 10 minutes of firm pressure or if blood is spurting due to possible arterial damage. Seek help if the wound is very deep, gaping, caused by a dirty object, or shows signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or foul odor.
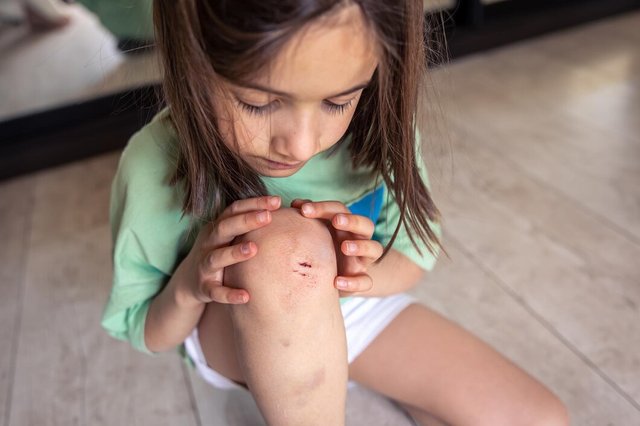
Wounds that also involve sensitive areas, for example, on the face, hands, or joints, as well as those exposing bone, muscle, or tendons, need immediate treatment to avoid complications and guarantee proper healing.
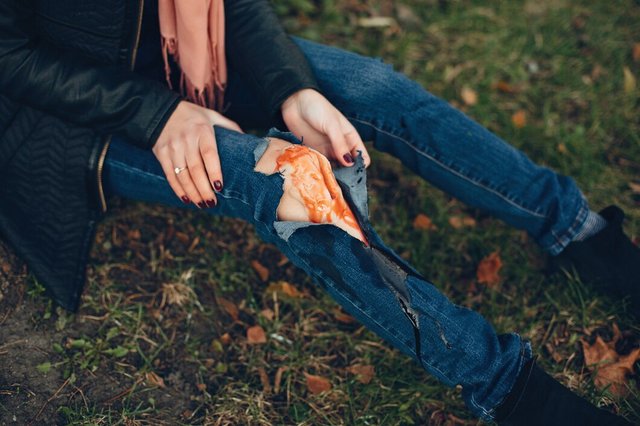

Hydrocolloid or foam dressings are good for deep wounds because they maintain a moist environment that heals faster and does not form scabs. These dressings also provide a barrier against bacteria while allowing the wound to breathe. Transparent film dressings can be useful for monitoring the wound without frequent changes.
Dress the wound using medical tape and an elastic bandage, thus holding it in place. Avoid restriction of circulation. These dressings need to be frequently changed for cleaning of the wound area and observation of signs of infections.