Greetings friends of Steemit and Healthy Steem
| How do antibiotics help us fight off infections? |
|---|
There are multiple types of antibiotics and also different mechanisms of action some antibiotics disrupt the cell membrane integrity others interfere with essential metabolic pathways or inhibit nucleic acid synthesis again others inhibit protein or cell wall synthesis altogether they have one in common they target essential processes in the cell and prevent bacteria from spreading either through killing them directly or inhibiting their growth.
One class of antibiotics inhibits the cell wall synthesis
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis
The bacterium has a cell membrane and also a cell wall which consists of peptidoglycan these are sugar molecules interlinked with peptide bonds more closely.
A bacterial cell wall looks like this without the essential peptide bonds the cell wall becomes extremely unstable as a consequence the cell can even burst due to the high osmotic pressure inside but how is the cell wall synthesized an enzyme called transpeptidase catalyzes the reaction necessary to cross-link peptidoglycan this mechanism is the target of an antibiotic that we already know penicillin.
Penicillin belongs to the group of beta-lactams and what they do is they inhibit the activity of the transpeptidase, no transpeptidase activity means no cell wall than to this. The cell wall becomes instable and bacteria are eliminated. Therefore most antibiotics of the beta-lactam family are considered bactericidal since mammalian cells do not have any peptidoglycan, these antibiotics do not interfere with any peptidoglycan, these antibiotics do not interfere with human cells.
| Inhibition of Protein Synthesis | |
|---|---|
 Wikipedia Wikipedia |  Wikipedia Wikipedia |
Other antibiotics can inhibit the protein synthesis
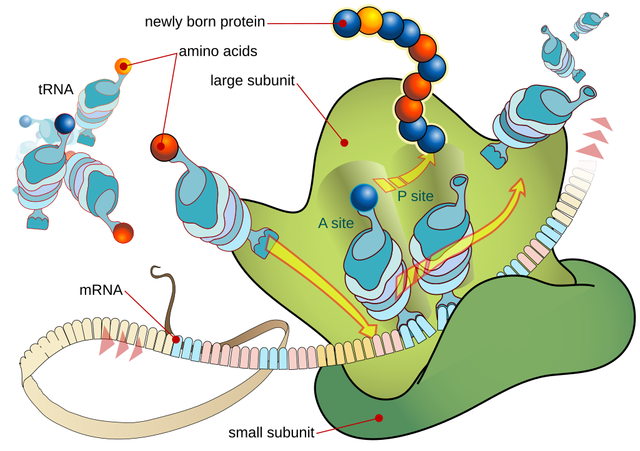
the bacterial mRNA needs to be translated into protein, ribosomes are the responsible catalytic machinery of translation.
They synthesize a polypeptide chain which will fold into protein when we take a closer look at the bacterial ribosome it consists of two subunits the larger 50s and the small 30s subunit. Tetracyclines is an antibiotic that interferes with the small 30s subunit tRNA can no longer bind to the ribosome and protein synthesis is inhibited. This does not directly kill the bacterium however it depletes them of protein required for growth this mechanism is therefore considered bacteriostatic.
How can this antibiotic specifically inhibit the translation of bacteria but does not interfere with our own protein synthesis program.
Mammals including humans have different ribosomal subunits a 60s and a 40s subunit upon medication we can translate our mRNA without any problem.
Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis
 WikipediaImage illustrates DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. The first two are nucleic acids.
WikipediaImage illustrates DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. The first two are nucleic acids.
Some antibiotics target one step before translation. These subtypes can inhibit nucleic acid synthesis.
The bacterial dna is usually transcribed by an enzyme called rna polymerase. It synthesizes mRNA in a process called transcription an antibiotic called Rifamycin can inhibit the enzyme activity of RNA polymerase this will stop mRNA synthesis and with this indirectly also protein production.
| What are some side effects of taking antibiotics? |
|---|
The most common side effects of antibiotics malfunctioning of the digestive system. These happened in around 1 in 10 people. side effects of antibiotics that affect the digestive system include vomiting nausea which is feeling like you may vomit, diarrhea bloating and indigestion, abdominal pain and loss of appetite.
| Why is antibiotic resistance a problem, and how can we avoid it? |
|---|
Antibiotics revolutionized medicine, however today they are heavily overused not only for humans they are also administered to livestock keeping the animals healthy and routinely prevent disease. Overusing antibiotics promotes antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic resistance is generally caused by simple mutations in the bacterial dna. Mutations occur almost all the time in all organisms but when an antibiotic is used and one microbe develops a resistance towards this drug caused by random mutation. This drug becomes ineffective, then other antibiotics have to be taken into consideration. They might work but again the high selection pressure on the microbes might promote mutations which could lead to multiple drug resistance in the worst case no antibiotic would be effective anymore and the result would be a supergerm which might cause the next big pandemic multi-resistant microbes are already among us.
science is permanently working on the problem by developing new antibiotics however we need to be more responsible with the use of antibiotics in thefuture.
| Do antibiotics affect our immune system? |
|---|
Most antibiotics have no effect on immune system.
| Can we treat diseases without using antibiotics? |
|---|
Mild bacterial infection can be cured without any antibiotics.
| How can we use antibiotics responsibly? |
|---|
Science is permanently working on the problem by developing new antibiotics however we need to be more responsible with the use of antibiotics in the future.
Thank you for reading my post.
I would like to invite three fellow Steemians to participate in the contest.
@sabbirakib
@eveetim
@chiagoziee

Nicely written, I understand that regular use of antibiotics may prolong healing in the body because of being adapted to the body system.
Thank you for the invitation sir.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
You've got a free upvote from witness fuli.
Peace & Love!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit