Dear readers, I have shared with you in the previous article what the technological process for processing beef is like, describing and showing visually what each process consists of. However, in this process there are many by-products that can be used in different productive areas, such as the agricultural sector and in the production of meat-based by-products. Without further ado, the following is a brief description of each by-product obtained from the industrial processing of bovine cattle.
Without further ado, the following is a brief description of each by-product obtained from the industrial processing of bovine cattle.

| By-products obtained |
|---|
- Blood: is one of the by-products obtained during the dressing process, it is estimated that 45 to 50% of the blood in the animal can be used, since, according to some specialists, at least 50% or more will be retained in the carcass in vessels and capillaries, depending on the physiological state of the animal.
This by-product is useful in different areas such as agriculture and livestock because according to Barreda (2014), blood contains about 16 to 18% of protein solids, which is why the industry processes blood to produce blood meal, which is an alternative for animal feed and can also be used as a fertilizer with a high nitrogen content; to obtain such meal the industry places the blood in a coagulator, with the intention of being able to separate in another process the solids of the blood from the water, and then these solids are dried.
It is important to note that alternatives such as those mentioned in the previous paragraph have been applied in the southern area of the lake in banana crops, obtaining excellent results in the management of the crop, it would also be interesting to try it as a pasture fertilizer, considering that it has considerable levels of nitrogen, which can favor the performance of the forage biomass.

Limb processing: It is said that bovine feet can be an essential raw material for the production of gelatins, but also bone meal can be obtained by processing the bones, which can be rich in minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which is an ideal mineral supplement for certain animals and can also be used as phosphate fertilizer in agriculture.
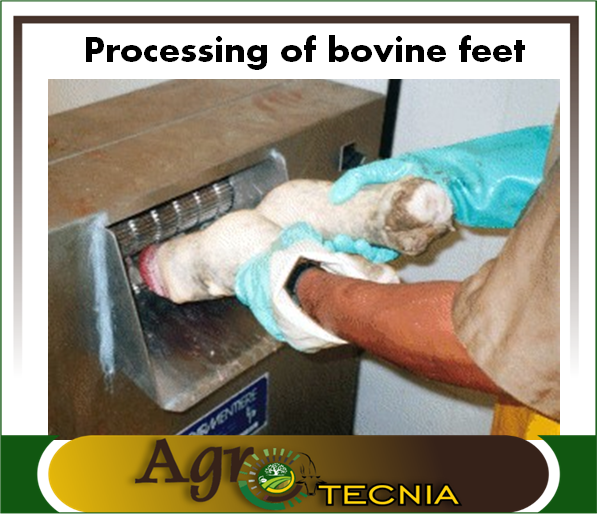
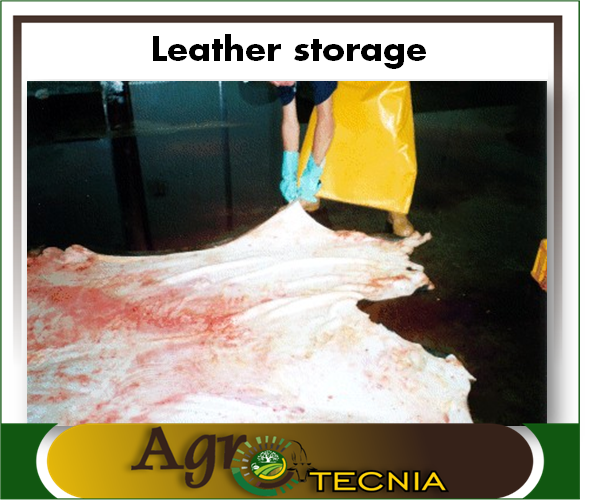
- Leather: Like bones, leather can be used to make gelatin, since according to Aldana (2001), it is rich in collagen and is also used to make cosmetics, packaging for sausages and its fat for making soaps. On the other hand, we know that leather is essential for the manufacture of shoes, handbags and other garments, for which leather must be processed in tanneries. At present, it is not known whether this industrial by-product can be processed, and it would be interesting to know if it can be used in agriculture, in some agronomic management or animal feed.

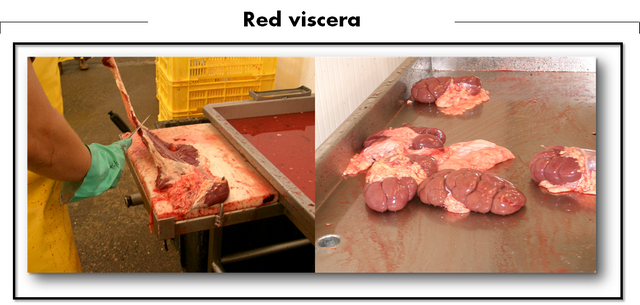
- Red viscera: among the red viscera are the liver, lungs, heart, kidneys, tongue, mammary gland among others, the slaughterhouses have qualified personnel for the sanitary supervision of these products in such a way that they certify that they can be consumed by humans. In the area south of Lake Maracaibo, it is very common for people to consume this type of products.
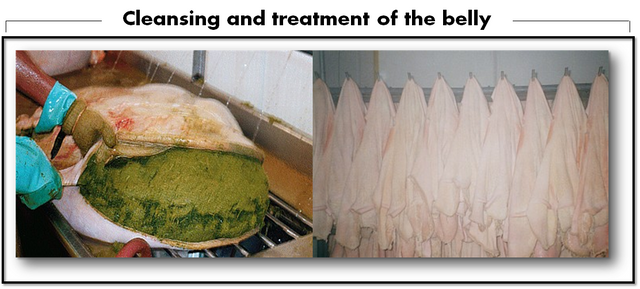
- White viscera: Within this classification are the stomach and intestines, in the case of the intestines are used as a casing for some sausages and also to make a product known in my area as chinchurria, which is made by washing the intestine very well and then a kind of braid is made.

As for the stomach there is a part known as the belly, where the animal ferments the food consumed, this structure is of fibrous consistency and is used for human consumption, people use lime to whiten it, since it has a green color because the grass consumed by the animal accumulates there. In Zulia there is a gastronomic dish called mondongo which is made with the belly.
Design by @amestyj with an image captured in a slaughterhouse in his geographical area.


| Final Considerations |
|---|
Dear readers, in industrial slaughterhouses apart from the mentioned by-products, another important by-product is gallstones, which is in great demand by the pharmaceutical industry as a base for some medicines, on the other hand, in slaughterhouses a lot of bovine manure is accumulated, which can be used for the production of organic fertilizers with the intention of generating a recycling of nutrients, such fertilizers have been widely tested obtaining great results in agricultural ecosystems.
On the other hand, you can see the multiple benefits that cattle provide after processing, only the by-products that are generated should be taken advantage of, to enhance different economic areas. I hope that this material will be useful for you and that it will increase your knowledge about agro industrial processes.
| Bibliographic references |
|---|
Aldana, H. (2001). Engineering and agribusiness. 2ed. Terranova editores. Bogota: Colombia.
Barreda, L. (2014). Meat by-products to prepare food biomaterials. University of Oviedo: Spain.
Guided visit to a slaughterhouse located in the southern area of Lake Maracaibo.

