A recent analysis involving the review of 2590 studies has provided an important alarm about the degree of plastic pollution faced by different marine species, and that is that at least 88% of marine species suffer the terrible consequences of ocean pollution, causing many of the species we consume already have plastic in their bodies.

Plastic pollution affects our oceans. Source: Wikimedia.org.
This analysis has been carried out by the Alfred Wegener Institute Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research, and was commissioned by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), whose purpose is to measure the impact of plastics and microplastics in the seas, According to this report, the situation goes beyond floating plastic pollution, since at least 2,144 species suffer from plastic pollution in their environment, and 90% of birds and 52% of turtles ingest it.
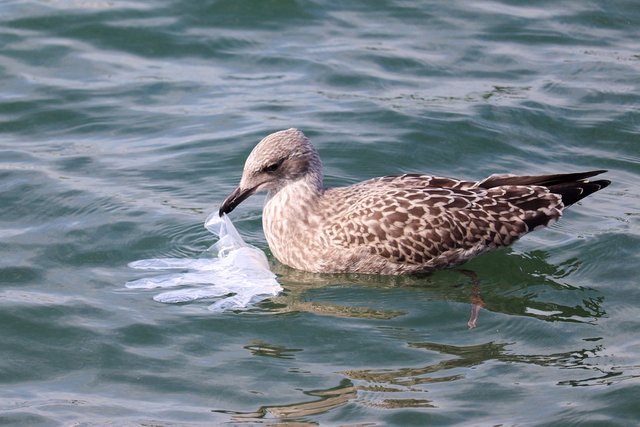

Many species ingest plastic or get trapped in it. Source: pixabay.com.
Plastic on our table
But not only that, the report highlights that in marine species that are part of our food chain, such as blue mussels, oysters and sardines, plastic has also been detected in their bodies. And although there is still not enough data available to know the effect that microplastics have on human health, the long-term cumulative effects could be harmful.
We are talking about a large number of substances that are part of the materials we call plastics, since in addition to the best known polymers, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polyurethane, PVC, among others, plastics contain many additives that have already been classified as dangerous, for example bisphenol A, phthalates and alkylphenol additives, are substances that are easily absorbed and behave as endocrine disruptors, and these substances have already entered the environment and the trophic chain.
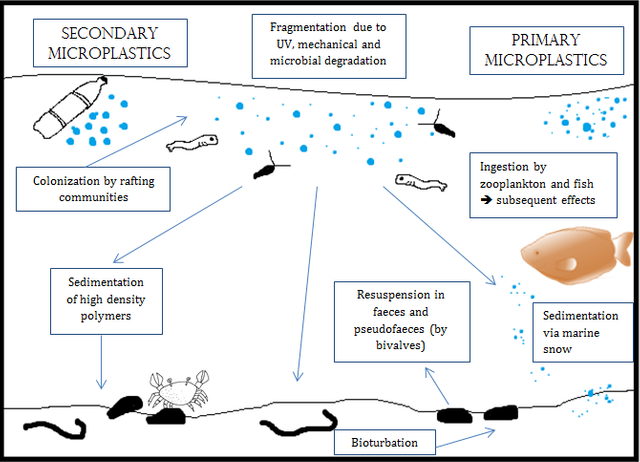
Microplastics impact on biological communities. Source: wikimedia.org.
Plastic is now omnipresent
An important aspect of this study is the analysis of the distribution of plastic, determining that this material has been distributed throughout the ocean, it has been detected in surface water samples as on the ocean floor, even from the poles to the coasts of the most remote islands, being detectable in marine species as large as whales, to the smallest, such as plankton.
The study has also pointed out an uneven distribution of plastics among the various regions of the oceans, species and ecosystems, highlighting that although there are areas with low plastic pollution, there are others terribly affected by this waste, among these areas include the five major oceanic gyre systems, areas near the main points of origin, such as long polluted rivers and ecosystems such as coral reefs, mangroves and deep water canyons, these points act as large accumulation areas.
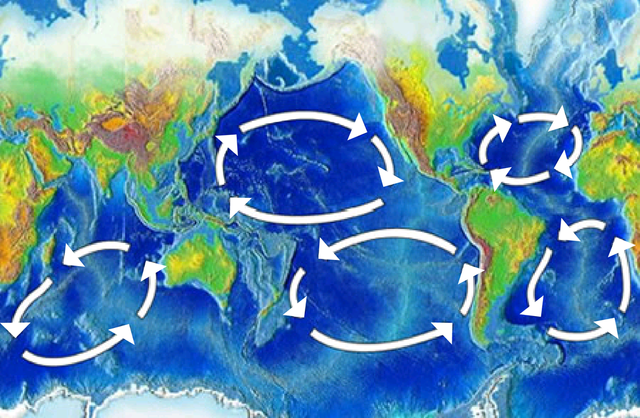
The five major oceanic gyres have become major plastic accumulation zones. Wikipedia.com.
According to particle size, an uneven distribution has also been observed, with the coastlines having the highest concentration of macroplastics, while the seabed has the highest concentration of microplastic particles.
On the other hand, although the average contamination levels in many scientific studies of the seabed, water column, surface, beach and sea ice amounted to 3,127 macroplastics/km2 and 200,000 microplastics/km2, critical points have been detected where this threshold has been exceeded, such as in the Mediterranean, eastern China, the Yellow Sea and even the Antarctic sea ice.
Not encouraging projections
According to the reports cited, and considering the rate of increase in the annual production of plastics and a scenario of continuity in the current situation, they predict a significant increase in emissions in the coming decades.
Some studies indicate that, at a minimum, annual emissions will triple between 2040 and 2060 under the current scenario; however, studies considering the expansion of the chemical industry predict that this will lead to a quadrupling of macroplastic concentrations in the oceans by 2050 and a 50-fold increase in microplastic concentrations by 2100.
And although the most optimistic scenarios, which consider global plastic substitution policies, better waste management and massive reduction of pollution sources, assume a reduction of plastic emissions between 30% and 90 per year, this still assumes that a large amount of plastics will reach the oceans, only at a slower rate.
In conclusion, it seems that plastic pollution looks inevitable when we start to put all these numbers together, but definitely, the magnitude of the problem is still in our hands, it depends on us, on the policies of governments against this threat, on what the industry does and us as a society, because at the end of the day a large amount of garbage reaches the oceans because of us, because of bad waste management, because of institutions and people who are not responsible for where they put their waste, let alone where it ends up.
Well friends, I hope that with this kind of studies we make a little more aware of how plastic pollution can affect us in the future. See you next time!

Greetings @emiliomoron, there are many studies that have shown the great degree of pollution that have our seas and oceans that affect all marine species, and the saddest thing is that we do not contribute as humans to avoid this.
Excellent article that you share with us.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hello my friend, thank you for reading, there are certainly many studies that have contributed to highlight this terrible problem, and this report is proof of that, and really society in general is not helping to mitigate the situation.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hello @emiliomoron,
the pollution of seas and lakes by plastic seems like a problem that will never end, the consumption of plastic items that will later be discarded has no control, so it is very possible to think that the solution would be aimed at reorienting the production of plastics ( pieces, articles, bags, etc.) to avoid that after use these are discarded and thus avoid their accumulation creating sources of contamination
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hi @tocho2, it certainly seems a problem that will not have a solution in the near future, it is necessary to redirect the way these products are produced so that they do not end up in the oceans or polluting elsewhere, because single-use plastics are doing a lot of damage to the environment.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
We are destroying our mother earth with our own hands we need to calm down to plastic waste other wise we have to face huge consicounse in future.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
@tipu curate
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 4/5) Get profit votes with @tipU :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks my friend!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit