Author: @madridbg, via Power Point 2010, using public domain images. Bruce Blaus
Greetings and welcome dear readers of this prestigious platform, continuing with the scientific approach that I usually carry out on the platform, in this installment we will be addressing what concerns chemical reactions and their influence on muscles with involuntary movements but essential for the life of any species .
In this sense, we will take as a reference a set of data reported by the Center for Biological Research of Mexico, which establishes that in the muscular system of mammals there are cells that remain actively active. involuntary and that are catalyzed through chemical reactions indispensable for life.
In this sense, it is necessary to explain that living beings have constant and involuntary movements, which are carried out without our control, so much so that it is estimated that while sleeping these types The system remains in operation, as does our heart, for example, that despite not being a smooth muscle, its work in the system does not stop and it is the one who marks the evolution of our existence.

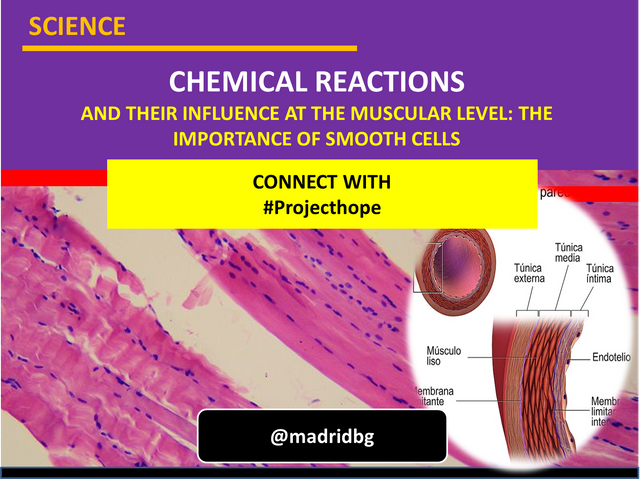
Fig. 2. Structure of the arterial wall as a function of smooth muscles. Author: Bruce Blaus
The above behavior is adopted by the smooth muscles, with the exception that its operation depends exclusively on the chemical reactions that carry out its functionality and that it is controlled by the brain.
These types of muscles have been found in different species, among which are: annelids, mollusks, coelenterates, mammals, among others, hence we will focus our attention on the latter, establishing characteristics such as size, which varies from 20 to 500 μm in length, depending on their structure, they lack striated patterns such as that found in skeletal muscles and in the heart.
Although they differ from skeletal muscles, smooth muscles have similar characteristics such as actin and myosin that provide contractile characteristics to them, in such a way this type of muscle is usually located in the area pelvic or abdominal cavity and are responsible for the functioning of the involuntary system that keeps the life of the species in operation.
With regard to muscle contraction, this is slower and more sustained and is produced by the interaction between fine filaments on thick ones, which is due to a chemical process associated with the concentration of calcium ions on myosin, which produces an induced phosphorylation process that generates their contraction.

Fig. 3. Muscle contraction process. Author: Boumphreyfr
Beyond contraction, this type of smooth structures are responsible for the synthesis of type III collagens, associated with those organs capable of producing expansion, in such a way we can conclude that the nervous system together with the endocrine and muscular systems represent the essence of life and the functionality of our body.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES CONSULTED

[1] Nicolás Federico Renna, Roberto Miguel Miatello. PHYSIOLOGY OF THE VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE. Article: Online Access
[2] Claudia González García. SMOOTH MUSCLE EXCITATION AND CONTRACTION. Article: Online Access
OF INTEREST

•

Grateful with the community @project.hope and with all the management team of the same one that they motivate us to continue working in a mutual and balanced growth.

